RS-LiDAR-16 User’s Manual
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Safety Notices........................................................................................................................................................ 6
2 Introduction........................................................................................................................................................... 7
3 Product Specifications........................................................................................................................................... 8
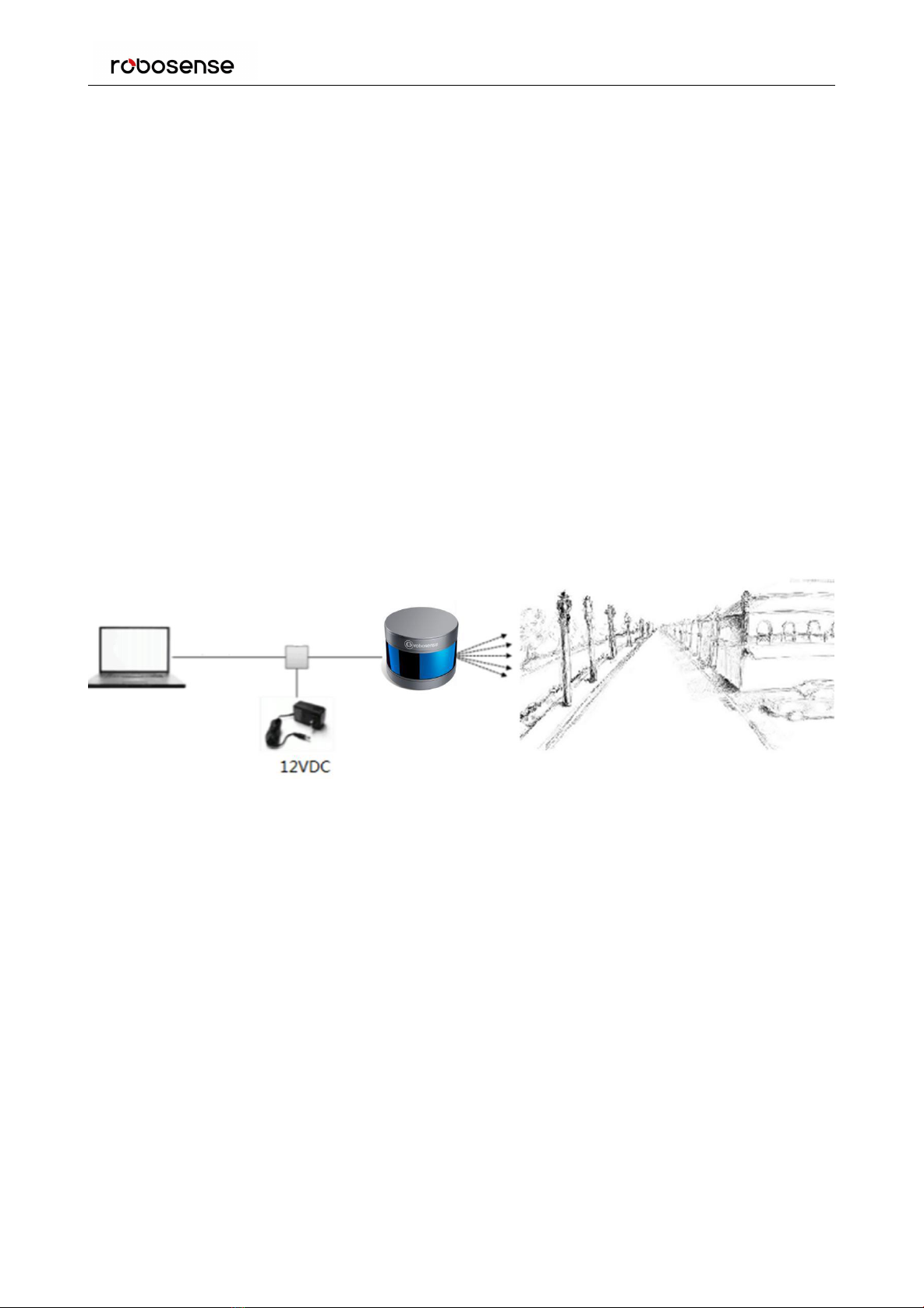
4 Connections................................................................................................................................................... 9
4.1 Power..........................................................................................................................................................9
4.2 Electrical Configuration.............................................................................................................................. 9
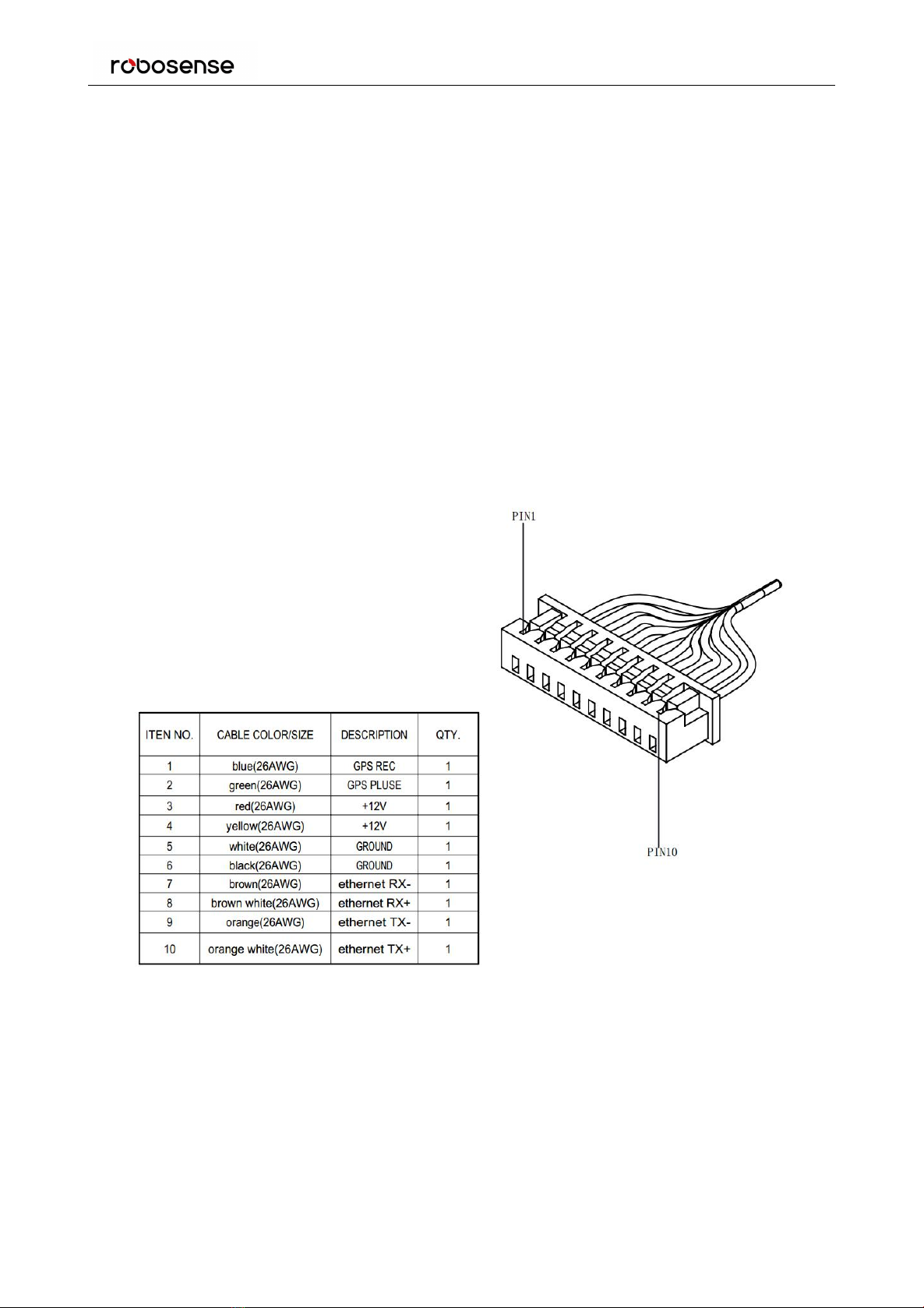
4.3 Electrical Interface......................................................................................................................................9
5 Communications Protocols................................................................................................................................. 11
5.1 MSOP........................................................................................................................................................... 11
5.1.1 Header...........................................................................................................................................12
5.1.2 Data Field.......................................................................................................................................13
5.1.3 Tail..................................................................................................................................................14
5.1.4 Demonstration Data......................................................................................................................15
5.2 DIFOP........................................................................................................................................................ 16
5.3 UCWP........................................................................................................................................................16
6 GPS Synchronization............................................................................................................................................19
6.1 GPS Synchronization Theory.................................................................................................................... 19
6.2 GPS Usage.................................................................................................................................................19
7 Phase Lock........................................................................................................................................................... 20
8 Point Cloud.......................................................................................................................................................... 21
8.1 Coordinate Mapping................................................................................................................................ 21
8.2 Point Cloud Presentation......................................................................................................................... 21
9 Laser Channels and Vertical Angles.....................................................................................................................23
10 Calibrated Reflectivity....................................................................................................................................... 25
11 Trouble Shooting............................................................................................................................................... 26
Appendix A ▪ Point Time Calculate............................................................................................................................28
Appendix B ▪ Information Registers.......................................................................................................................... 29
B.1 Motor(MOT_SPD).................................................................................................................................. 29
B.2 Ethernet(ETH)........................................................................................................................................ 29
B.3 Motor Phase Offset (MOT_PHASE)............................................................................................................. 30
B.4 Top Board Firmware (TOP_FRM).................................................................................................................30
B.5 Bottom Board Firmware (BOT_FRM).......................................................................................................... 30
B.6 Corrected Pitch (COR_PITCH)......................................................................................................................30
B.7 Serial Number(SN)................................................................................................................................. 31
B.8 Software Version(SOFTWARE_VER)...................................................................................................... 31
B.9 UTC Time(UTC_TIME)............................................................................................................................ 31
B.10 STATUS....................................................................................................................................................... 33
B.11 Fault Diagnosis.......................................................................................................................................... 33
B.12ASCII code in GPSRMC Packet....................................................................................................................35
Appendix C ▪ RSView................................................................................................................................................. 36