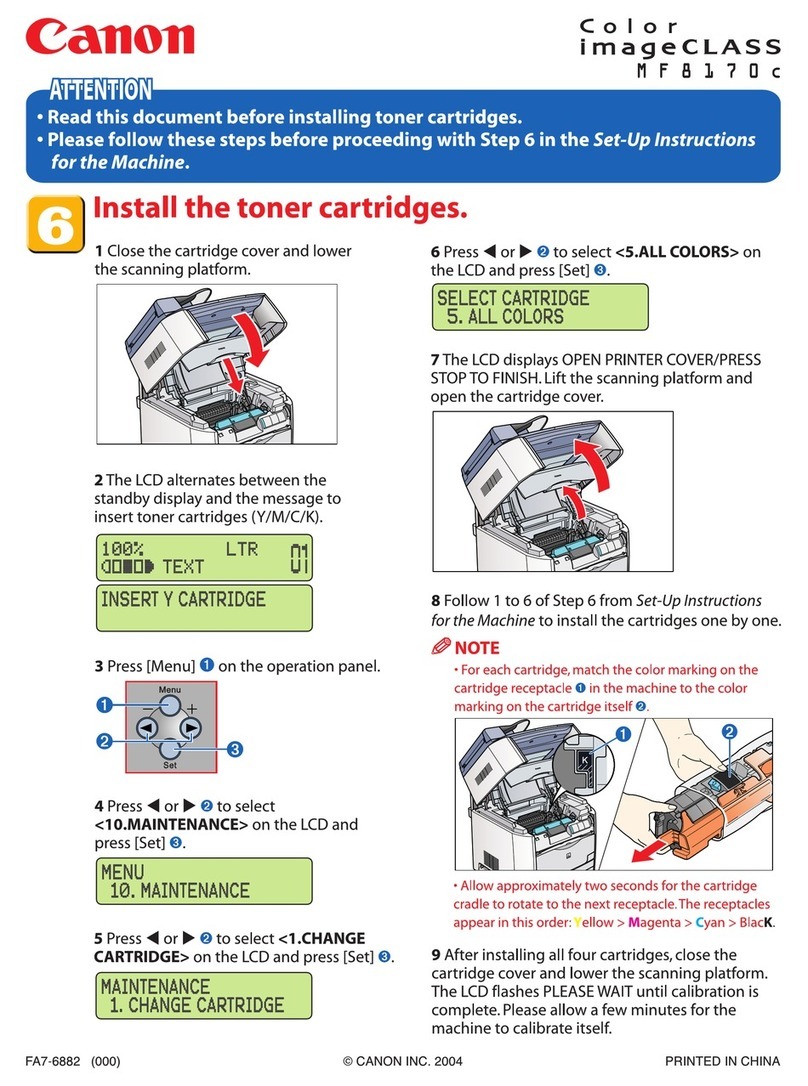
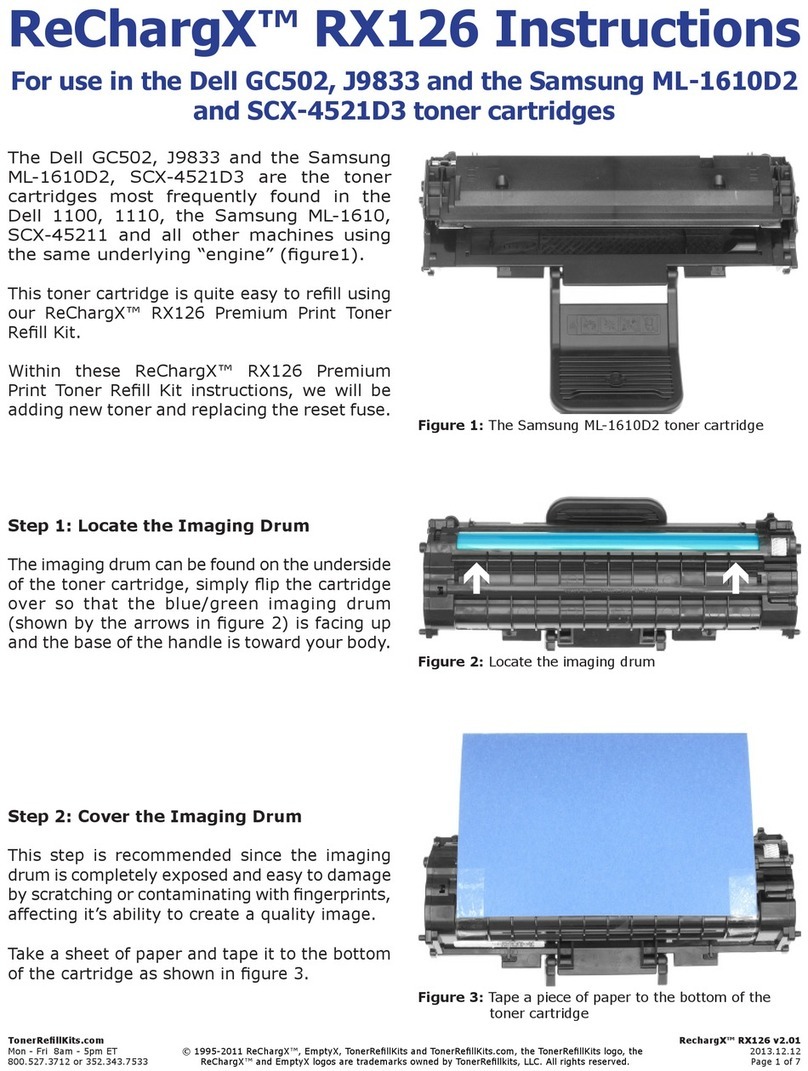
1-3
!Always monitor the output of the paper detector. Incorrect activation of the thermal head may
damage and reduce the longevity of the thermal head and the platen.
Since a reflection type photo interrupter is used in the paper detector, the detector may be
affected by light from outside. Design the outer case so that the paper detector is not
affected by light from outside.
!Allow for movement of the FPC when designing the outer case because the FPC connected
will shift 1 to 2 mm from the thermal head moving. Also, design the outer case so that it
prevents the paper feed out from being caught in the platen.
!Since this printer does not have a platen position detector, mount a detector to the outer case
to monitor whether or not the platen is properly set. When the platen is not properly set, the
printer cannot feed paper and print normally. Incorrect setting of the thermal head may reduce
the longevity of the thermal head.
!When using the LTPA245A:
The printer has no platen block support function. For the platen block support, prepare the
plastic (poly-carbonate is recommended) platen support for snap fitting in the paper holder
cover and fit the platen block shaft into it. For the dimensions of the platen support, the platen
block positioning, and securing, follow the instructions shown in Figures 6-4 and 6-5. Metal or
aluminum platen support cannot fit the platen block shaft.
!When using the LTPA245A:
When removing the platen block, follow the instructions shown in Figure 7-4 and continue to
press the lock arm lever until the A portion of the lock arm (see Figure 7-4) comes up against
the head block. If the lock arm lever is not pressed until the end, it may not be possible to
remove the platen block. Design the outer case so that such lock arm lever operation can be
performed.
Regarding the center of the
rotation of the paper holder cover
on which the platen block is
mounted, follow the instructions
shown in Figure 7-1.
Platen support:
Prepare the plastic (poly-carbonate is
recommended) platen support for snap
fitting in the paper holder cover and fit
the platen block shaft into it. For the
dimensions of the platen support, the
platen block positioning, and securing,
follow the instructions shown in Figures
6-4 and 6-5.
Design so that the paper feed
load is 0.49N (50 gf) or less.
The lever of the lock arm should
be used when removing the
platen block. It should never be
pulled up by force.
Since the printer mechanism
does not have a function to
prevent paper from sliding,
design the outer case so that
the paper is guarded securely.