3
GETTING STARTED SAFETY / SPECIFICATIONS ASSEMBLY / INSTALLATION OPERATION TROUBLESHOOTING MAINTENANCE /REPAIR
GETTING STARTED
Save this manual
You will need the manual for the safety warnings and precau-
tions, assembly instructions, operating and maintenance
procedures, parts list and diagram. Keep your invoice with this
manual. Write the invoice number on the inside of the front cover.
Keep this manual and invoice in a safe and dry place for future
reference.
Structural requirements
Make sure all supporting structures and load attaching
devices are strong enough to hold intended loads. If in
doubt, consult a qualified structural engineer.
Electrical requirements
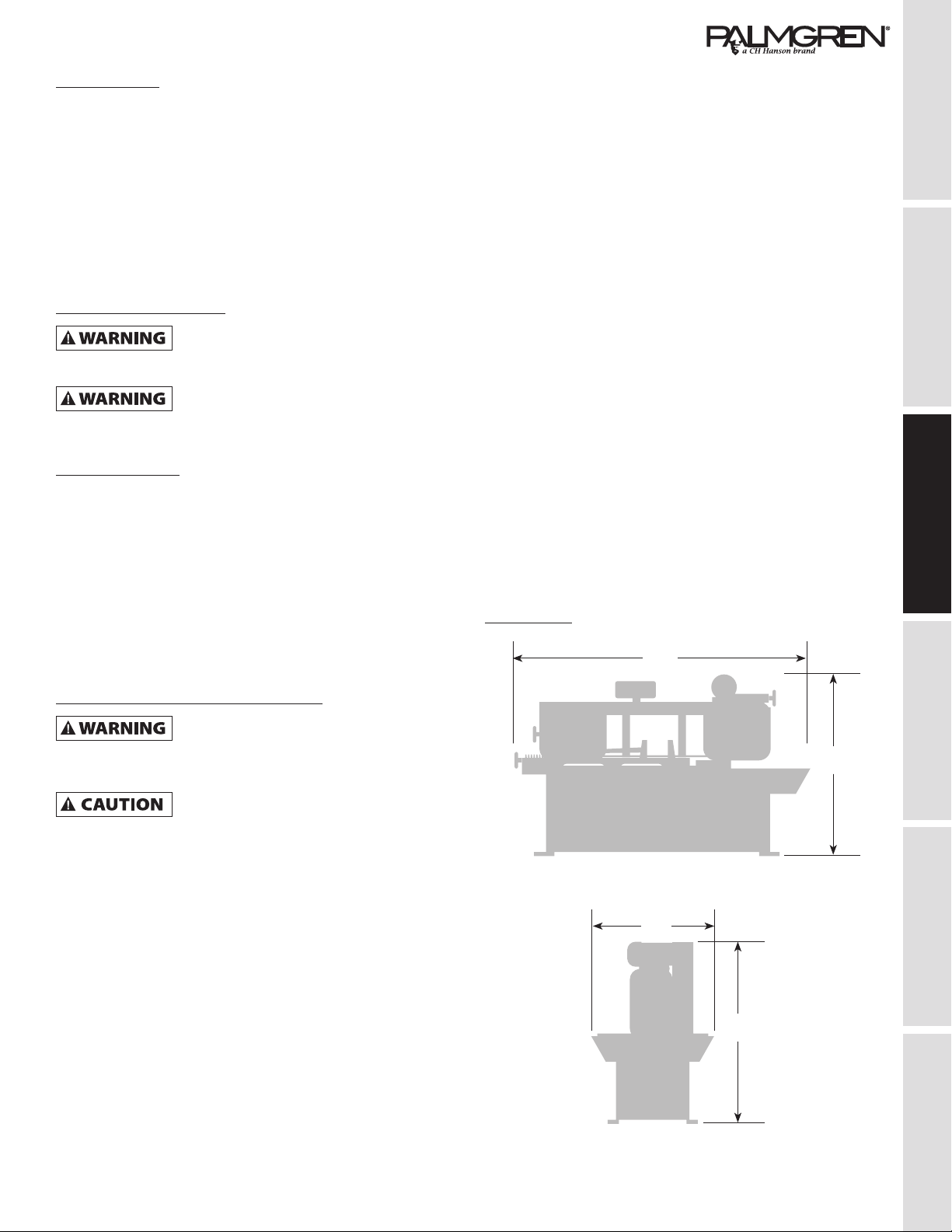
The power supply to the Model 9683315, 10” Band Saw
needs to be 220V AC, 3-phase, 3.2 amps, 60 HZ.
Tools needed
Standard professional mechanic’s hand tool set (socket set,
pliers and spirit level, etc.).
UNPACKING
When unpacking, check to make sure all parts listed below are
included. If any parts are missing or broken, please contact your
local retailer.
IMPORTANT: Many unpainted steel surfaces have been
coated with a protectant. To ensure proper fit and operation,
remove coating. Coating can be easily removed with mild
solvents, such as mineral spirits, and a soft cloth. Avoid getting
solution on paint or any of the rubber/plastic parts. Solvents may
deteriorate these finishes. Use soap and water on paint, plastic
or rubber components. After cleaning, cover all exposed surfaces
with a light coating of oil.
Never use highly volatile solvents. Non-
flammable solvents are recommended to
avoid possible fire hazard.
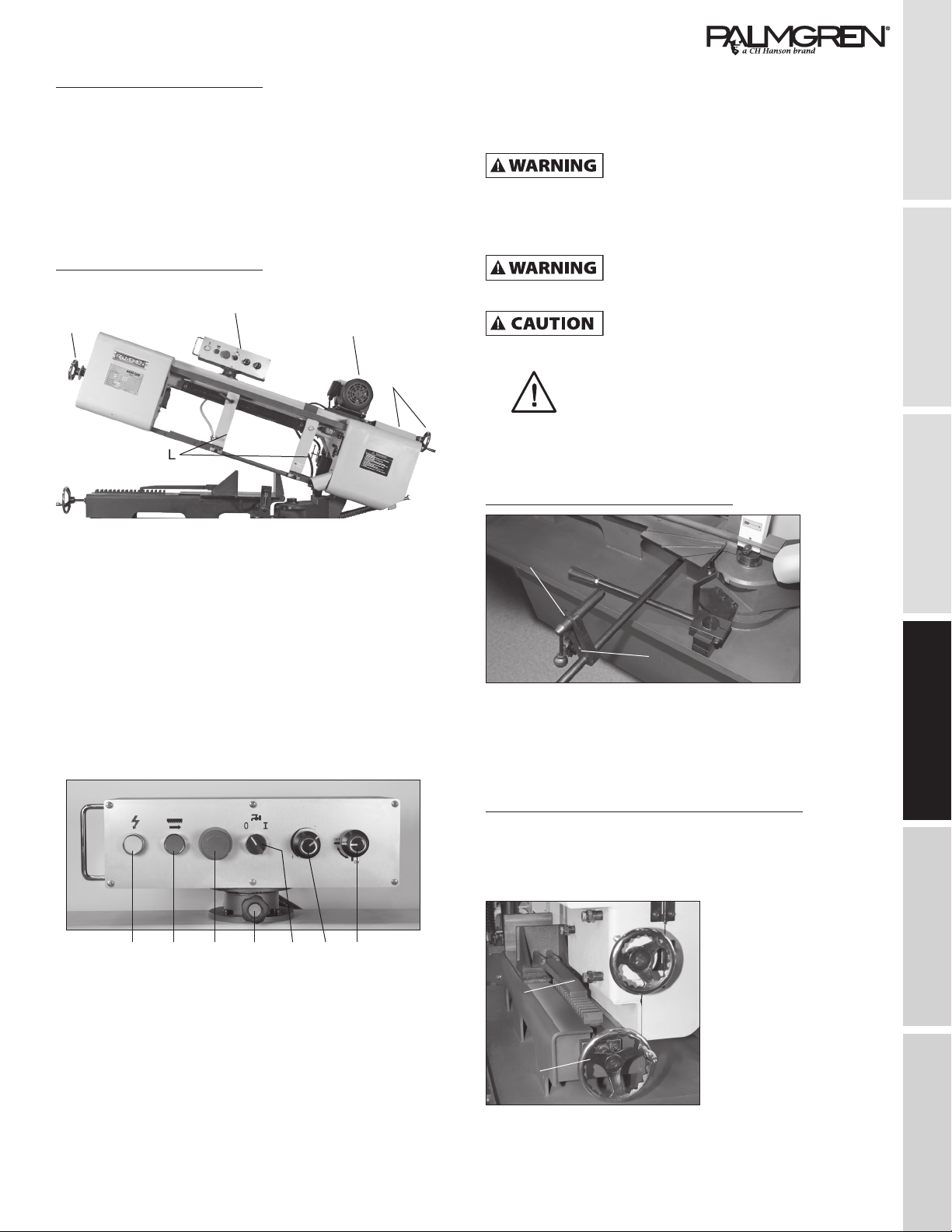
Contents of Model 9683315 10” Band Saw
• Complete Band Saw
• Depth Stop Rod (for assembly see page 6)
• Depth Stop (for assembly see page 6)
• Operating instructions
Unpack
Remove all the over packing materials, but leave unit
attached to its pallet. Do not discard packing materials
until after the machine has been inspected for damage and
completeness. Locate loose parts and set aside.
Inspect
After unpacking the unit, carefully inspect for any
damage that may have occurred during transit. Check
for loose, missing, or damaged parts. Shipping damage
claims must be filed with the carrier.
This machine and its accessories should be visually inspected
before use, in addition to regular periodic maintenance
inspections. Be sure that the voltage labeled on the unit matches
your power supply.
SAFETY RULES
For you own safety, read all of the
instructions and precautions before
operating the tool.
Always disconnect the machine from its
power source before changing blades or
carrying out any maintenance procedure even in the case of
irregular machine operation.
PROPOSITION 65 WARNING: Some dust created by
using power tools contain chemicals known to the state
of California to cause cancer, birth defects or other
reproductive harm. Some examples of these chemicals are:
• Lead from lead-based paints
• Crystalline silica from bricks and cement and other masonry
products
• Arsenic and chromium from chemically-treated lumber
Your risk from these exposures varies, depending on how often
you do this type of work. To reduce your exposure to these
chemicals: work in a well ventilated area and work with approved
safety equipment. Always wear OSHA/NIOSH approved, properly
fitting face mask or respirator when using such tools.
Always follow proper operating
procedures as defined in this manual even
if you are familiar with the use of this or similar tools.
Remember that being careless for even a fraction of a
second can result in severe personal injury.
Read all instructions before using this tool
• Dress properly. Do not wear loose clothing, shirts with
sleeves that are too long, gloves that are too big, jewelry or
chains as they can be caught in moving parts. Protective,
electrically non-conductive clothes and non-skid footwear are
recommended when working. Wear restrictive hair covering
to contain long hair.
• Use eye and ear protection. Always wear ANSI approved
impact safety goggles.
• Stay alert. Watch what you are doing, use common sense.
Do not operate any tool when you are tired.
• Guard against electrical shock. Prevent body contact with
grounded surface such as pipes, radiators, ranges and
refrigerator enclosures.
• Do not operate tool if under the influence of alcohol or drugs.
Read warning labels on prescriptions to determine if your
judgement or reflexes will be impaired. If there is any doubt,
do not operate the tool.
Prepare work area for job
• Keep work area clean and free of equipment, tools or other
objects. Cluttered areas invite injuries.
• Observe work area conditions. Do not use machines or
power tools in damp or wet locations. Do not expose to rain.