SPX Cooling Technologies MARLEY Geareducer Series User manual

Geareducer®models 1800 - 2000
OPERATION - MAINTENANCE – REPAIR
Z0493651_A ISSUED 02/2017 READ AND UNDERSTAND THIS MANUAL PRIOR TO OPERATING OR SERVICING THIS PRODUCT
user manual

3
operation and service instructions
Protection Against Corrosion
Geareducer® units ship fromthe factory with aprotective coating of
epoxy enamel paint on all unmachined parts and with rust-proofing
oil and grease on machined surfaces. Machined surface coatings
normally protect the Geareducer against atmospheric corrosion
during storage periods for up to six months. However, if oil is
added to the Geareducer, the new oil will dissolve the rust-proofing
grease and require that the Geareducer be run once a week to
keep a protective coating of oil on all interior machined surfaces.
Check Geareducer exterior yearly and touch up with epoxy paint if
required. If your Geareducer is equipped with an oil gauge and drain
line, coat any exposed threads at pipe joints to prevent corrosion.
Alignment
In order to assure long service life, the Geareducer and motor must
be level, and the drive shaft or coupling must be properly aligned.
Refer to the alignment instructions in the Driveshaft or Coupling
Manual shipped with the cooling tower. Copies are also available
from your local Marley sales representative.
Initial Operation
Check to be sure that the Geareducer is filled with oil and that
there are no visible oil leaks. If equipped with an external dipstick/
oil level gauge, be sure the oil full mark corresponds with the full
level at the Geareducer.
Note—If this tower is equipped with a two-speed motor, allow a
time delay of at least 20 seconds when switching from high speed
to low speed. Allow a time delay of at least two minutes when
changing direction of fan rotation. Failure to provide these delays
may significantly reduce equipment service life.
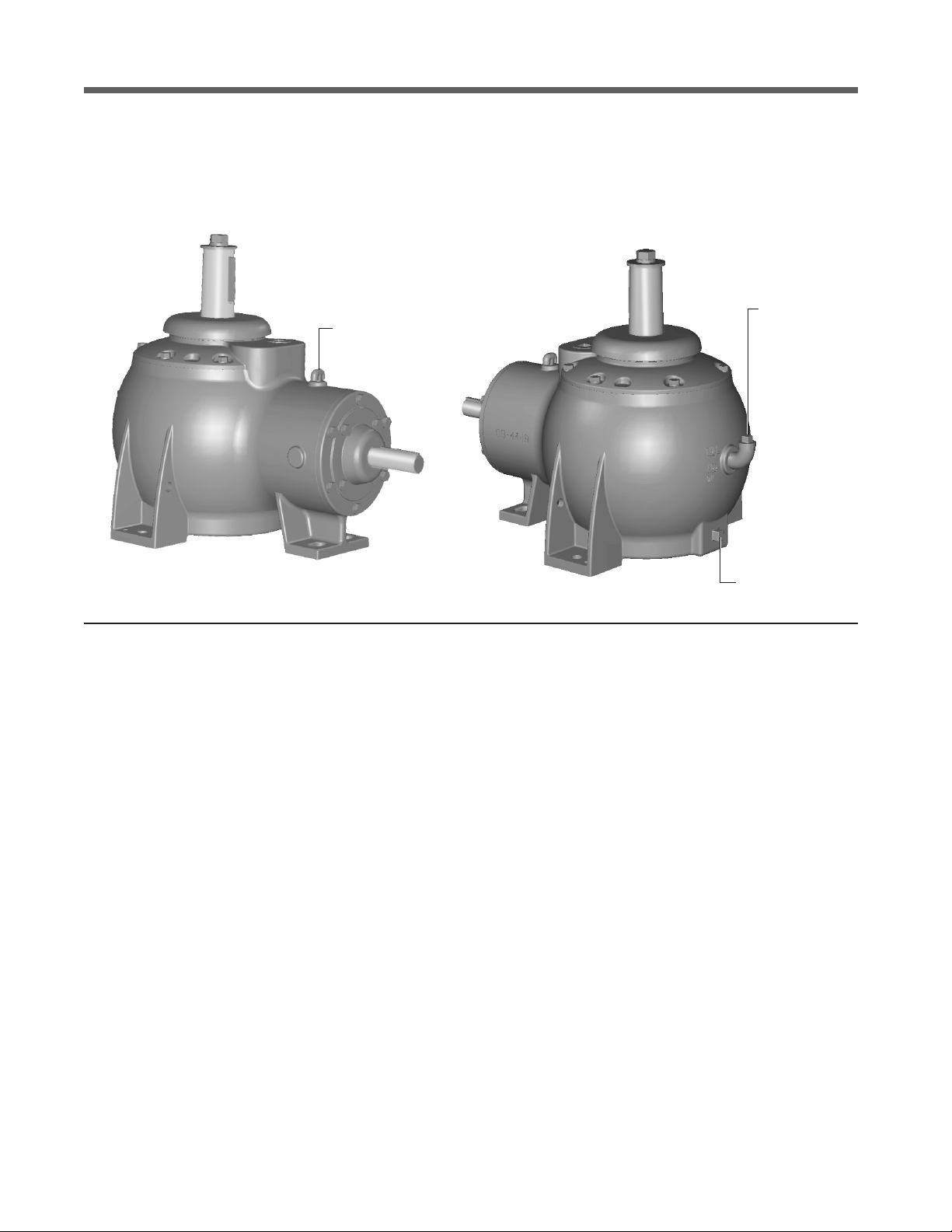
Figure 1 Service Fittings
Drain Plug
Vent
Oil Level Check
and Fill
➠
4
operation and service instructions
Lubricants
To insure maximum performance and servicelife,it is recommended
Marley factory lubricants be used in all Marley Geareducers.
Marley lubricants can be purchased through your local Marley
sales representative.
Note—Geareducer is designed for 5-year oil change intervals. To
maintain five-year change intervals, use only Marley Gearlube.
Marley Gearlube must be inspected every six months to ensure
the oil has not been contaminated. If turbine-type mineral oil is
used the oil must be changed every six months.
Table 1 Synthetic oil—5-year oil change interval
Winter or Summer Severe Duty/High Temperature
Air Temperature at Geareducer
Below 110°F (43°C) Above 110°F (43°C)
ISO 150 ISO 220
If lubricants other than Marley factory lubricants are used, they must
not contain any additives (such as detergents orEP additives) which
are adversely affected by moisture and could reduce the service
life of the Geareducer. The responsibility for use of lubricants other
than Marley factory lubricants rests with the customer/owner and
the lubricant supplier.
Seasonal temperature changes may require one viscosity of oil for
summer operation and another for winter operation. Refer to the
tables below for the seasonal selection information.
Maintenance Service Monthly Semi-annually Seasonal Startup or Annually
Geareducer Drive:
Inspect and tighten all fasteners including oil plug x x
Check for and repair oil leaks x x x
Check oil level x R x
Change oil R R
Make sure vent is open x x
Check driveshaft or coupling alignment x
Inspect and tighten driveshaft or coupling fasteners x
Check driveshaft or coupling bushing / flex elements for unusual wear x
Lube Lines (if equipped)
Check for oil leaks in hoses and fittings x R x
R– Refer to instructions within this manual
Note: It is recommended at least weekly, that the general operation and condition be observed. Pay particular attention to any changes in sound or
vibration that may signify a need for closer inspection.

5
Scheduled Maintenance
Warning—Makecertain that mechanical equipment is inoperable
during periods of maintenance—or during any situation of possible
endangerment to personnel. If your electrical system contains
a disconnect switch, lock it out until the period of exposure to
injury is over.
Monthly—Check Geareducer oil level. Shut down the unit and
allow 5 minutes for the oil level to stabilize. Add oil if required,
noting the addition in your maintenance log. If equipped with an
external dipstick/oil level gauge, small quantities of oil can be
added at that location.
Semi-annually—Check that all the assembly bolts and cap screws
are tight, that oil plugs and pipe connections are in place and free
from leaks, and that the vent on the Geareducer (and external
dipstick/oil level gauge, if present) is clear—a clogged vent can
lead to oil leaks. Intermittent operation and extended periods of
downtime can cause condensation of water in the oil. If using
Marley Gearlube, the oil condition must be inspected every six
months—see Changing Geareducer Oil for maximizing service
life. If using turbine-type mineral oil, change oil—see Changing
Geareducer Oil for instructions.
Annually— Check mechanical equipment anchor bolts, drive shaft
coupling bolts, and coupling set screws. Tighten as required.
Every 5 Years—Change oil. Geareducer was designed for 5-year
oil change intervals. Perform Monthly and Every Six Months
maintenance checks prescribed above. To maintain five-year
change intervals, use only Marley Gearlube.
Changing Geareducer Oil
Drain the Geareducer oil by removing the drain plug. See
Figure 1 for location. If equipped with an external dipstick/oil
level gauge, remove the drain plug at that location, and drain the
entire system.
To maximize service life of the Geareducer, remove a sample from
the drained oil and look for evidence of foreign material, such as
water, metal shavings or sludge, or send the oil sample to an oil
analysis lab for inspection. If you find unacceptable condensation
or sludge, flush the Geareducer with mineral oil before refilling.
After inspection is complete, fill the Geareducer with 9.5 quarts
(9 liters) of oil. See Figure 1 for location. If the Geareducer is
equipped with an external dipstick/oil level gauge an additional 2
to 3 quarts (1.9 to 2.8 liters) of oil will be required. Be certain that
the vent on the Geareducer (and external dipstick/oil level gauge,
if present) is not plugged. Verify that the gauge/drain line is full
and that there aren't any leaks at the connections.
operation and service instructions
Protection Against Corrosion
Check Geareducer exterior yearly and touch up with epoxy paint if
required. If your Geareducer is equipped with an oil gauge and drain
line, coat any exposed threads at pipe joints to prevent corrosion.
Repair and Overhaul
The Model 1800 and 2000 Geareducer is assembled using
specialized tools and fixtures.Bearings and gearsets are unique and
not available from other sources. Geareducers can be repaired in
the field—however, major repairs require the use of a fully equipped
machine shop. Refer to the Field Repair section of this manual
for further instructions.
If your Geareducerever needsreplacement orrepair, werecommend
returning the unit to a Marley factory service center. Contact your
Marley sales representative to discuss course of action. A factory
reconditioned Geareducer carries a one year warranty. The Marley
cooling tower order number will be required if the Geareducer is
shipped back to the factory for repair. Obtain a “Customer Return
Material” tag from the Marley sales representative in you area.
To find your Marley sales representative call 913 664 7400 or
check the internet at spxcooling.com

6
Figure 2
parts list
PINION CAGE
GEAREDUCER
CASE
BOTTOM CAP
AIR VENT
PINION CAGE
CAP
501
504
505
503
311
411
102
412
502
420
103
104312
101
5
101
202
201
203
COVER
DOWEL PIN
BEARING
RETAINER
WATER
SLINGER
210
420
320
301

7
1 Complete Geareducer Assembly.
5 Ring Gear Hub.
100 Spiral Bevel Gear Set.
101 Set of matched spiral bevel gears including
integral pinion shaft with key.
Gear ratios as follows:
4.80 to 1 3.75 to 1 2.71 to 1
4.09 to 1 3.27 to 1 5.375 to 1
102 Ring gear attaching hardware.
103 Locknuts.
104 Lockwasher.
200 Fan Shaft Set.
201 Fan shaft.
202 Ring gear hub key.
203 Fan key.
210 Fan attaching hardware.
Cap screws and washers.
301 Oil Slinger.
310 Set of Two Pinion Shaft Bearings.
311 Head, tapered roller bearing.
312 Tail, tapered roller bearing.
320 Pinion Cage Shims.
410 Fan Shaft Bearing Set.
411 Lower tapered roller bearing.
412 Upper tapered roller bearing.
420 Fan Shaft Shims.
500 O-Rings Set.
502 Water slinger O-ring.
503 Pinion cage O-ring.
504 Pinion cage cap O-ring.
505 Pinion seal O-ring.
501 Pinion Shaft Oil Seal.
parts list

8
field repair
General
Geareducers can be repaired in the field—however, major repairs
require the use of a fully equipped machine shop. When field repair
or replacement of parts is necessary, the following procedure is
recommended for the disassembly and assembly of the unit. If any
O-ring, oil seal or gasket is to be reused, care should be taken
not to damage it during disassembly. Parts which contain O-rings
or seals should not be jerked or twisted past a shoulder or edge.
These parts are marked with an asterisk (*) in the description
below. O-rings, oil seal and gaskets should be carefully inspected
for damage before being reinstalled. New O-rings and oil seal
should be installed during a major overhaul.
Disassembly
Part numbers and references—refer to Figure 2
1. Drain oil.
2. Remove outer ring of bolts in pinion cage cap and remove
pinion subassembly*.
Note—Thethicknessof theshim pack(320) is important in resetting
the gears. The shim pack should either be saved or carefully
measured with a micrometer. If the gears are to be replaced,
record the pinion setting distance that is etched on the pinion gear.
3. Remove water slinger*.
4. Remove bearing retainer and shim pack (420) from top of
case.
Note—The thickness of this shim pack is important in the backlash
setting of the gears. The shim pack should either be saved or
carefully measured with a micrometer.
5. Drive dowel pins down into case.
6. Remove bolts and case cover and lift fan shaft assembly out
of the case.
7. Turn case over and remove bottom cap and shims.
Note—The thickness of this shim pack is important in setting the
fan shaft bearing endplay. This pack should be saved or carefully
measured with a micrometer.
8. Remove bearing cups (411 and 412) from the Geareducer
case and cover.
Pinion Cage Disassembly
1. Remove pinion cage cap* from pinion cage.
2. Remove O-rings* (503 and 504).
3. Slide seal off of pinion shaft and remove O-ring (505).
3. Remove locknuts and lockwasher (103 and 104) then press
pinion shaft (101) out of pinion cage. This will free tail bearing
cone (312).
4. Press oil slinger (301) and head bearing cone (311) from the
pinion shaft.
5. Press bearing cups (311 and 312) out of pinion cage.
Fan Shaft Disassembly
1. Remove ring gear (101) from the ring gear hub
(5).
2. Press ring gear hub and lower bearing cone (411) off of the
fan shaft (201).
3. Remove lower fan shaft key (202).
4. Press the top bearing cone (412) off of the shaft.

9
Assembly
Before assembling a new pinion gear in the pinion cage, check
match numbers on pinion gear and spiral bevel ring gear to be
certain that they are a matched set. Gears are lapped in matched
sets at the factory and should not be separated. Numbers are
etched on both the pinion and ring gear as illustrated in Figure 3.
All parts that are to be reused should be thoroughly cleaned before
being reinstalled. Replace bearings if necessary.
Pinion Cage Subassembly
1. Place oil slinger (301) on pinion shaft.
2. Press head bearing cone (311) on pinion shaft making sure
oil slinger and bearing are against gear.
3. Press bearing cups (311 and 312) into pinion cage.
4. Lower pinion cage on pinion shaft, until head bearing cone
and cup mate.
5. Press tail bearing cone (312) on pinion shaft until it mates
with its bearing cup.
MATCHED NUMBER TO BE COMPARED WITH THE SAME
NUMBER ON THE RING GEAR. (EXAMPLE CO-43)
PINION SETTING DISTANCE. (EXAMPLE 4.860)
BACKLASH (NORMAL) AT WHICH THE GEARS WERE
LAPPED. (EXAMPLE .010)
MATCHED NUMBER TO BE COMPARED WITH THE SAME
NUMBER ON THE PINION GEAR. (EXAMPLE C0-43)
THE PINION SETTING DISTANCE IS THE DISTANCE
THE END OF THE PINION SHOULD BE FROM THE
CENTERLINE OF THE RING GEAR SHAFT.
Figure 3 Gear Match Numbers and Setting Data
6. Install locknuts and lockwasher (103 and 104). Tighten nuts
on bearing cone until 5 to 15 in·lbƒ (565-1695 mN·m) of
bearing preload is obtained. Bearing preload is the resistance
in the bearings to shaft rotation measured in in·lbƒ required
to rotate the shaft at uniform velocity. Preload is necessary
to insure the stability of the gear engagement. Crimp the
lockwasher to hold the two nuts in place.
7. Install O-ring (503) in groove on pinion cage. Install
O-ring (505) on pinion shaft outboard of locking-nut threads
8. Install oil seal* (501) onto the pinion shaft.
9. Position O-ring (504) in groove in cap and place cap on shaft.
Slide cap up against pinion cage and install bolts.
10. Record the pinion setting distance that is etched on the pinion
gear.
field repair
10
Installation of Fan Shaft
1. Press ring gear hub (5) and the upper and lower bearing
cones (411 and 412) on the fan shaft (201). Install ring gear
(101) on ring gear hub and tighten cap screws to 55 ft·lbƒ
(75 N·m) .
2 Install the bottom cap using old shim pack or make up
equivalent thickness shim pack (420).
3. Press bottom fan shaft bearing cup (411) in bore.
4. Install fan shaft assembly in case.
5. Press upper fan shaft bearing cup (412) in cover. Apply a
bead of sealant to the cover flange inboard of the bolt holes.
Install cover on case. Install dowel pins in cover and drive flush
with top of cover.
6. Install cap screws and tighten to 20 ft·lbƒ (27 N·m).
7. Install bearing retainer using old shim pack (420) or equivalent
and tighten cap screws to 20 ft·lbƒ (27 N·m).
5. Rotate the fan shaft several turns in each direction to seat the
bearing rollers. With a dial indicator and using the Geareducer
case as a reference, measure and adjust the fan shaftbearings
to .001-.003" (.025-.076mm) endplay. The endplay is adjusted
by adding shims (420) under the bearing retainer.
Installation of Pinion Cage
1. Find the difference between the pinion setting distance of
the old gear and the new pinion gear and adjust the old shim
pack (320) or make a new shim pack to compensate for the
different setting distances.
Example:
Pinion setting distance of old gear 4.883
Pinion setting distance of new gear 4.878
Difference .005
Remove .005 from shim pack.
2. Install pinion cage subassembly into case.
Note—Engage pinion gear tooth with "X" marked on end between
ring gear teeth markedwith "X’s". Care must be takennot to damage
the pinion gear teeth by forcing them into the ring gear teeth.
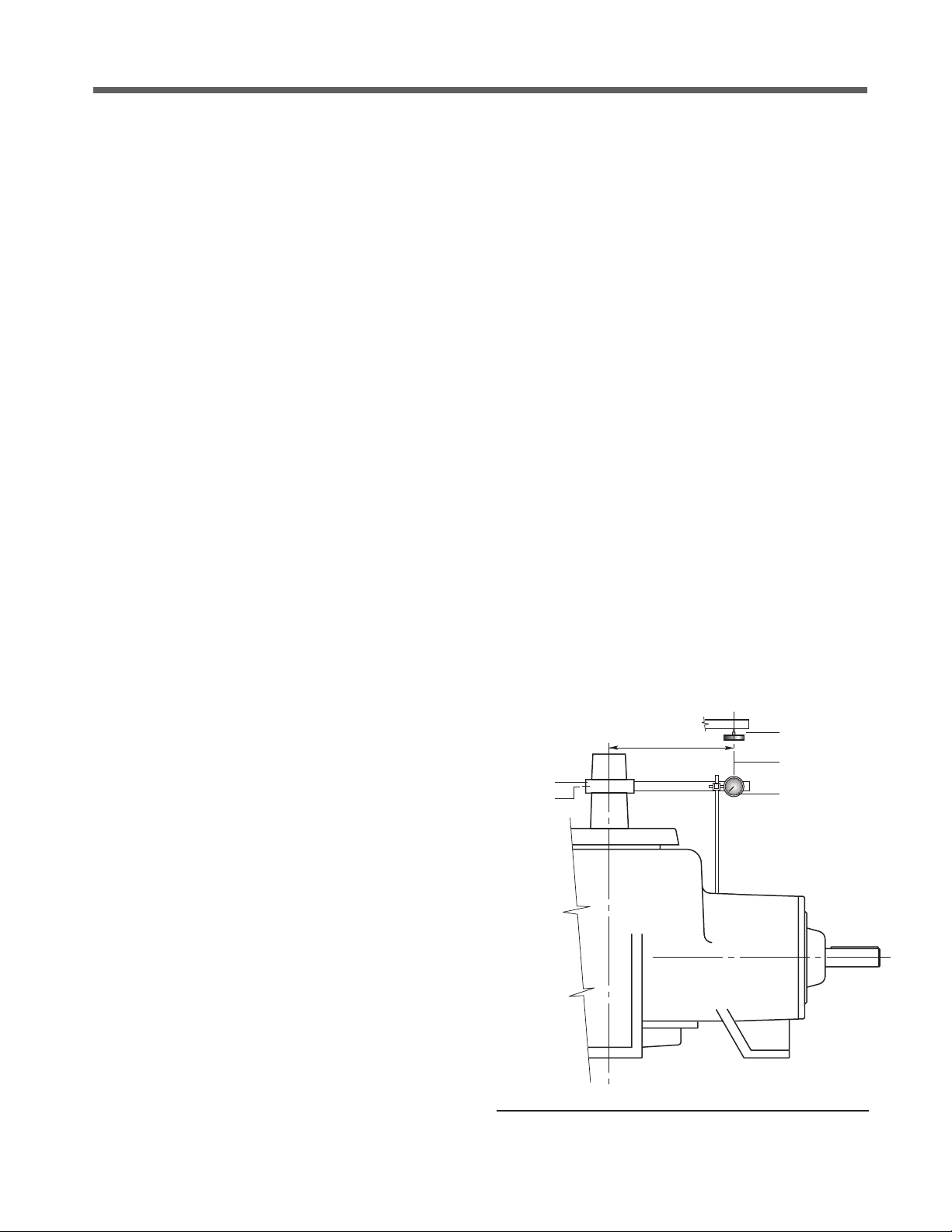
Gear Setting Procedure
The proper mounting of the gear set is essential to obtain long
life and smooth operation of the gears. The pinion and ring gears
were positioned approximately in the preceding steps. The correct
gear position is determined by the gear backlash.
With the "X" marked tooth on the pinion gear engaged between
the two "X" marked teeth on the ring gear, check the backlash with
a dial indicator as shown in Figure 5. Lock the pinion shaft against
rotation. The amount of movement of the fan shaft, measured
at a distance equal to the outside radius of the ring gear is the
backlash. The backlash on all ratios should be between .007 and
.014" (.18 and .36mm). With the "X" teeth engaged, the backlash
should be approximately in the middle of the allowable range.
Check the backlash at three other points around the ring gear to
be sure the backlash is within the specified limits. Adjust ring gear
axially by removing or adding shims (420) at bottom bearing cap.
Note—To maintain bearing adjustment corresponding shim (420)
adjustment must be made at the bearing retainer.
Example: Removing .003" shims at the bottom bearing retainer
requires the addition of .003" shims at the top bearing retainer
to maintain correct bearing adjustment.
Recheck the backlash to make sure it is within the proper limits.
COLLAR
SET SCREW
TOP VIEW
OF INDICATOR
POINT OF MEASUREMENT
OUTSIDE RADIUS OF GEAR
DIAL INDICATOR
Figure 5 Gear Backlash Measurement
field repair

11
Final Assembly
1. Remove bottom cap and apply a bead of sealant to the bottom
cap flange inboard of the bolt holes. Reinstall the bottom
bearing retainer cap and tighten the cap screws to 20 ft·lbƒ
(27 N·m).
2. Install O-ring (502) in water slinger.
3. Install water slinger on fan shaft (201).
4. Replace air vent and all pipe plugs.
5. Fill with lubricant selected from Table I.
field repair

Z0493651_A (M00-1218C) | ISSUED 02/2017
COPYRIGHT © 2017 SPX CORPORATION
In the interest of technological progress, all products are subject to design
and/or material change without notice.
Geareducer
USER MANUAL
SPX COOLING TECHNOLOGIES, INC.
7401 WEST 129 STREET
OVERLAND PARK, KS 66213 USA
spxcooling.com
This manual suits for next models
2
Table of contents
Other SPX Cooling Technologies Industrial Equipment manuals
Popular Industrial Equipment manuals by other brands

SAINT-GOBAIN
SAINT-GOBAIN NORTON clipper TR 232 S&L operating instructions

Fröling
Fröling EF 250 Installation and operating instructions

SignWarehouse
SignWarehouse enduraPRESS CS15AR TS user manual

Festo
Festo DG..-...-GA Series operating instructions

Dixon Bayco
Dixon Bayco 6200X Installation & operating instructions

TEDA
TEDA XQ114/6B Operation manual












