4© 2022 Pitsco Education, LLC. All rights reserved.
Drones in the Air
Up, up, and away! Drones have taken everybody’s imagination by storm in recent years.
Promises of packages being delivered to your door with everything from hot fresh pizza
to a new item from your favorite retailer, as well as the ability of first responders to reach
remote locations with lifesaving equipment in a moment’s notice – these are the dreams
of a future with drones. But what is needed for any of this future to happen, engineering
drones for these and other tasks? Welcome to the world of aerospace engineering, you
now have the opportunity to figure out this future!
Did You Know?
In remote areas of Africa, drones are used for delivering medical shipments because it
would take longer to deliver the items over land. You can read more about this lifesaving
use for drones here: https://dronedj.com/2022/02/18/zipline-expands-drone-deliveries-
of-medical-supplies-to-kenya/.
Design and Iterate
You have a system for building and adding to your drone that makes it quick and simple
to make changes to the basic design of the drone. This will enable you to design, build,
and test a drone and then make improvements to test the drone again. This design,
test, and redesign process is known as iteration. Depending on the time you have
available, the system you have will enable you to compare multiple possible solutions to
a problem based on how well each solution is likely to meet the parameters that have
been set.
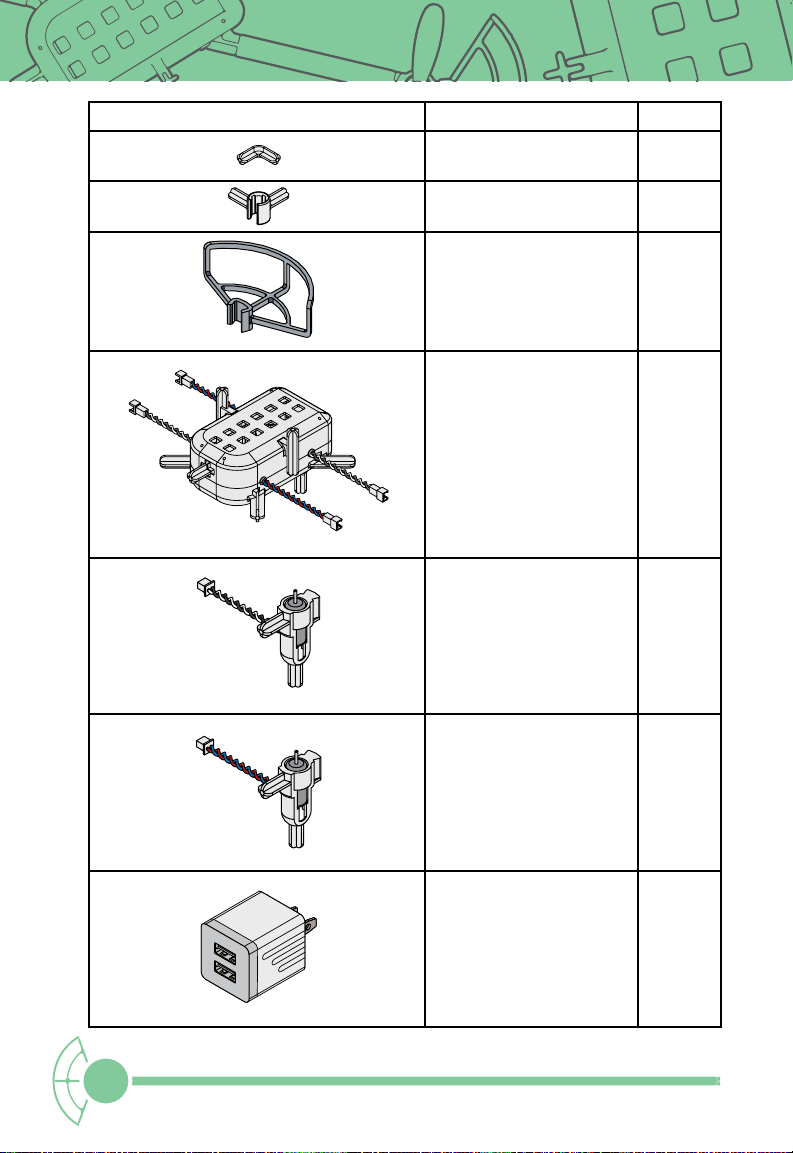
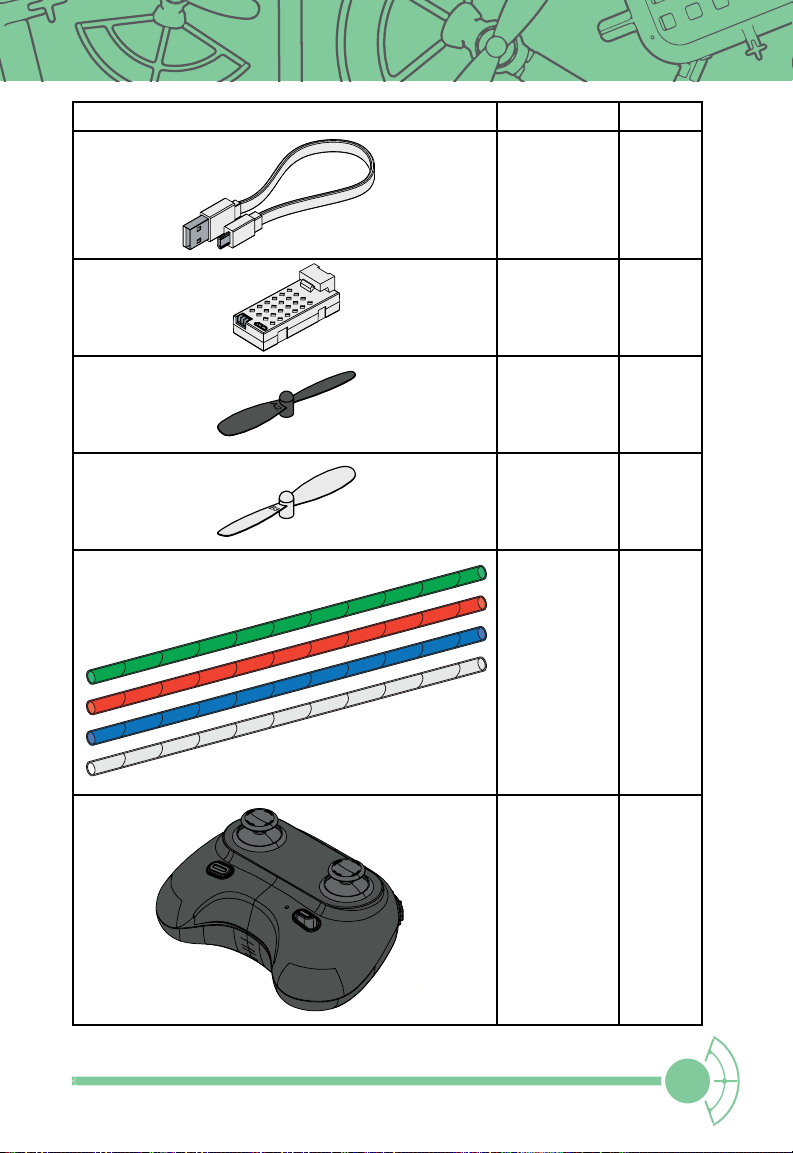
Batteries and Charging
In order for your drone to operate at maximum capacity, the batteries should be fully
charged. Locate the charger, Micro USB cable, and batteries. Plug these in while building
your drone.
Glossary
terms:
Aerospace Engineer – an engineer who
works with designing, building, and testing
aircraft, including drones, to meet goals
iteration – refining a product or process
by tweaking the later version and then
starting over
GETTING STARTEDGETTING STARTED