Documentation Center
RAK19001 WisBlock Dual IO Base Board
Datasheet
WisBlock Dual IO Base Board Overview
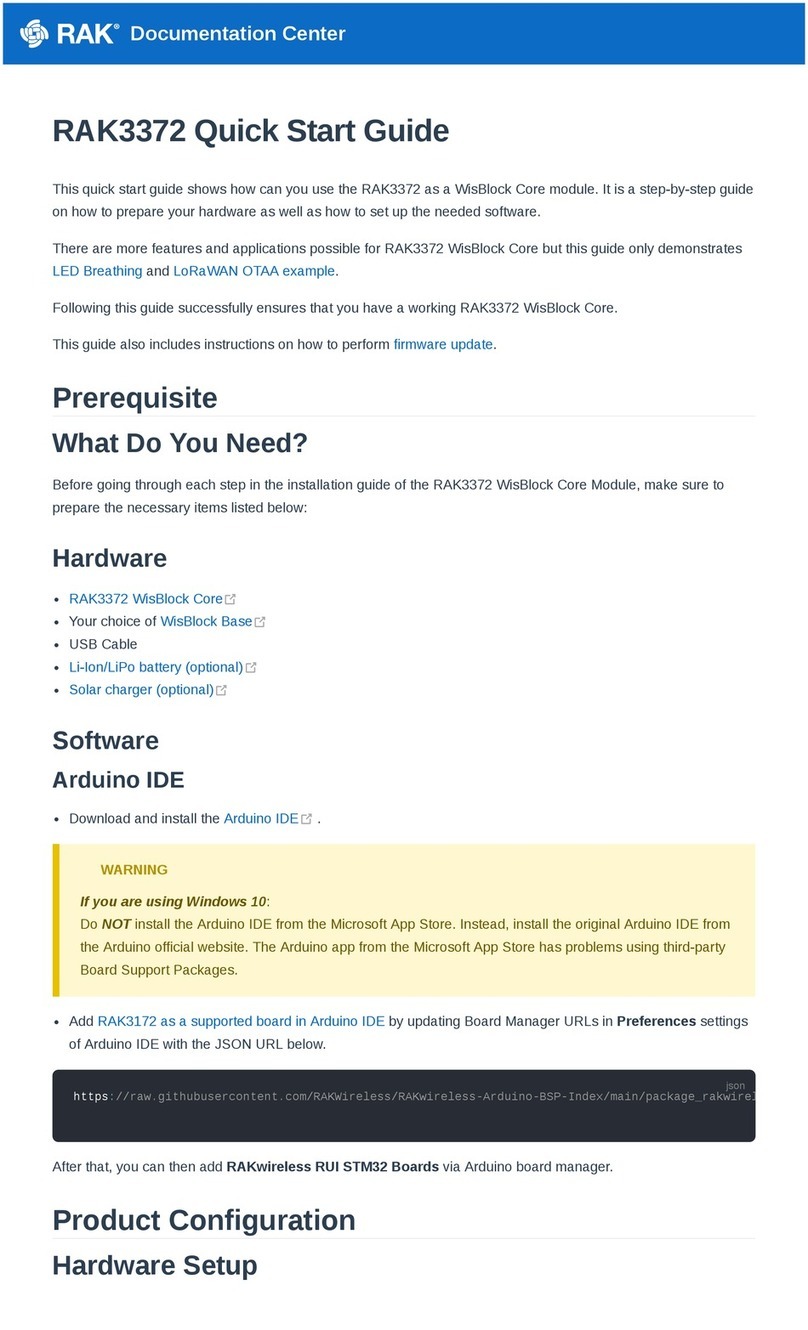
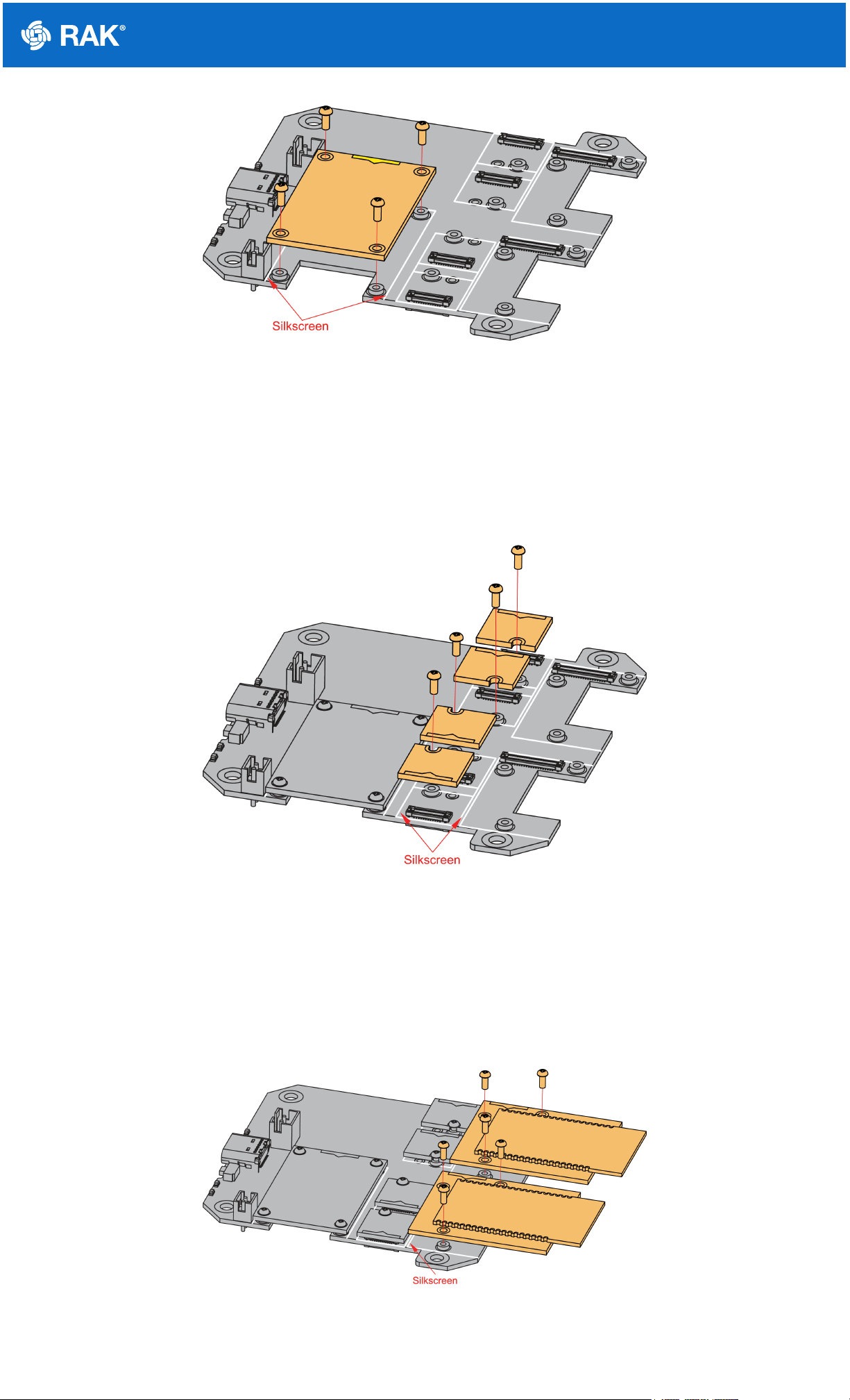
RAK19001 is a WisBlock Base board that connects WisBlock Core and WisBlock Modules. It provides the
power supply and interconnection to the modules attached to it. It has one slot reserved for the WisBlock Core
module, two IO slots, and six sensor slots A to F for WisBlock Modules. Also, there are two 2.54 mm pitch
headers that expose all key input-output pins of the WisBlock Core that includes UART, I2C, SPI, and many IO
Pins.
For convenience, there is a Type-C USB connector that is connected directly to WisBlock Core MCU’s USB port (if
supported) or to a USB-UART converter depending on the WisBlock Core. The USB-C connection can be used for
uploading firmware, serial communication, and charging A rechargeable battery. RAK19001 also includes a slide
switch to select between rechargeable and non-rechargeable batteries.
WisBlock Modules are connected to the RAK19001 WisBlock Base board via high-speed board-to-board
connectors. They provide secure and reliable interconnection to ensure the signal integrity of each data bus. A
set of screws are used for fixing the modules, which makes it reliable even in an environment with lots of
vibrations.
Additionally, it has two user-definable LEDs, one power supply/charging indicator LED, and one user-defined
button.
If you can't find a module that fits your IoT requirements, use the standard connectors of WisBlock to develop your
own specific function module. WisBlock supports open-source hardware architecture and you can find tutorials
showing how to create your own Awesome WisBlock module.
Main Features
Flexible building block design, which enables modular functionality and expansion
High-speed interconnection connectors in the WisBlock Base board to ensure signal integrity
Multiple headers and modules slots for WisBlock modules
Two (2) IO slots
Six (6) sensor (A to F) slots
All key input-output pins of WisBlock Core are exposed via headers
Access to various communication bus via headers: I2C, SPI, UART, and USB
One user-defined push button switch
Power supply
Supports both 5 V USB, 3.7 V rechargeable battery, and 3.3 to 5.5 V non-rechargeable battery as power
supply
The power supply for the WisBlock modules boards can be controlled by the WisBlock Core modules to
minimize power consumption
Slide switch to select between a rechargeable or non-rechargeable battery
Size
60 x 67 mm
Specifications
Overview