Sharp EL-9900 User manual
Other Sharp Calculator manuals

Sharp
Sharp EL-240S User manual
Sharp
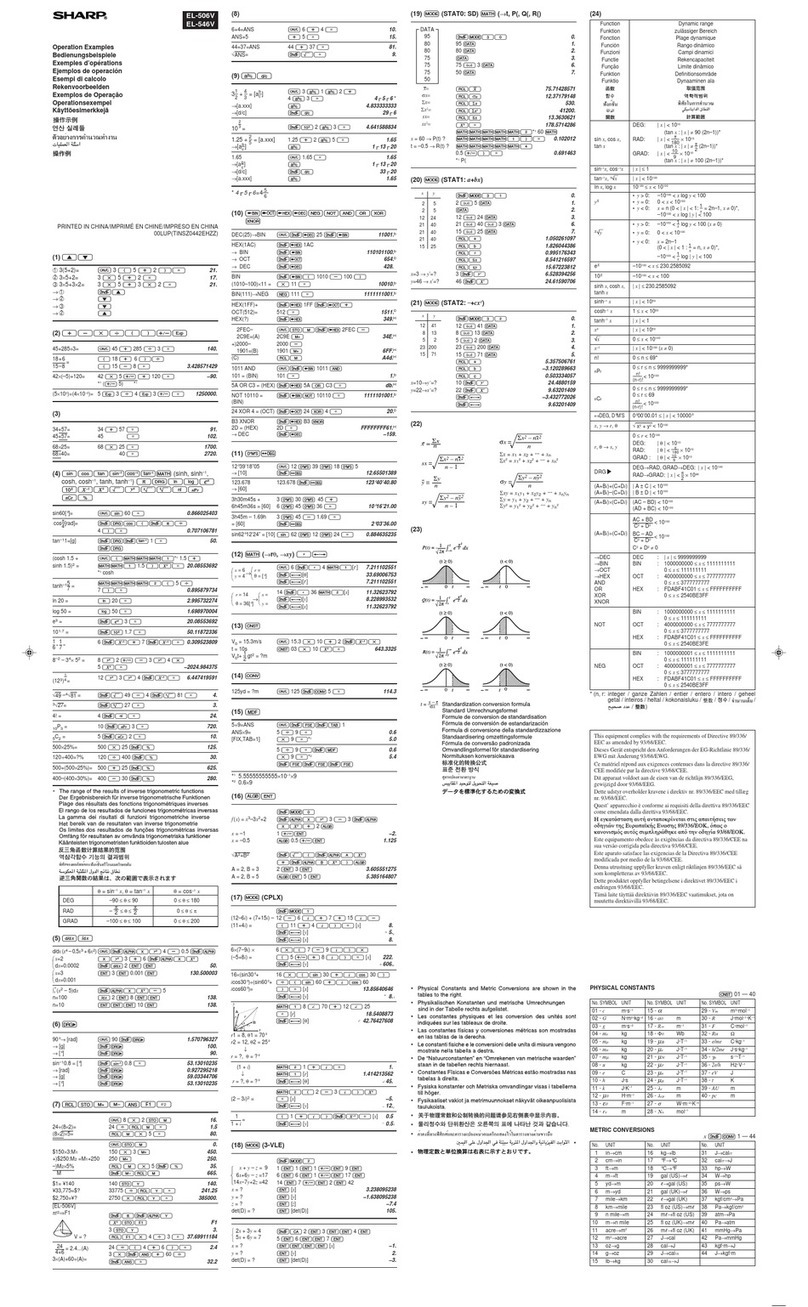
Sharp EL-506VB User manual

Sharp
Sharp EL-364 BBK - El364bbk 12 Digit Slim Design User manual

Sharp
Sharp EL-2910R User manual

Sharp
Sharp EL 2196BL - Heavy Duty Color Printing... User manual

Sharp
Sharp Elsi Mate EL-331A User manual

Sharp
Sharp ELSI MATE EL-330A User manual

Sharp
Sharp EL-1801V User manual

Sharp
Sharp EL-2607P User manual

Sharp
Sharp ELSI MATE EL-334W User manual

Sharp
Sharp Elsi Mate EL-792C User manual

Sharp
Sharp EL-506V User manual

Sharp
Sharp EL1197GIII - Heavy Duty Serial Printing... User manual

Sharp
Sharp EL-506V Installation manual
Sharp
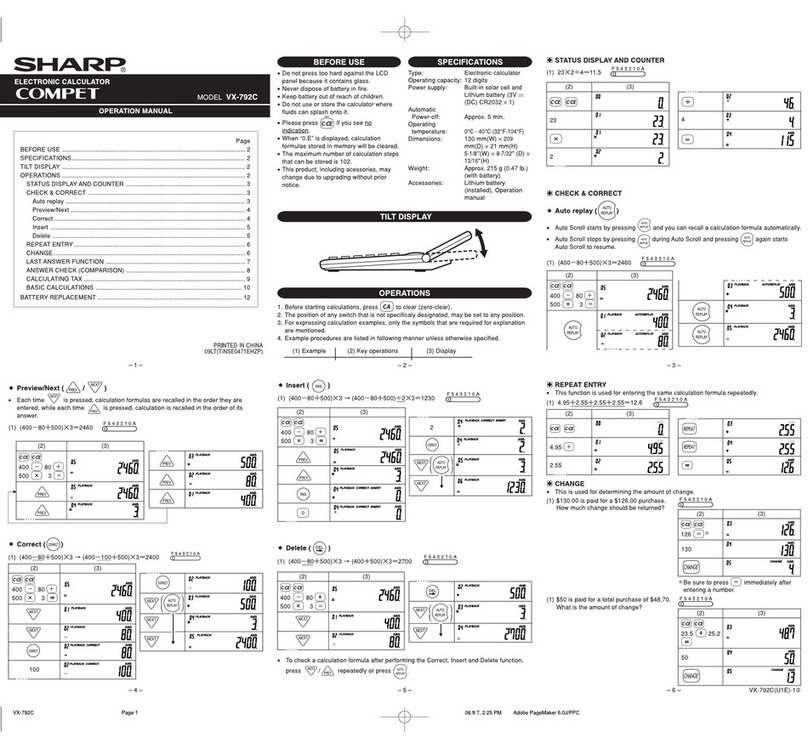
Sharp Compet VX-792C User manual

Sharp
Sharp EL-1901 User manual

Sharp
Sharp EL-501X User manual

Sharp
Sharp EL-2630PIII User manual

Sharp
Sharp EL-337M User manual

Sharp
Sharp ELSIMATE EL-320W User manual