TELink FR1 Instruction Manual

Telink FR1 PCB Design Guideline
AN-22051900-E1
Ver.1.0.0
2022/05/19
Keyword
Layout, FR1, PCB
Brief
This is Telink FR1 PCB design guideline which mainly introduces considerations when designing FR1 boards.

Telink FR1 PCB Design Guideline
AN-22051900-E1 Ver. 1.0.0
2
Published by
Telink Semiconductor
Bldg 3, 1500 Zuchongzhi Rd,
Zhangjiang Hi-Tech Park, Shanghai, China
© Telink Semiconductor
All Rights Reserved
Legal Disclaimer
This document is provided as-is. Telink Semiconductor reserves the right to make improvements without
further notice to this document or any products herein. This document may contain technical inaccuracies or
typographical errors. Telink Semiconductor disclaims any and all liability for any errors, inaccuracies or
incompleteness contained herein.
Copyright © 2022 Telink Semiconductor (Shanghai) Co. , Ltd.
Information
For further information on the technology, product and business term, please contact Telink Semiconductor
Company (www.telink-semi.com).
For sales or technical support, please send email to the address of:
telinksales@telink-semi.com
telinksupport@telink-semi.com

Telink FR1 PCB Design Guideline
AN-22051900-E1 Ver. 1.0.0
3
Revision History
Version Change Description Date Author
V1.0.0 Initial release. 2022/05 Junyao MAO,
Weixiang WANG

Telink FR1 PCB Design Guideline
AN-22051900-E1 Ver. 1.0.0
4
Table of Contents
Revision History ................................................................................................................................3
Table of Contents..............................................................................................................................4
List of Figures ...................................................................................................................................5
1. Overview ...................................................................................................................................6
2. Application Board Structure ID ...................................................................................................7
2.1 Single-layer board.................................................................................................................7
2.2 Doulbe-layer board ...............................................................................................................8
2.2.1 Component and copper wire layer + carbon film alignment layer ...........................................8
2.2.2 Component and copper wire layer + carbon film and copper wire layer...................................9
3. Key Points of FR1 Board Design................................................................................................ 10
3.1 Board layer ........................................................................................................................ 10
3.1.1 Board thickness selection ............................................................................................... 10
3.1.2 Introduction of board structure........................................................................................ 10
3.2 Carbon film routing ..............................................................................................................11
4. Layout Regulations................................................................................................................. 13
4.1 Package............................................................................................................................. 13
4.2 Solder pads and vias............................................................................................................ 13
4.3 Notes ................................................................................................................................ 15
5. Routing Notes........................................................................................................................ 18

Telink FR1 PCB Design Guideline
AN-22051900-E1 Ver. 1.0.0
5
List of Figures
Figure 2-1 Single-layer board........................................................................................................7
Figure 2-2 Component layer + carbon film layer ..............................................................................8
Figure 2-3 Double layer routing + carbon film routing ......................................................................9
Figure 3-1 Stack structure .......................................................................................................... 10
Figure 3-2 Carbon film routing.................................................................................................... 12
Figure 4-1 Package forms........................................................................................................... 13
Figure 4-2 Package design for Telink IC ....................................................................................... 14
Figure 4-3 Via hole on carbon film .............................................................................................. 15
Figure 4-4 Layout for RF circuit................................................................................................... 16
Figure 4-5 Layout for power capacitors ........................................................................................ 17
Figure 5-1 Routing example 1 ..................................................................................................... 19
Figure 5-2 Routing example 2 .................................................................................................... 19
Figure 5-3 Routing example 3 ....................................................................................................20

Telink FR1 PCB Design Guideline
AN-22051900-E1 Ver. 1.0.0
6
1. Overview
With the same PCB size and the same quantity of components, generally the fewer the number of PCB
layers, the more difficult the design.
Due to cost concern, PCB designs are increasingly preferred to use FR1 boards, single-layer boards, which
leads to more obvious problems in wireless communication, including power interference, RF high harmonics,
and etc.
This document uses the Telink SoC chips as a basis and the remote control design as an example to illustrate
how to guide the design of FR1 boards to achieve fast development and avoid multiple iterations.

Telink FR1 PCB Design Guideline
AN-22051900-E1 Ver. 1.0.0
7
2. Application Board Structure ID
According to the complexity of the components, taking into account cost and the difficulty of routing, the the
PCB design for Telink chips can be divided into single-layer boards or double-layer boards.
2.1 Single-layer board
In single-layer board design, make sure that all components and keys can be placed on the same side and
there should be enough space for the PCB antenna. This is suitable for boards with a small number of
components and routings.
The remote control board shown below can be designed as a single-layer board.
Figure 2-1 Single-layer board

Telink FR1 PCB Design Guideline
AN-22051900-E1 Ver. 1.0.0
8
2.2 Doulbe-layer board
2.2.1 Component and copper wire layer + carbon film routing layer
One layer of this double-layer board is used to place components and route copper wire, and the other layer
is for carbon film routing. For example, in a remote control design, we place the components on one layer
and the keys on the other layer. The keys need to be designed as carbon film keys and the keys routing is
connected to the component layer via carbon film via holes. Note that carbon film vias are chosen for cost
concerns.
The remote control board shown below can be designed as this type of double-layer board.
Figure 2-2 Component layer + carbon film layer

Telink FR1 PCB Design Guideline
AN-22051900-E1 Ver. 1.0.0
9
2.2.2 Component and copper wire layer + carbon film and copper wire layer
One layer of this double-layer board is used to place components and copper wire routing, and the other
layer is for carbon film routing + copper wire routing. For example, in a remote control design, we place the
components on one layer and the keys on the other layer. The keys need to be designed as carbon film keys
and the keys routing is connected to the component layer via carbon film via holes. When there are many
components and the routing is complex, if the design shown in 2.2.1 cannot be completed routing, then in
addition to the carbon film routing on another layer, it is necessary to add copper routing and connect the
component side routing through the carbon film via holes. Note that carbon film vias are chosen for cost
concerns.
The board shown below can be designed as this type of double-layer board.
Figure 2-3 Double layer routing + carbon film routing
Telink FR1 PCB Design Guideline
AN-22051900-E1 Ver. 1.0.0
10
3. Key Points of FR1 Board Design
3.1 Board layer
3.1.1 Board thickness selection
In order to reduce cost, FR1 or CEM-1 boards are generally used to produce PCB boards.
•The thickness of FR1 board is recommended to be 1.6mm.
•The thickness of CEM-1 board is recommended to be 1.2mm or 1.0mm.
Note:
1)
CEM-1 is more suitable for making thinner boards than FR1, and CEM-1 is less likely to warp boards
than FR1 over wave soldering.
2)
Whether FR1 or CEM-1 is used, the rules and notes for PCB design are the same.
3.1.2 Introduction of board structure
In general, FR1 circuit board is single surface board, however, we need create another layer in addition to the
Top layer and Bottom layer, called the carbon film layer. As shown in the figure below, the Key layer is the
carbon film layer.
Figure 3-1 Stack structure

Telink FR1 PCB Design Guideline
AN-22051900-E1 Ver. 1.0.0
11
3.2 Carbon film routing
Carbon film routing is generally 1mm width routing, and the process of carbon film via hole is shown in the
table below.
Table 3-1 Design of carbon film via hole
No. Item Requirement and
description
Process limit capabilities, which can lead to
reduced yields or increased production difficulties
109 Carbon grouting board Preferred FR1
thickness 1.6mm board
When using 1.2mm or 1.0mm thickness for card
type remote control, it is recommended to use
CEM-1 board to ensure the strength and avoid
board warping.
110 Drilling diameter of carbon
grouting hole 0.7mm
111 Diameter of copper plate for
carbon grouting hole 1.4mm
Copper plates at least 0.35mm larger than the hole
on one side, design as 15mm or 1.6mm if there is
enough space.
112 Diameter of weld-resistant
openings 1.3mm Copper plate with green oil on one side 0.05mm
113 Diameter of insulated opening 1.6mm 0.1mm greater than copper plate on one side when
insulated
114 Diameter of the carbon film on
the surface of the grouting hole 1.8mm
When there is no protective oil, in principle the
carbon film is required to be 0.2mm larger on one
side of the copper plate to avoid revealing copper.
When it is not possible to meet the carbon film
single-side is 0.2mm larger than copper, set the
carbon film and copper have the same width or
single-side is 0.05mm larger, but in this case we
need to print protective oil.
115 Diameter of the carbon film on
the skimmer surface 1.8mm
Minimum 1.6mm; when there is no protective oil,
in principle, it requires that one side carbon film is
0.3mm larger than copper plate to avoid revealing
copper
116 Diameter of carbon hole
protection oil 2.3mm Minimum 2.0mm, one side is larger than copper
0.2mm at least
117
Width of back carbon grouting
hole edge from carbon bridge
edge
≥2.3mm
Optimum 2.5 mm. The back carbon coverage width
is at least 2.1 mm due to oil spillage of 0.65 mm on
one side of the hole.

Telink FR1 PCB Design Guideline
AN-22051900-E1 Ver. 1.0.0
12
No. Item Requirement and
description
Process limit capabilities, which can lead to
reduced yields or increased production difficulties
118
Distance between the edges of
adjacent copper plates on
different networks
≥1.0mm
At least 0.9mm, distance from the edge of the
carbon plate to the edge of the carbon plate is at
least 0.5mm.
119
Distance between the edges of
adjacent copper plates on the
same network
≥0.5mm
At least 0.4mm: the distance between the copper
wire and the adjacent non-connecting carbon
surface is 0.4mm or more (if the joint is a carbon
point to be filled through, it must be kept at
0.7mm or more).
120
Distance between the edge of
the carbon plate and the edge of
the green oil covered wire
≥0.5mm
The principle is to avoid short circuits caused by
carbon oil seepage in case of pinholes in the single
layer of green oil; the edge of the carbon plate is at
least 0.1mm from the insulation layer covering the
wire when there is an insulation layer underneath
the carbon film.
121 Carbon hole resistance <100 ohms/hole
122 Carbon hole reliability design
Designed for parallel
connection of two
holes when space is
available
Reduce open circuit scrap and reduce circuit
resistance.
Carbon film wire and carbon film via hole impedance are relatively high, so the carbon film wire should not
be less than 1mm. Due to the manufacturing process for carbon film via hole, the carbon film wires are easy
to short circuit with other holes and wires, so the routing around the carbon film hole should avoid the hole
more than 1mm, as shown in the figure below.
Figure 3-2 Carbon film routing

Telink FR1 PCB Design Guideline
AN-22051900-E1 Ver. 1.0.0
13
4. Layout Regulations
4.1 Package
The package forms of battery, LED, and MIC are shown in the figure below.
Figure 4-1 Package forms
4.2 Solder pads and via holes
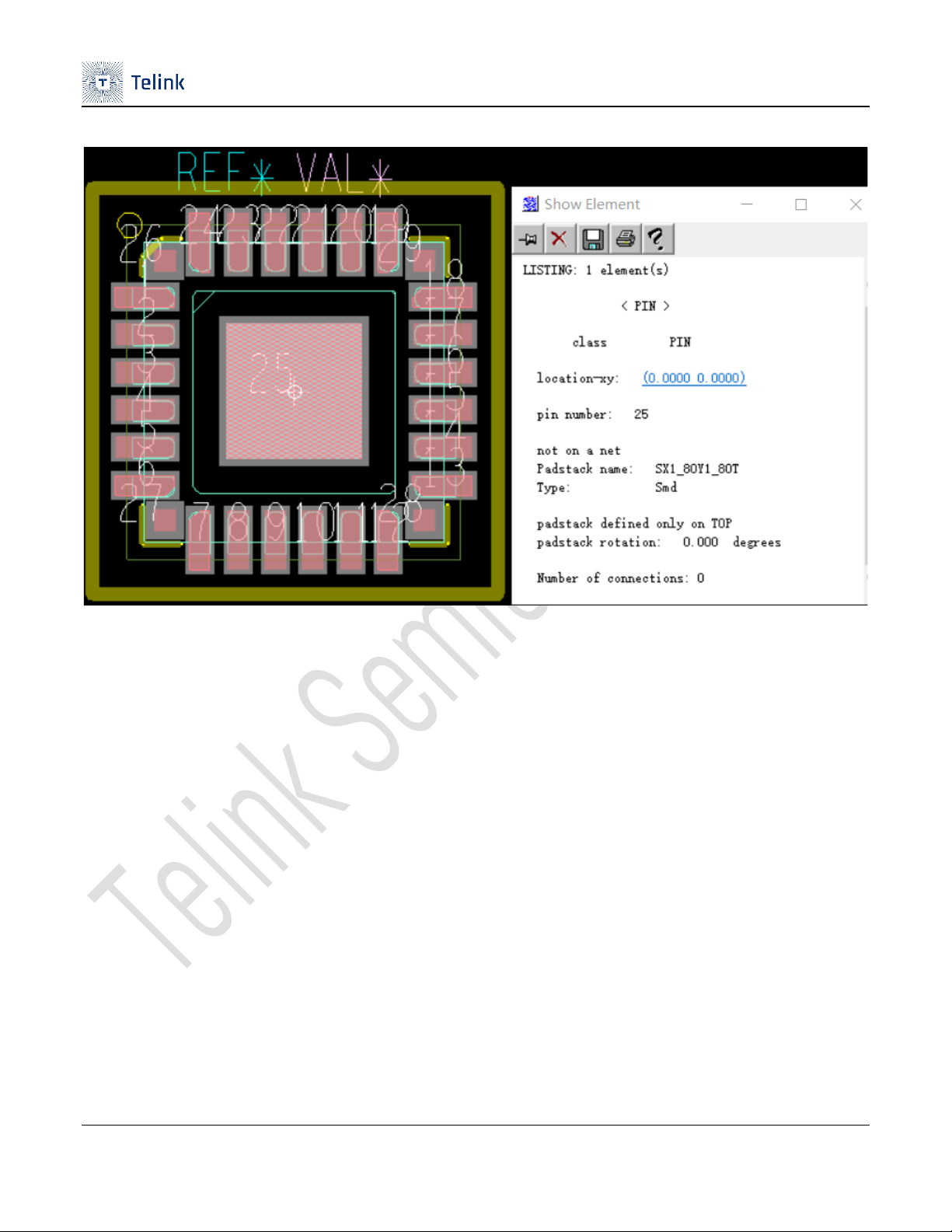
The PCB package design of Telink IC is as shown in Figure 4-2.
The carbon film via hole is shown in Figure 4-3, the hole diameter is greater than 0.7mm, outer diameter
1.4mm. The air gap between carbon film hole and copper wire is 2.5mm or more.
Telink FR1 PCB Design Guideline
AN-22051900-E1 Ver. 1.0.0
14
Figure 4-2 Package design for Telink IC

Telink FR1 PCB Design Guideline
AN-22051900-E1 Ver. 1.0.0
15
Figure 4-3 Via hole on carbon film
4.3 Notes
First of all, the layout should consider the placement of the chip, based on the antenna, and reserve
enough space for the antenna first, so as to determine the location of the chip.
According to the board structure requirement, place the components (battery holder, keys, MIC, and
etc., while paying attention that do not place components in the location column area).
The components used for RF matching are close to the RF pins. The ANT circuit is isolated from the
chip and other circuits by ground to avoid signal crosstalk. The capacitors of the LC filter are placed
on both sides of the RF routing as shown in Figure 4-4. The purpose of placing on both sides of the
RF routing is to allow better harmonic regulation. It is best to place a 0R (0 ohm) resistor at its RF
end to improve ground return on both sides of the RF circuit, as shown in Figure 4-4.
The placement of the various capacitors needs to be arranged as suggested below, as shown in Figure
4-5.

Telink FR1 PCB Design Guideline
AN-22051900-E1 Ver. 1.0.0
16
Before supplying power to the chip, the power must be filtered through a capacitor. The
power supply route is: the positive end of the battery spring tab →the filter capacitor →the
power pin of the chip.
The filter capacitor for the chip's power pin should be placed as close as possible to the
corresponding pin of the chip.
Figure 4-4 Layout for RF circuit

Telink FR1 PCB Design Guideline
AN-22051900-E1 Ver. 1.0.0
17
Figure 4-5 Layout for power capacitors

Telink FR1 PCB Design Guideline
AN-22051900-E1 Ver. 1.0.0
18
5. Routing Notes
Please be noted of the following routing points.
Prioritize the power and RF circuit routings, power wires should be as thick as possible (0.5mm ~ 1mm),
as close as possible to the power supply components or chip end in the use of star alignment
respectively power supply.
Then comes the normal routing, prioritize to route audio lines, and audio lines should have complete
copper on both sides, as shown in Figure 5-1.
For via hole, carbon film hole is needed, pay attention that put the carbon film hole as far as possible
with the routing and other carbon film hole, at least 1mm, to prevent short circuit.
Keep the width of the carbon film routing at 1mm or more to reduce carbon film impedance.
The ground is the main focus for FR1 board design.
Due to the high current jumps during RF operation, the smaller the GND impedance, the better, to
help reduce RF noise. For single-layer board, we should connect each component's ground with
wires after the power routing is completed, giving priority to ensuring that the ground line can go
through, and adding the 0R cross-line resistor at locations where it has blocks.
Ground wire should be as thick as 1mm and above, and routed in a ground shape.
Routing does not require excessive division of the ground plane, that is, the same direction routing
is together, and the routing distance should not be too long to affect the ground backflow. Priority
to ensure that the chip center ground and the power supply negative ground has a good ground
connection.
The crystal should be grounded as much as possible, and the RF components should be completely
grounded and covered with solid copper, as shown in Figure 5-1.
Avoid large areas of solid copper, in the wave soldering process, abnormal heat dissipation, the board is
easy to bulge. When encountering large areas of copper coverage, choose a mesh structure to facilitate
heat dissipation. For key circuits, such as RF, crystal, audio lines, and etc., the complete copper coverage
can be used directly. In addition, for some areas of narrow space, the complete copper should be laid out
to strengthen the ground reflow, as shown in Figure 5-1.

Telink FR1 PCB Design Guideline
AN-22051900-E1 Ver. 1.0.0
19
Figure 5-1 Routing example 1
In order to make a good connection between the chip and the ground and improve the RF performance,
it can be connected to the system ground through the chip's four corner ground, as shown in the location
of the red arrow in Figure 5-2.
Figure 5-2 Routing example 2

Telink FR1 PCB Design Guideline
AN-22051900-E1 Ver. 1.0.0
20
After the overall routing is complete, for the copper plates where the ground plane is disconnected from
the chip ground or power ground due to the routing, we should use 1206 package resistor to across the
line to make it connected with the chip ground or power ground copper, as shown in Figure 5-3.
Figure 5-3 Routing example 3
Table of contents
Other TELink Control Unit manuals
Popular Control Unit manuals by other brands

Xylem
Xylem Lowara Gen Series Installation and operating instructions

AUMA
AUMA AUMATIC AC 01.2 manual

GO Systemelektronik
GO Systemelektronik BlueConnect manual

Aprimatic
Aprimatic T2 installation instructions

Whelen Engineering Company
Whelen Engineering Company CenCom Core-R CEM4HC installation guide

Elko
Elko EST3 manual

Nordson
Nordson Encore HD Customer product manual

WIN Enterprises
WIN Enterprises MB-73240 user manual

Alcad
Alcad 905-ZA Quick programming guide

SMC Corporation
SMC Corporation EX250-SCN1 Technical specification

Beckmann
Beckmann EMS-8 -DU Series user manual

SMART Embedded Computing
SMART Embedded Computing PrAMC-7311 Installation and use






