Toshiba G1IF4 User manual
Other Toshiba Recording Equipment manuals

Toshiba
Toshiba NV Series User manual

Toshiba
Toshiba Strata DK Backup User manual

Toshiba
Toshiba RBM-Y0384FUL User manual

Toshiba
Toshiba BMS-IFMB1280U-E User manual

Toshiba
Toshiba BMS-IFWH4E2 User manual

Toshiba
Toshiba BMS-IFBN1280U-E User manual
Toshiba
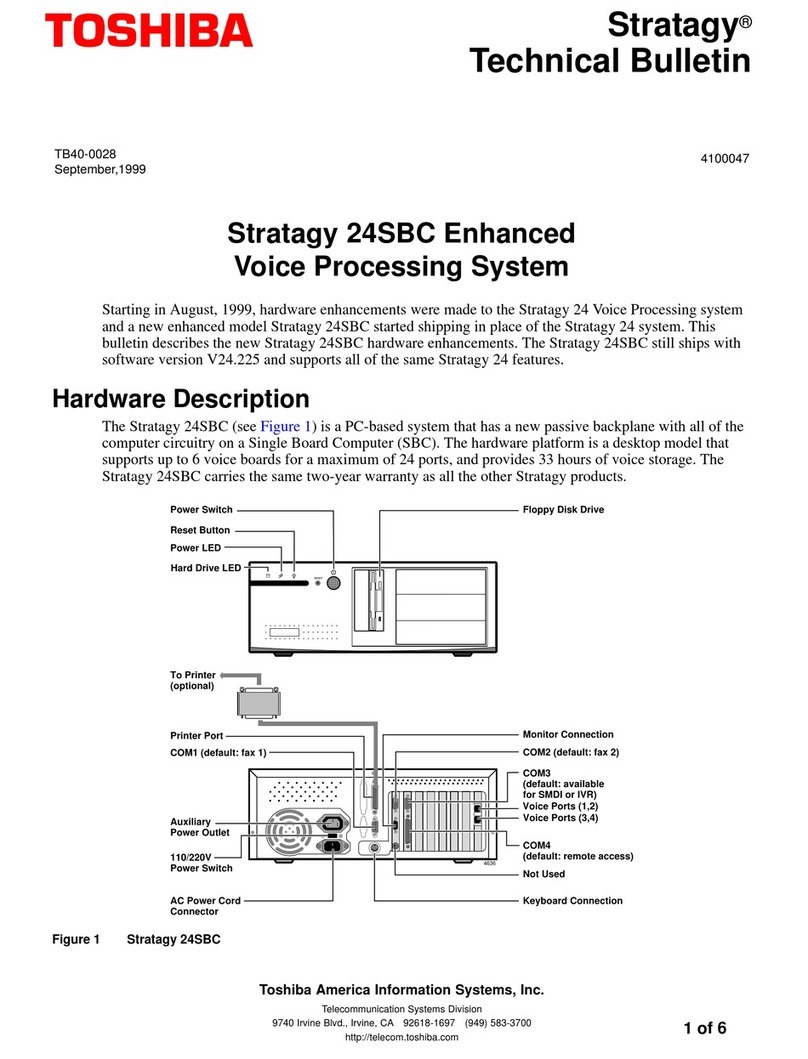
Toshiba Stratagy 24SBC Service manual

Toshiba
Toshiba TCB-IFMB641TLE User manual

Toshiba
Toshiba BMS-IFMB0AWR-E User manual

Toshiba
Toshiba Black Pear User manual

Toshiba
Toshiba TCB-IFGSM1E User manual
Toshiba
Toshiba TCS-NET User instructions

Toshiba
Toshiba Surveillix EAV Series User manual
Toshiba
Toshiba LonWorks TCB-IFLN642TLUL User manual

Toshiba
Toshiba RAV-DXC010 User manual

Toshiba
Toshiba HWS-IFAIP01U-E 0-10V User manual

Toshiba
Toshiba OIS PLUS Series User manual
Toshiba
Toshiba W-705 User manual

Toshiba
Toshiba TCB-IFGSM1E User manual

Toshiba
Toshiba TCB-IFDMX01UP-E User manual