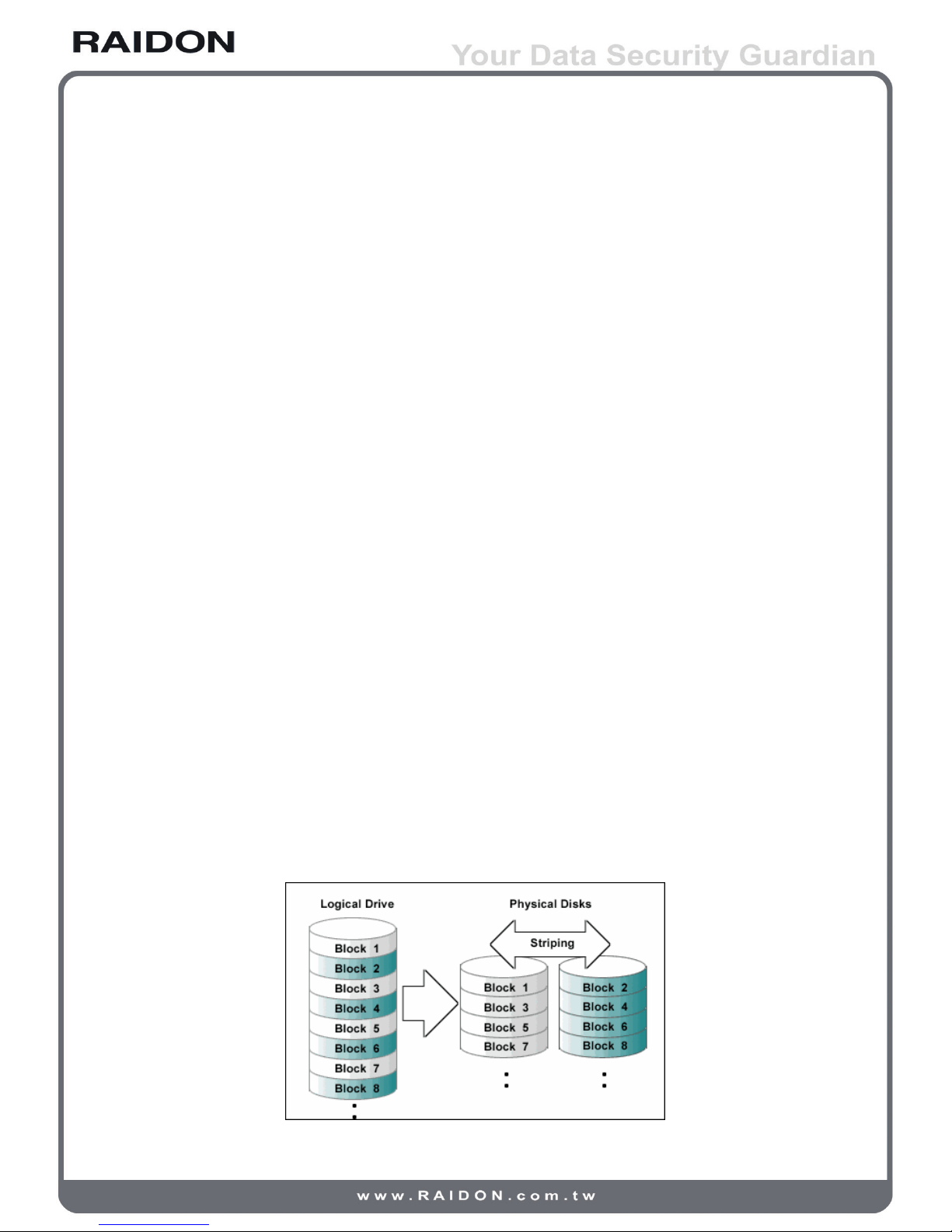
RAID 0 simply data striped over several disks and gives a performance advantage, as it is possible to
read parts of a le in parallel, but comes with no parity information for redundancy, if either one of the
array disks fails will cause the failure to entire array, thus the fault-tolerance of RAID 0 is even lower
than any single hard disk. Although it should not consider as one of the RAID applications, but the term
of RAID 0 is still widely used in these arrays because of the fundamental principle of RAID structures.
Note : 1. We strongly suggest you to use two hard disks with the same model and brand for the best compatibility.
2. When creating RAID 0 with two different sizes of hard disks, the total disk volume will be restricted and
calculated from the least capacity hard disk as example shown below:
Ex: 1×320GB HDD + 1×500GB HDD Total Capacity=320GB×2=640GB
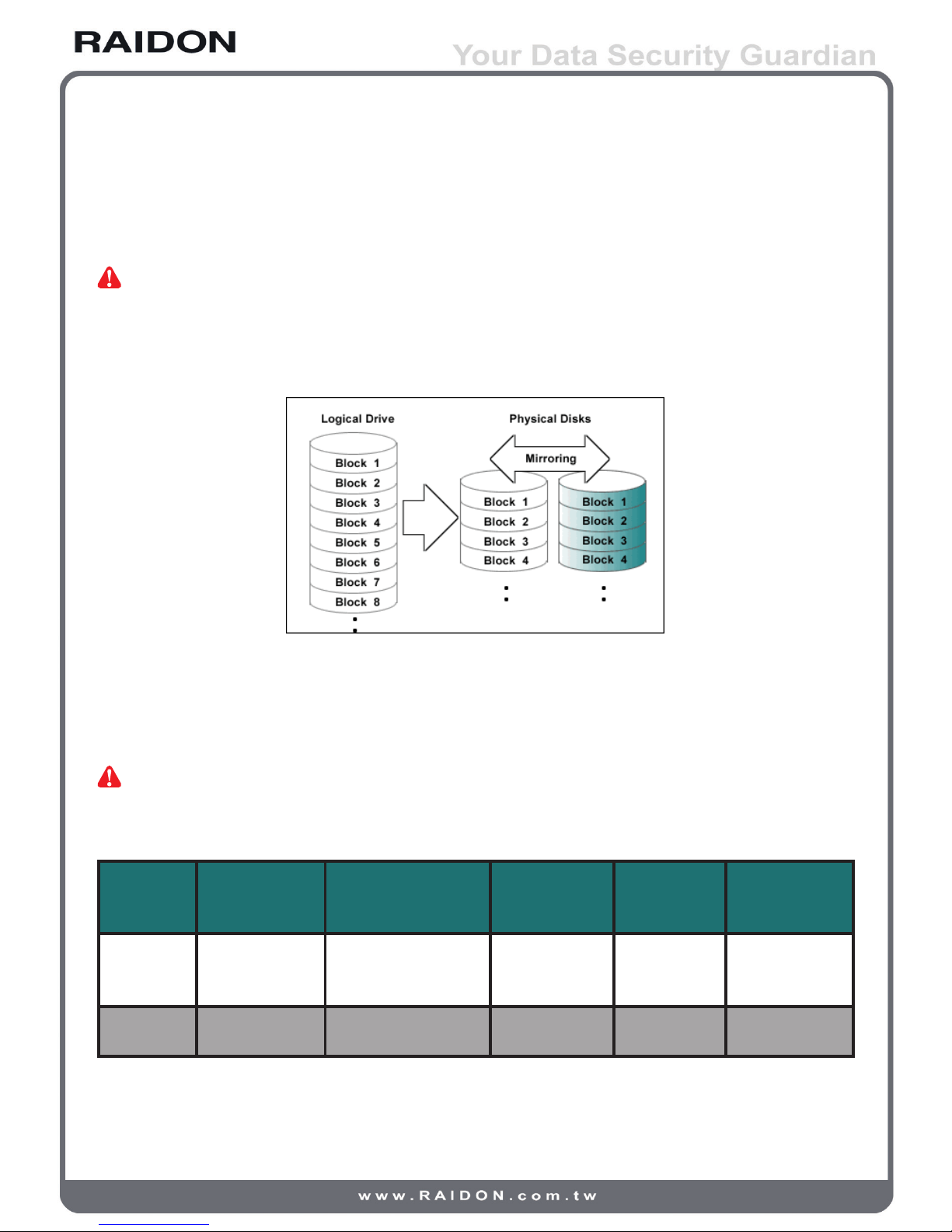
RAID 1 : Mirroring (High security; at least 2 hard disks required)
RAID 1 (commonly referred to as mirroring array) creates from hard disks in pairs with an exact copy
of a set of data inputted simultaneously and each disk can be addressed independently. Mirroring array
provides high reliability to redundancy, because the array does not fail unless the paired up hard disks
fails at the same time. For instance, in a mirroring array of ve-paired hard disks, even as many as ve
hard disks failed at once, the array still exists as long as each pair remains with one working hard disk.
Note : We strongly suggest you to use two hard disks with the same model and brand for the best compatibility.
If there are differences in capacity from two hard drives, the total disk volume will be calculated from the
least capacity hard disk as shown below: Ex: 1×320GB HDD + 1×500GB Total Capacity=320GB
Below is the comparison between 2 RAID levels:
RAID Level Basic Operation
Method
Hard Disk Available
Capacity Data Reliability Data Transfer
Speed
Minimum
Number of Hard
Disks
0
Striping data
across each
drive
Total capacity of all
the hard disks Low Highest 2
1 Mirroring Half of total capacity
of all the hard disks High Lower 2
RAID introduction 5