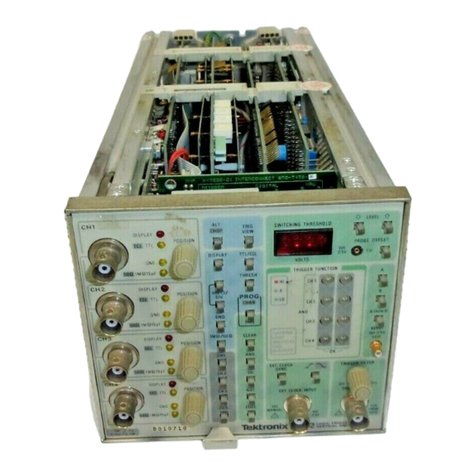
Tektronix 7a15a User manual
Other Tektronix Amplifier manuals

Tektronix
Tektronix 2A61 User manual

Tektronix
Tektronix AM 502 User manual

Tektronix
Tektronix 7A16 User manual
Tektronix
Tektronix Z User manual

Tektronix
Tektronix 11A52 Owner's manual

Tektronix
Tektronix TYPE CA User manual

Tektronix
Tektronix 7A16A User manual
Tektronix
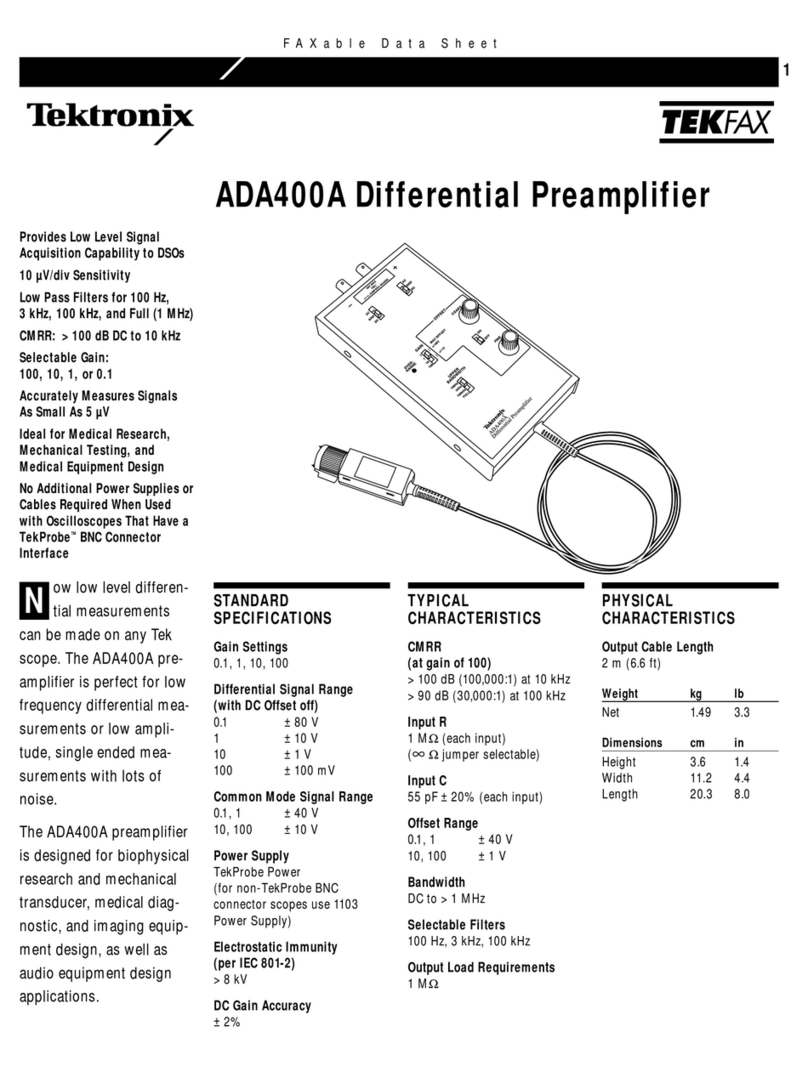
Tektronix TEKFAX ADA400A User manual

Tektronix
Tektronix 7K11 User manual

Tektronix
Tektronix TEKFAX ADA400A User manual

Tektronix
Tektronix 7A13 User manual
Tektronix
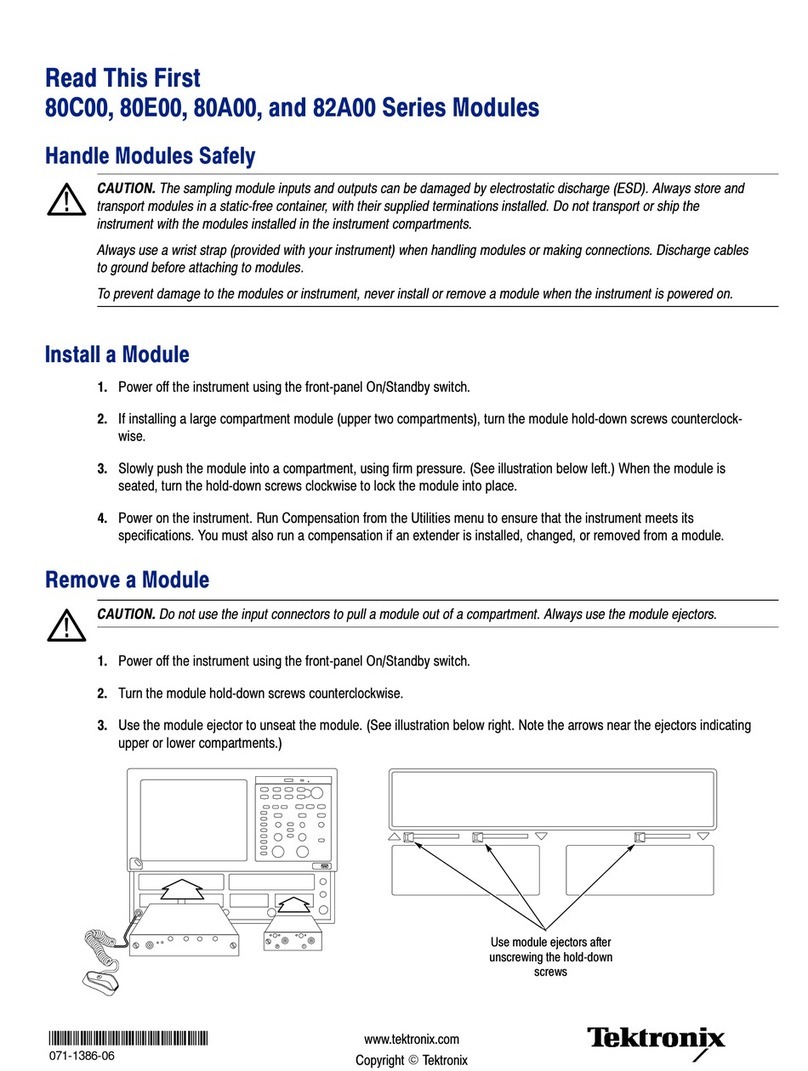
Tektronix 80C11 User manual

Tektronix
Tektronix 5A15N User manual

Tektronix
Tektronix 11A32 Assembly instructions

Tektronix
Tektronix 7A18 User manual
Tektronix
Tektronix 1A7 User manual

Tektronix
Tektronix 7A18A User manual

Tektronix
Tektronix 7A24 User manual

Tektronix
Tektronix 7A16A User manual

Tektronix
Tektronix 7A29 User manual