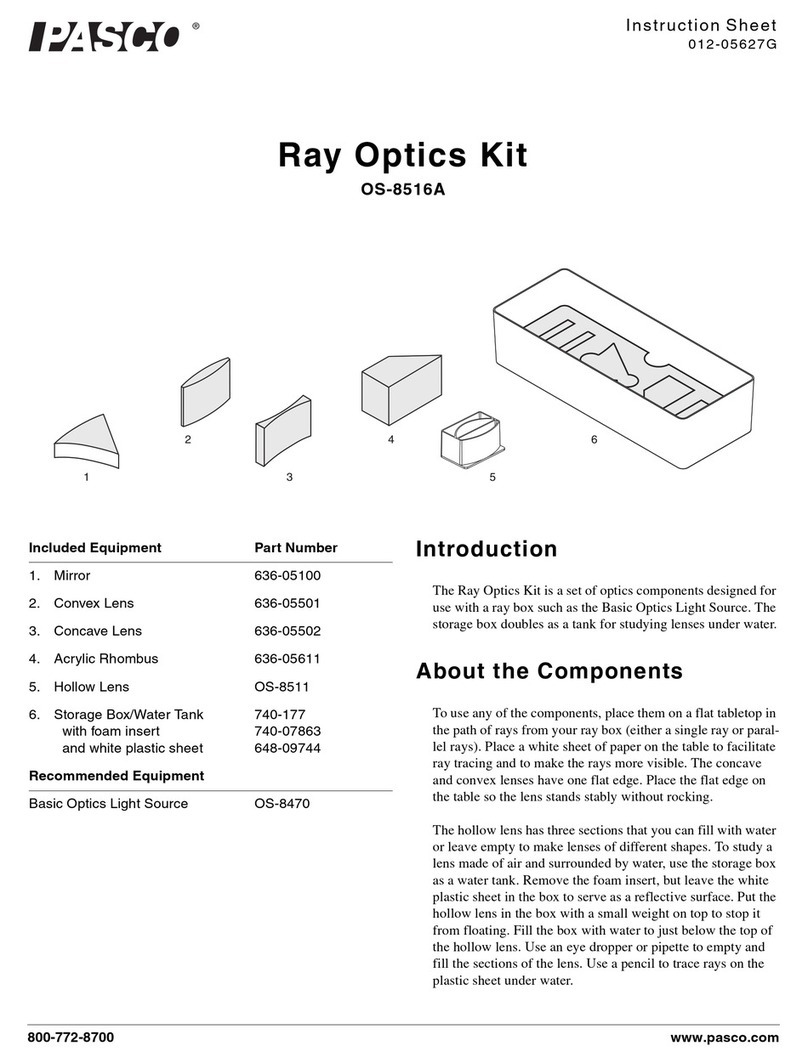
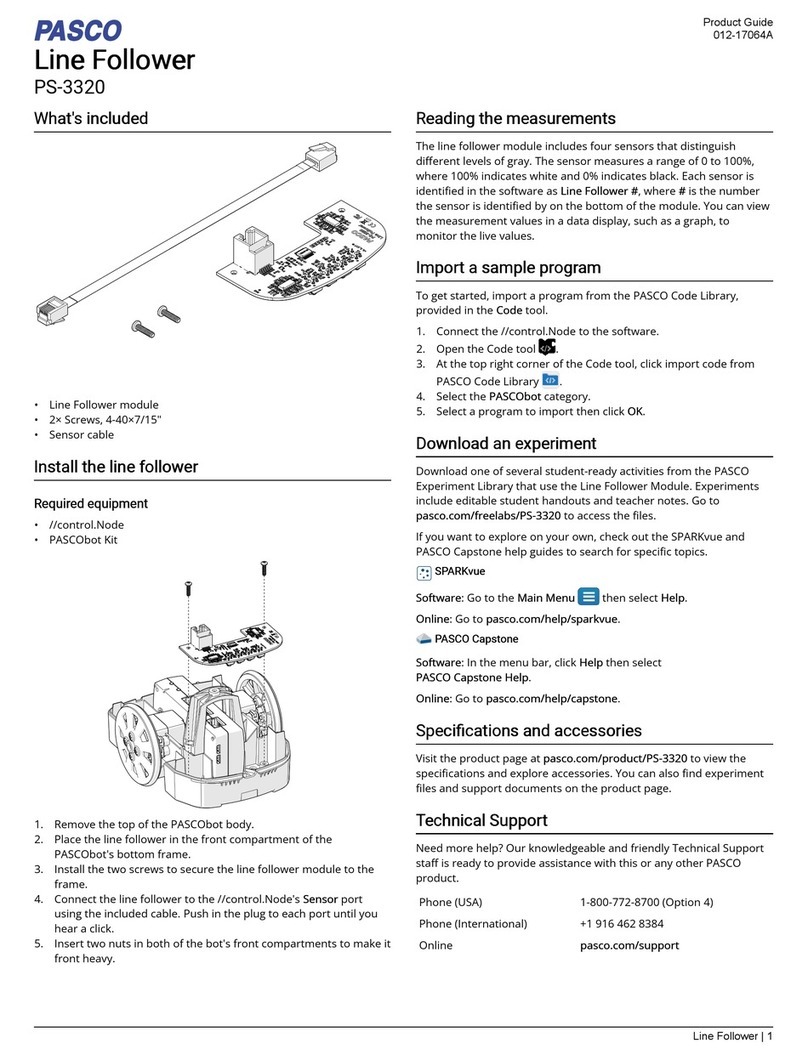
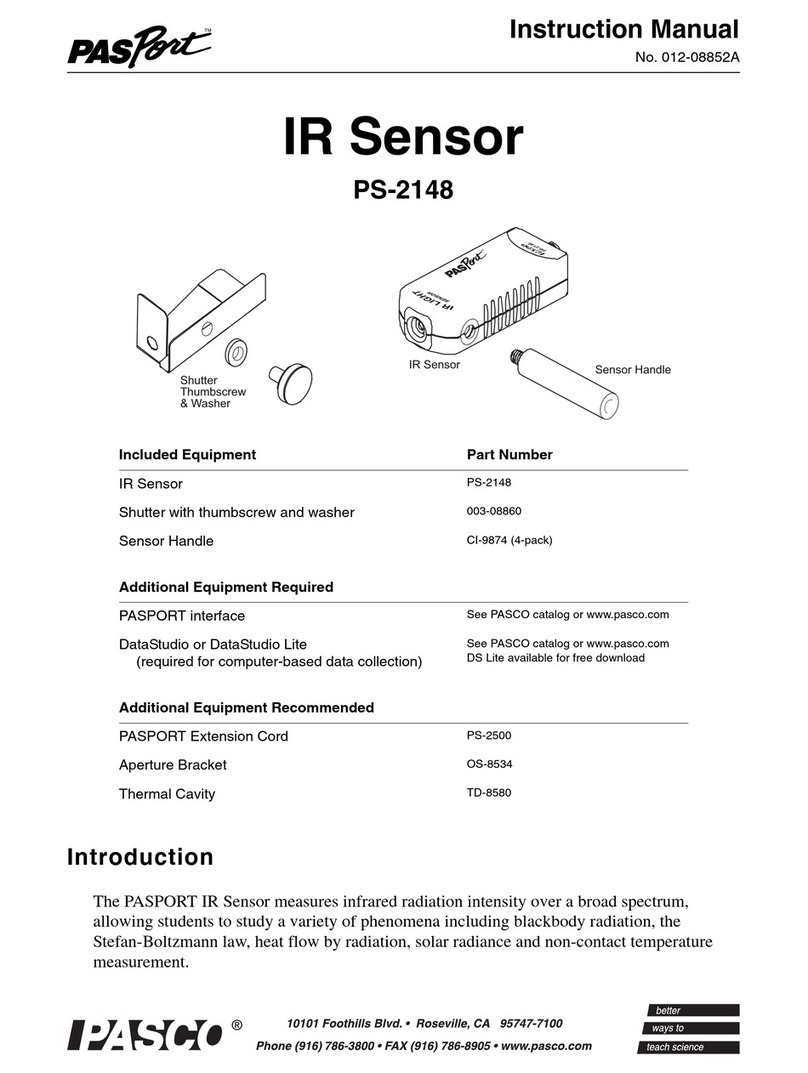
2
FaradayIcePail 012-04393C
®
Open
Closed
Figure 2
➤➤
➤➤
➤NOTE:
➀The charged object must be inserted at least into the
lower half of the ice pail. Try inserting it, for ex-
ample, approximately one centimeter below the top
of the pail and attempt to explain your results.
➁There may be a small charge retained on the exposed
plastic between the aluminum disk and the aluminum
rod on the charge producers. This residual charge
does not transfer readily when the disk is touched to
the pail. Therefore, (before starting the experiment)
breathe on the exposed plastic of the charge producer
so that the moisture in your breath will tend to re-
move any residual charge.
Procedure B
①Starting with initially uncharged charge producers,
rub the blue and white materials together. Using the
Faraday Ice Pail, measure the magnitude and polarity
of their charges. By using the results from Procedure
A it is not necessary to touch the charge producer to
the pail. What relationship exists between these
charges produced by contact?
➁Ground the charge producers and rub them together
inside the ice pail. What is the reading on the elec-
trometer. Remove one charge producer and note the
electrometer reading. Replace this charge producer
but remove the other and note the electrometer read-
ing.
➂Ground the charge producers again. Rub the white
material against the aluminum proof plane. Measure
the magnitude and polarity of the charges. Now rub
the blue material against the aluminum surface and
record your measurements.
➃Construct a list of materials such that if a material
lower on the list is rubbed against a material higher
on the list, the charge on the higher listed material is
always positive. Such a list is called an electrostatic se-
ries.
To Reach PASCO
For Technical Support call us at 1-800-772-8700 (toll-
free within the U.S.) or (916) 786-3800.
Tech support fax: (916) 786-3292
➁Ground the ice pail (i.e., connect the inner pail to the
shield) by touching the inner pail and the outer shield
at the same time with the finger of one hand. (See
Figure 2) While conducting the experiment it may be
convenient to continually rest one hand on the upper
edge of the shield. This also grounds the experi-
menter, providing the electrometer is connected to
both ground and shield and it allows the ice pail to be
easily grounded whenever necessary.
➤NOTE: When removing your finger from the
inner pail after grounding it, make certain that you
are still touching the outer shield. DO NOT re-
move your hand from the shield before releasing
the inner pail, as this sequence will not effectively
ground the inner pail.
➂Make sure the electrometer reads “zero”, indicating
that there is no charge on the ice pail.
Procedure A
➀Rub two charge producers together to create a charge
on them.
➁Insert one of the wands into the ice pail but do not let
it touch the pail. Note the electrometer reading.
➂Remove the object from the pail and again note the
electrometer reading.
➃Insert the wand again, allow it to touch the ice pail
and then remove it. Note the electrometer reading.
➄Momentarily ground the ice pail and then touch the
object to the pail again. Note the electrometer read-
ing. Does any charge remain on the object?
What is the conclusion about the induced charge on the
ice pail, as compared to the charge on the charge pro-
ducer?