Sigrand SG-16BG User manual

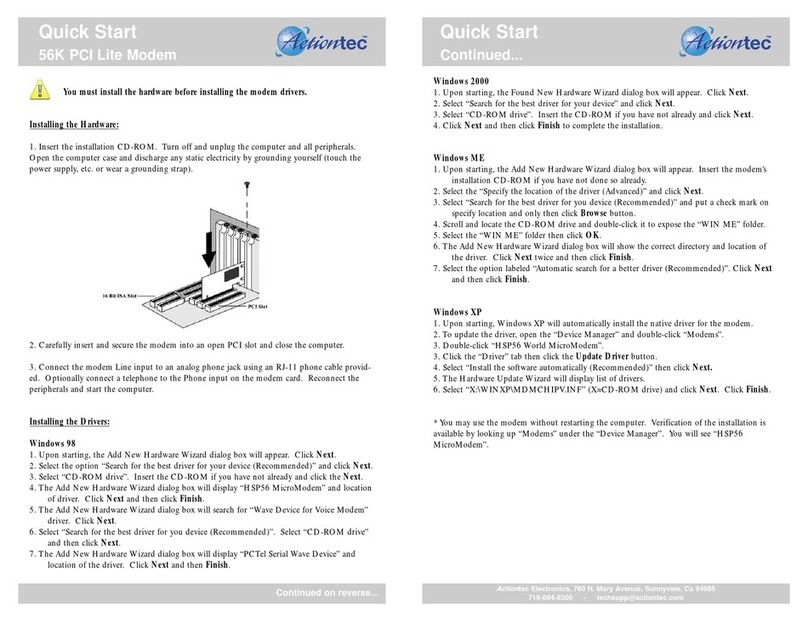
SIGRAND
Integrated access device
SHDSL modem
Sigrand SG-16BG
User's Guide
v. 2.5
Novosibirsk
2006
1

© 2005, 2006 Sigrand LLC
All trademarks and registered trademarks mentioned hereina ter are the
property o their respective owners.
2

Contents
Contents page
How to use this Guide 5
1. Modem description 7
1.1 DSL inter ace speci ications 8
1.1.1 Maximum reach per ormance 9
1.1.2 File trans er per ormance 10
1.2 Ethernet inter ace speci ications 11
1.3 Ethernet Bridge speci ications 11
1.4 E1 inter ace speci ications 11
1.5 RS-232C inter ace speci ications 11
1.6 Power supply unit 12
1.7 Miscellaneous data 12
1.8 Shipment contents 12
1.9 Environmental speci ications 12
1.10 Appearance, controls, indicators and connectors 13
1.10.1 Front panel and indicators 13
1.10.2 Rear panel and connectors 14
2. Modem setup directions 17
2.1 Connecting modem to a line 17
2.1.1 Requirements to a communication line 17
2.2 Choosing modem management method 18
2.3 ”Master”/”slave” mode 18
2.4 Setting DSL rate 18
2.4.1 Setting DSL rate or remote modem 18
2.4.2 Rate selection guidelines 19
2.5 Е1 inter ace setup 20
2.5.1 Connecting Е1 inter ace 20
2.5.2 Con iguring Е1 inter ace 20
2.5.2.1 Bandwidth sharing between Ethernet and E1
inter aces
20
3. Modem management via console port 22
3.1 Terminal setup 22
3.2 General purpose commands 22
The help command 23
3

The info command 23
The stat command 24
The default command 24
The reboot command 25
3.3 DSL inter ace management 25
The help dsl command 25
The dsl command 26
3.3.1 “Master”/”slave” mode selection 26
The dsl master and dsl slave commands 26
3.3.2 Setting DSL rate 26
3.3.2.1 Setting DSL rate rom “master” modem 27
The dsl rate command 27
3.3.2.2 Setting DSL rate manually both sides 27
3.3.3 Line coding selection 28
The dsl code command 29
3.3.4 Link statistics 29
The dsl stat command 29
The dsl stat reset command 30
3.3.5 How to orce a retrain 30
The dsl retrain command 30
3.4 Ethernet inter aces management 31
The help eth commands 31
The eth command 31
3.4.1 Rate and duplex type 31
The eth auto, eth /auto, eth rate, eth
half, eth full commands
32
3.4.2 Flow control 33
The eth flow eth /flow commands 33
3.5 Е1 inter ace management 34
The help e1 command 34
The e1 command 34
3.5.1 Long/Short Haul modes 34
The e1 short and e1 long commands 34
3.5.2 Framing modes and super rame options 35
The e1 framed and e1 /framed commands 35
4

3.5.3 Line coding 36
The e1 code command 36
3.5.4 Е1 inter ace statistics 36
The e1 stat command 36
3.5.5 Timeslot map 37
The e1 map command 38
3.5.5.1 Timeslot 0 40
3.5.5.2 Timeslot 16 41
4. Updating built-in modem irmware 42
Ho to use this Guide
To ease using this Guide the ollowing notational conventions are provided
here (icons as well as relevant onts):
Icons
Icon Meaning Explanation
Pay attention!
The text marked by this icon
contains in ormation making easy
setup and maintenance o
equipment
Important
in ormation!
The text marked by this icon
contains important in ormation
explaining details o operation o
equipment or so tware. This
allows to save your time and
e orts while equipment setup
Do not make this!
Knowing this in ormation allow
you to avoid actions that can
cause damage to hardware
and/or personal injury
5

Font usage
Designation Explanation
Picture on the screen
This ont shows contents o
terminal screen while modem
setup.
Name of keyboard button
This ont shows computer
keyboard buttons, e.g. ”Enter”,
which are used in the console
management mode.
Select Property in the File
menu
Italic notes the ragments o this
Guide containing important
in ormation (together with the
relevant icons). It also marks
so tware buttons o menu in the
text.
dsl stat
Bold ont is used to designate
modem management commands
while a terminal session.
Before starting installation of the modem we
recommend you to look for a updated version of this
User's Guide as well as the firmware and the drivers
available at our site www.sigrand.com
6

1. Modem description
The Sigrand SG-16BG modem is a SНDSL-modem. It is able to exchange
heterogeneous IP and TDM tra ic through Ethernet inter aces and an E1
port.
LAN inter aces work through a built-in Ethernet-bridge and are designed to
connect distributed local area networks as well as remote computers and
other devices equipped with an Ethernet inter ace.
The bridge can transmit VLAN IEEE 802.1Q tags through the DSL inter ace
and the Ethernet inter aces.
Connection o TDM-based communication equipment such as telco
equipment, routers and access servers is provided through the Е1 inter ace
(G.703/G.704, 2048 kbps).
The SHDSL inter ace o the modem con orms to ITU-T G.991.2.bis
standard and uses ТСРАМ (Trellis-Coded Pulse Amplitude Modulation) line
coding.
Features o the ТСРАМ line coding:
The ТСРАМ line coding used by G.991.2 (G.SHDSL) compatible modems
has a ew modes. The modes di er in complexity o coding algorithm. The
modes with larger number o modulation positions (ТСРАМ16, ТСРАМ32)
are applicable or higher rates, the modes with less number o modulation
positions (ТСРАМ4, ТСРАМ8) are applied or lower rates. Respectively,
the more complicated the coding algorithm the worse the channel noise
immunity and vice versa.
So take special attention to the ТСРАМ line coding algorithm selection
while con iguring the line rate. It may be necessary to change the line
coding to achieve the best result.
Table 1 shows the line coding options and respective data rate ranges.
able 1
Line coding Data rate range (kbps)
TCPAM32 256 – 6016
7

TCPAM16 192 – 3840
TCPAM8 192 – 1216
TCPAM4 64 – 704
Manual line coding selection is available only in the console
management mode – see chapter 3 of this Guide
Compatibility:
The Sigrand SG-16BG modem line coding is compatible with all Sigrand
SG-16 series and Granch SBNI16 series modems.
Limitations of compatibility:
Interoperability with the Granch SBNI16 modems is
supported only within the compatible data rate range from
64 to 4608 kbps.
The modem eatures the ollowing inter aces:
•one SHDSL inter ace (con orms to ITU-T G.991.2.bis standard)
providing the data rate range rom 192 to 5696 kbps and the optional
extended range rom 64 to 6016 kbps
•two Ethernet 10/100Mb (IEEE 802.3) inter aces with Auto-Negotiation
and Auto MDI/MDI-X
•one Е1 inter ace (G.703/G.704, 2048 kbps)
•one EIA-232C (RS-232C) inter ace or modem management.
1.1 DSL interface specifications
Link type point-to-point
Number o wires per line 2 (one pair)
Permitted cabling any UTP
Line coding TCPAM
Input/output impedance, Ω135
Data rate range, kbps 64-6016
Data rate step, kbps 64
8

Transmission type ull duplex
Data trans er mode synchronous, by packets
Packet type HDLC
Checksum type CRC32
Connector type RJ-45
Galvanic decoupling trans ormer
breakdown voltage, min, V
1500
Surge protector triggering voltage
(di erential), V
30
Arrester breakdown voltage (common-
mode), V
350
1.1.1 Maximum reach performance
Brie in ormation about the maximum reach per ormance o the Sigrand
SG-16BG modem is shown on Table 2. The Bit Error Rate (BER) at the
maximum reach is equal to or less than 10-7. The speci ied reach is proved
by testing at the Sigrand lab re erence line. Full version o the rate table is
available at our site www.sigrand.com. An actual reach may vary against
the shown data due to variations o cable per ormance.
able 2
Data rate
(kbps) Line coding Rating
TPP50-0.4
cable
(26 AWG)
TPP50-0.5
cable
(24 AWG)
6016 ТСРАМ32 Length (km/ t) 1.8/3500 2.2/7200
R (Ω)476 420
4608 ТСРАМ32 Length (km/ t) 2.0/6500 2.6/8500
R (Ω)560 455
3072 TCPAM16 Length (km/ t) 3.0/9800 4.2/13700
R (Ω)840 736
2304 TCPAM16 Length (km/ t) 3.8/12400 5.4/17700
R (Ω)1064 945
9

1536 TCPAM16 Length (km/ t) 4.4/14400 6.4/20100
R (Ω)1232 1120
1024 TCPAM8 Length (km/ t) 5.0/16400 7.6/24900
R (Ω)1400 1330
512 TCPAM8 Length (km/ t) 5.8/19000 9.0/29500
R (Ω)1624 1575
256 TCPAM8 Length (km/ t) 6.6/21600 10.0/32800
R (Ω)1848 1750
128 TCPAM4 Length (km/ t) 7.4/24200 11.4/37400
R (Ω)2072 1995
64 TCPAM4 Length (km/ t) 7.4/24200 11.4/37400
R (Ω)2072 1995
1.1.2 File transfer performance
Per ormance o the SG-16BG modem during ile trans erring by F P
protocol is shown on Table 3. The table contains average readings
obtained on a line with error rate less than 10-7.
able 3
Line data
rate
(kbps)
File trans er
per ormance
(KBps)
Line data
rate
(kbps)
File trans er
per ormance
(KBps)
6016 700 1792 209
5696 662 1536 179
4608 536 1280 149
4096 478 1024 119
3584 418 768 89
3072 354 512 59
2560 304 256 29
2304 261 192 22
2048 234 128 15
10

1.2 Ethernet interface specifications
Inter ace type 10/100 Base-T
Number o ports 2
Data rate, Mbps 10/100
Duplex type Hal and ull duplex
Compatibility ANSI/IEEE Std 802.3
Auto MDI/MDI-X available
1.3 Ethernet Bridge specifications
MAC-address table size 2048
Maximum packet size, bytes 1536
Packet bu er size, KBytes: 512 (340 packets)
1.4 E1 interface specifications
Type o inter ace RJ-45, Balanced
Number o wires per line 4
Line coding HDB3, AMI
Data rate, kbps 2048
Maximum reach, km ( t)
TPP50-0.4 cable (26 AWG) 1.2 (3900)
TPP50-0.5 cable (24 AWG) 2.4 (7800)
Frame type G.704
Super rame types CRC4, CAS
Un ramed mode available
1.5 RS-232C interface specifications
Baud rate 9600, 57600
Protocol parameters 8-N-1
Flow control N/A
Connector type RJ-45 (DB-9F with converter)
11

1.6 Po er supply unit
Type BPN-12-1V
Input voltage 220V/50Hz
Output voltage 12V
Maximum load current 1A
Polarity o central contact o connector positive
1.7 Miscellaneous data
Overall modem dimensions:
height, mm/in. 45/1.77
•width, mm/in. 225/8.86
•depth, mm/in. 165/6.5
Weight, g/lb 450/1
Weight with PSU, g/lb 1025/2.26
Power consumption, W 6
1.8 Shipment contents
Sigrand SG-16BG modem 1 pc.
Power supply unit 1 pc.
Guide 1 pc.
Cable with converter RJ-45-DB-9 1 pc.
Package 1 pc.
1.9 Environmental specifications
The modem is designed to operate under o ice conditions as ollows:
air temperature 10 .. 40 °C (50 .. 104 °F)
relative air humidity up to 85 %
atmosphere pressure 84 .. 107 kPa (630 .. 802
mmHg)
12

1.10 Appearance, controls, indicators and connectors.
The Sigrand SG-16BG modem should be connected either to a computer
equipped with an Ethernet or Fast Ethernet card or to an Ethernet-switch.
We recommend to connect the modem to an Ethernet
switch, not a hub, since our equipment is optimized for
interaction with Ethernet switches.
The modem is manageable by switches placed on the rear panel as well as
by console management port (ch. 4.1).To manage the modem as well as to
monitor its status you should have an ANSI-compatible terminal emulation
so tware installed on your computer. Con igure your terminal program
according to ch. 1.3 o this Guide.
1.10.1 Front panel and indicators
The ront panel indicators display the status o device operation.
Figure 1
Purpose of Sigrand SG-16BG indicators
able 3
Indicator Status Explanation
POWER
POWER On Modem is on
O Modem is o
DSL
LINK On Active link to remote modem
O No link to remote modem
13

SNR
LINK on
Blink Bad Signal/noise ratio
O Good Signal/noise ratio
LINK o Blink Link activation in progress
O No link
ERR LINK on Blink A packet with error
received
O No error
LINK o On Fatal error
ETHERNET ( channels 1 and 2)
LINK
On Valid Ethernet link detected
O Ethernet link not detected
Blink Tra ic exchange
100M LINK on On 100Base-TX link detected
O 10Base-TX link detected
FD/C LINK on
On Full duplex
O Hal duplex
Blink Collision detected
Е1
LINK On Signal rom Е1 equipment detected
O No signal rom Е1 equipment
SYNC
On Frame synchronization detected or
Un ramed mode
O Frame synchronization not detected
TEST On Test mode
O Operation mode
1.10.2 Rear panel and connectors
Layout o connectors and switches on the rear panel o the Sigrand SG-
16BG modem
Figure 2
14

Purpose of connectors and s itches of the Sigrand SG-16BG
modem
able 4
Power supply unit plug 9-12V DC
RS-232C console port or modem management RS232
DSL line connector DSL
Terminal to connect to protective ground PGND
Dial to select ixed rate or DSL channel RATE
DIP switches to set up modem operation mode SET
Ethernet 10/100Base-T socket 1 ETH1
Ethernet 10/100Base-T socket 2 ETH2
E1 inter ace socket E1
Fig. 3
The “RATE” dial and the “SET” DIP switches ( ig.3) speci y operation mode
o the DSL channel. The dial sets DSL channel data rate ( ig.4).
Fig. 4
15

The “SET1” DIP switch selects “Master/Slave” mode, the “SET2” switch
de ines a method o the DSL channel rate negotiation and the “SET4”
switch sets a mode o modem management. Purpose o the switches are
shown on Table 5.
able 5
Switch Purpose Position Meaning
SET1 Operation
mode
ON Master modem (STU-C)
OFF Slave modem (STU-R)
SET2
Local or
Preactivation
rate select
ON Rate is exchanged by
Preactivation
OFF Rate is set locally on
each modem
SET3
RS-232C
console port
data rate
ON 57600 bps
OFF 9600 bps
SET4
Modem
management
method
ON by console port
OFF by DIP switches
Attention!
Reboot the modem to activate a new modem operation
mode, changed by the DIP switches!
16

2. Modem setup directions
2.1 Connecting modem to a line
Make sure the line has no foreign devices varying its
specifications such as fuses, inductors, load coils and
other similar line conditioning devices. hese devices
may cause serious modem performance limitations or
even completely prevent operation of an xDSL modem!
Make sure that the communication line in use has
neither external voltage supply nor attached foreign
telco devices! Ignoring this rule may cause permanent
damage to both the modems and those foreign telco
equipment!
2.1.1 Requirements to a communication line
The line must comply with the ollowing requirements or proper operation
and per ormance:
•It must have neither leakage to ground nor to other wires (both
connected and loosed). It should not have taps (branches).
•Both wires must belong to the same twisted pair i a multi-pair cable is
used.
•Parallel connection o a ew pairs (e. g., to reduce the line resistance)
is not permitted.
Ignoring the a orementioned requirements may cause signi icant modem
per ormance limitations or even completely prevent operation o an xDSL
modem.
A ter you veri y that the line comply with the a orementioned requirements -
•Fix the supplied RJ-45 plug on the cable in accordance with igure 5.
The Sigrand SG-16BG modem uses only one pair o pins, namely 4
and 5. Other pins are not assigned.
•Attach the cable to the DSL connector o the modem.
17

Fig.5
2.2 Choosing modem management method
There are two ways to manage the modem:
•by the DIP-switches placed on the rear panel o the modem (see
ig.4);
•by a terminal program via the RS-232C console port.
Both modes have certain advantages over each other so a user is ree to
choose either setup mode according to actual requirements or modem
operation.
Setup by switches is described here as the most simple method.
Management by a terminal program is described in Chapter 3.
To use setup by switches, set the SET4 switch to OFF state. For quick
re erence use the sticker at the bottom side o the modem enclosure.
2.3 ”Master”/”slave” mode
Two modems operating peer-to-peer must be con igured by the SET1 DIP
switch ( ig. 3, table 4) such as one modem is set up as a “master” (SET1 is
ON) and another one as a “slave” (SET1 is OFF). We recommend to use
as a “master” the modem which is more accessible or management and
maintenance.
2.4 Setting DSL rate
Fixed rate value is set by dial switch RATE ( igures 2 and 4). One o 16
ixed data rates have to be selected by the dial.
2.4.1 Setting DSL rate for remote modem
This eature is available only or modems with irmware version 2.5 or
higher.
18

The SET2 switch has the ollowing meaning:
•i SET2 is OFF, the rate is set manually at both ends o the line.
(I this case modem uses Annex A or compatibility with irmware
version 2.4 and lower)
•i SET2 is ON, the DSL rate is set by the dial switch RATE o the
“master” modem. (In this case Annex F is used.)
The SET2 switch must be set to the same position or both modems.
o operate properly peer-to-peer, the modems settings
should match each other! Do not forget to configure the
remote modem beforehand!
2.4.2 Rate selection guidelines
Be ore setting the data rate you should have known the per ormance o the
line the modems are intended or. I the line per ormance is unavailable,
apply the ollowing technique to select the proper data rate:
•Measure resistance o the line. To do this, make short-circuit on either
line side and attach an ohmmeter to another one. Then determine a
maximum rate providing reliable communication by table 2.
•Switch care ully the dial to the required position with a screwdriver.
Reboot both modems to activate the new settings. I the remote rate
setting is used (SET2 is ON), change the “master” modem rate only.
Link activation takes up to 2 or 3 minutes to succeed.
•I the link is not activated (the DSL LINK LED is not getting light)
during the mentioned time, set a smaller value on the rate dial and do
the next attempt to activate the link.
•I you can't get the link activated, consider to use console
management mode (Chapter 3). In this mode you can try to succeed
by varying the line coding (Chart 1) as well.
19

2.5 Е1 interface setup
2.5.1 Connecting Е1 interface
Equipment attached to the modem is required to have a balanced Е1 port,
typically implemented as an RJ-45 socket. The inter ace uses 2 loops, one
to receive, another to transmit the data. Pins 1 and 2 are assigned to the
Е1 receiver input, pins 4 and 5 are assigned to the transmitter output
(Table 6, igure 5). Other pins are not assigned. It is not necessary to
recognize polarity o the connection.
able 6
Pin Е1 circuit
1 Receive + (Rx Tip)
2 Receive – (Rx Ring)
4 Transmit + (Tx Tip)
5 Transmit – (Tx Ring)
2.5.2 Configuring Е1 interface
In the DIP switches setup mode (SET4 is OFF) the E1 port always has the
ollowing ixed settings:
•Long-Haul mode
•HDB3 line coding
•CRC4 and CAS super rames are disabled
The RATE dial de ines the DSL inter ace rate and the number o mapped E1
timeslots, as shown in the Table 8.
2.5.2.1 Band idth sharing bet een Ethernet and E1 interfaces
The DSL channel rate is shared between the Ethernet and the E1
inter aces. The range o the E1 timeslots destined to transmit data is
selected together with the DSL rate by the RATE dial. The ollowing rules
apply:
20
Table of contents
Other Sigrand Modem manuals