Contents
GENERAL......................................................................................................................41
1.1 ABOUT THIS MANUAL ....................................................................................................4
1.2 FUNCTION OVERVIEW ....................................................................................................4
1.3 BENEFITS AND POSSIBILITIES .........................................................................................4
TECHNICAL STRUCTURE ........................................................................................52
2.1 CONNECTIONS................................................................................................................5
2.2 INDICATIONS..................................................................................................................6
2.3 TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS ..........................................................................................6
2.4 SUPPLY VOLTAGE...........................................................................................................6
2.5 M-BUS SPECIFICATIONS.................................................................................................7
2.6 ETHERNET CONNECTION ................................................................................................7
2.7 SERIAL CONNECTION (RS232) .......................................................................................7
2.8 DRAWINGS.....................................................................................................................8
2.9 COMMUNICATION CABLES .............................................................................................9
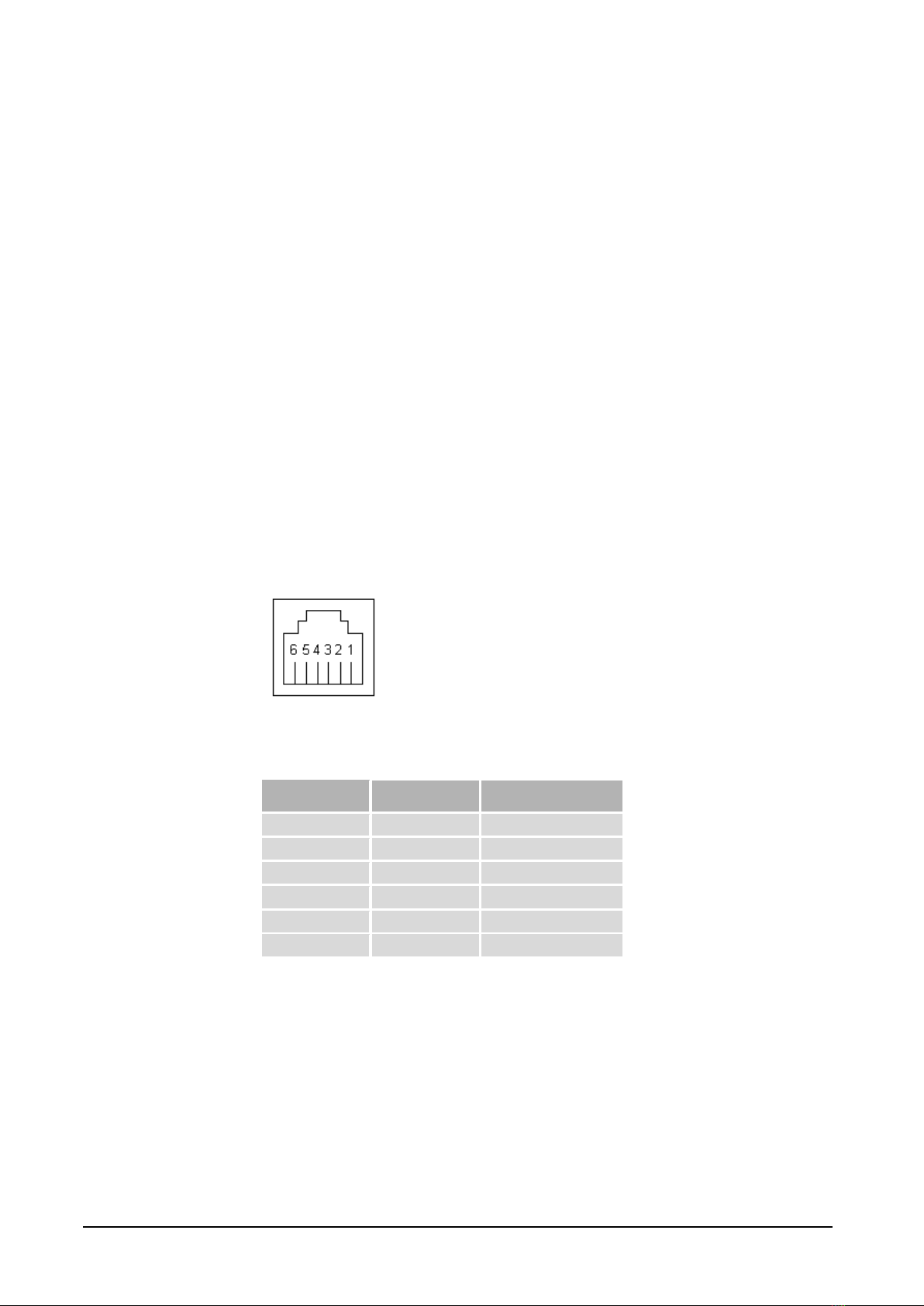
2.9.1 Pin connection for module contact RJ12 ................................................................9
2.9.2 Adapter 1: Serial to M-Bus...................................................................................10
2.9.3 Adapter 2: Configuration......................................................................................10
2.9.4 Adapter 3: Ethernet to serial port.........................................................................10
2.9.5 Adapter 4 and 5: Spy.............................................................................................11
GET STARTED STEP BY STEP ...............................................................................123
3.1 NECESSARY INFORMATION ..........................................................................................12
3.1.1 Hardware address.................................................................................................12
3.1.2 IP Address.............................................................................................................12
3.1.3 TCP/UDP..............................................................................................................12
3.1.4 Port number..........................................................................................................12
3.2 USING M-BUS WIZARD................................................................................................13
3.3 ADJUSTMENTS FOR TCP/UDP AND PORT NUMBER ......................................................13
3.4 COMMUNICATION TOWARD METERS ............................................................................14
3.4.1 The right communication speed............................................................................14
3.4.2 Adjusting the meter’s communication speed.........................................................14
3.4.3 Manufacturer specific configuration software......................................................14
3.4.4 Important parameter adjustments.........................................................................14
M-BUS WIZARD .........................................................................................................154
4.1 STARTING M-BUS WIZARD..........................................................................................15
4.2 FINDING THE GATEWAY AND CHANGE IP ADDRESS......................................................16
4.3 COMMUNICATION TEST (PING).....................................................................................19
4.4 CONFIGURATION PARAMETERS ....................................................................................20
4.5 METER SETTINGS .........................................................................................................23
OTHER CONFIGURATION METHODS.................................................................285
5.1 USING THE SERIAL PORT...............................................................................................28
5.2USING TELNET.............................................................................................................29