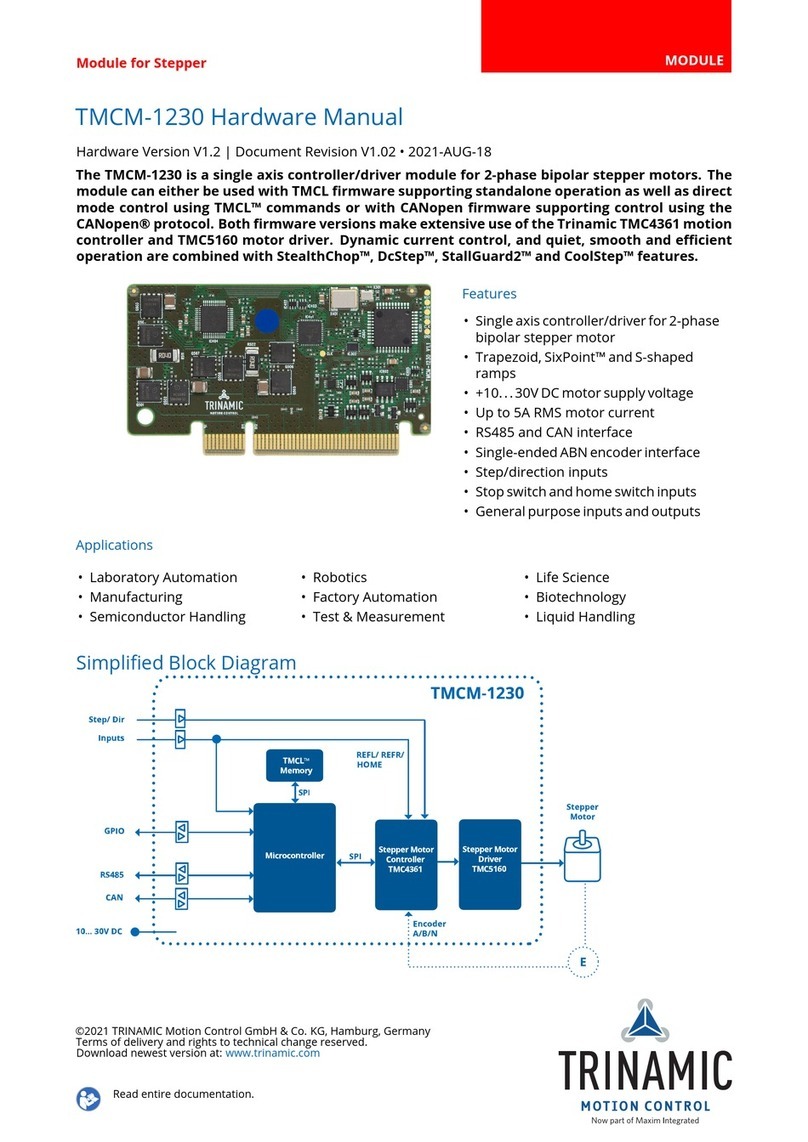
Trinamic TMCM-035 User manual

TMCM-035 Manual (V2.09 / February 27th, 2009) 2/18
Copyright © 2007-2009, TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
Table of Contents
1Features........................................................................................................................................................................................3
Life support policy.............................................................................................................................................................................4
2Electrical and Mechanical Interfacing..................................................................................................................................5
2.1 Dimensions ........................................................................................................................................................................5
2.2 Connecting the Module ..................................................................................................................................................6
3Operational Ratings..................................................................................................................................................................7
4Functional Description.............................................................................................................................................................7
4.1 Power Supply ....................................................................................................................................................................8
4.2 Motor Connection.............................................................................................................................................................8
4.3 Interfaces ............................................................................................................................................................................8
4.3.1 SPI ..................................................................................................................................................................................8
4.3.2 Analog ...........................................................................................................................................................................9
4.3.3 Step / Direction.........................................................................................................................................................11
4.4 Current setting ................................................................................................................................................................12
4.4.1 Fine current adjustment in SPI mode: ..............................................................................................................12
4.4.2 Standby current reduction for Step-/ Direction mode...................................................................................13
4.4.3 Continuous Current restrictions / Thermal conditions..................................................................................13
4.5 Mixed decay and slow decay ......................................................................................................................................14
4.6 Microstep resolution adjustments.............................................................................................................................14
4.6.1 Microstep resolution with step / direction interface.....................................................................................14
4.6.2 Increasing Microstep resolution with SPI interface ......................................................................................14
4.6.3 64 Microstep resolution with SPI interface since TMCM-035 V2.0 .............................................................15
5Hardware Revision..................................................................................................................................................................18
6Documentation Revision.......................................................................................................................................................18
7References .................................................................................................................................................................................18
List of Figures
Figure 2.1: Dimensions.....................................................................................................................................................................5
Figure 2.2: Pin order of the connector ........................................................................................................................................5
Figure 4.1: Main parts of the TMCM-035......................................................................................................................................7
Figure 4.2: How to connect the motor........................................................................................................................................8
Figure 4.3: Analog control.............................................................................................................................................................10
Figure 4.4: Step / Direction signal timing ................................................................................................................................11
Figure 4.5: SPI word assignment in 64 microstep mode ....................................................................................................15
Figure 4.6: Application with 3 TMCM-035 controlled by a TMCM-301...............................................................................16
Figure 4.7: Driver chain configuration for up to 3 TMCM-035 in use with TMCM-301.................................................17
Figure 4.8: Microstep table for 64 microsteps in use with TMCM-301 .............................................................................17
List of Tables
Table 1.1: Order codes......................................................................................................................................................................3
Table 2.1: Pinout 68-Pin Connector...............................................................................................................................................6
Table 3.1: Operational Ratings .......................................................................................................................................................7
Table 4.1: SPI interface connections ............................................................................................................................................8
Table 4.2: Connecting a TMCM-035 to a TMCM-301 ..................................................................................................................9
Table 4.3: Analog interface connections .....................................................................................................................................9
Table 4.4: Connecting a TMCM-035 to a TMCM-100 (analog) ...............................................................................................10
Table 4.5: Step / Direction interface connections...................................................................................................................11
Table 4.6: Connecting a TMCM-035 to a TMCM-100 (step / direction)...............................................................................11
Table 4.7: Current setting ..............................................................................................................................................................12
Table 4.8: Current fine adjustment with RSA and RSB.........................................................................................................13
Table 5.1: Hardware revision ........................................................................................................................................................18
Table 6.1: Documentation Revisions ..........................................................................................................................................18

TMCM-035 Manual (V2.09 / February 27th, 2009) 3/18
Copyright © 2007-2009, TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
1Features
The TMCM-035 is a compact motor driver module for highly dynamic or high torque axis. It can be
combined with the driver-less modules TMCM-100, TMCM-301 or TMCM-302 or with any step / direction
controller. Its small size and low power dissipation, together with the variety of three different
control interfaces, make it an optimum solution for integration on any user board. The board can be
connected to a baseboard or customized electronics with a pin connector. Applications are consumer
and industrial controls, CNC power stages, lab automation, robotics, pick- and place machines
The TMCM-035 drives a two-phase bipolar stepping motor, with a maximum coil current of 5A and a
maximum voltage of 50V. It is based on the TMC239 or TMC249 stepper motor driver chip. The
interface between the control logic and the TMCM-035 module can be either Step / Direction, SPI or an
analogue interface. The maximum motor current can be selected via external inputs. Since the new
Version V2.0 of the board, the module has been extended from maximum 16 to 32 and 64 microsteps.
Applications
Driver module for a highly dynamic or high torque axis
Easy integration through three different control interfaces into any user board
Electrical Data
Up to 3.5A RMS coil current (5A peak)
14V to 50V DC motor supply voltage
5V DC logic supply voltage
Supported motors
two-phase bipolar motors with 0.3A to 3.5A coil current
Interface
Step / Direction input (TTL/CMOS signal)
SPITM interface
Classical analog interface
Highlights
Up 64 times microstepping, since version 2.0 (prev. versions up to 16)
Motor current settings via internal and / or external resistors
Up to 245kHz microstep frequency
TRINAMIC driver technology: No heat sink required
StallGuardTM optional for SPI operation
Standby reduction programmable
“mixed-decay” mode for good microstep performance mode
low EME design for ease of use
Other
68 pin connector carries all signals
RoHS compliant
Size: 80x50mm² (credit card)
Order code
Description
TMCM-035/SG (-option)
1-axis driver 3.5A / 50V with StallGuard
Related products
BB-035, BB-301
Option
-H
horizontal pin connector (standard)
-V
vertical pin connector (on request)
Table 1.1: Order codes

TMCM-035 Manual (V2.09 / February 27th, 2009) 4/18
Copyright © 2007-2009, TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
Life support policy
TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG does not
authorize or warrant any of its products for use in life
support systems, without the specific written consent
of TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG.
Life support systems are equipment intended to
support or sustain life, and whose failure to perform,
when properly used in accordance with instructions
provided, can be reasonably expected to result in
personal injury or death.
© TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG 2009
Information given in this data sheet is believed to be
accurate and reliable. However no responsibility is
assumed for the consequences of its use or for any
infringement of patents or other rights of third
parties, which may result form its use.
Specifications are subject to change without notice.

TMCM-035 Manual (V2.09 / February 27th, 2009) 5/18
Copyright © 2007-2009, TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
2Electrical and Mechanical Interfacing
2.1 Dimensions
Horizontal
Connector: Header
Connector:
5
2 (PCB)
Note :
all dimensions in mm
6
C
C
2 (PCB)
2
2
68-Pin Connector
436.9
39.1
50
R1.1
46
2.2
4
977
80
77.8
R1.25
3.2
8.20
1.7
since V2.1
Figure 2.1: Dimensions
The size of the module (80x50mm) is the same as of the other Trinamic motion control modules. It
also uses the same connector.
The 68 pin connector has a 2.0mm pitch.
Bord outline changes since TMCM-035 V2.1
second notch (lower one) on each side for other type of plate holder
clearance in the board close to the 64 pin connector to allow easier mounting. The pins of a
horizontal connector are completely free and the opposite part wont abut against the board.
PCB
1
268
67
Figure 2.2: Pin order of the connector

TMCM-035 Manual (V2.09 / February 27th, 2009) 6/18
Copyright © 2007-2009, TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
2.2 Connecting the Module
The pin assignments of the connector are as follows:
Pin
Dir.
Description
Pin
Dir.
Description
1
In
+5VDC (+/- 5%) Imax=50mA
2
In
GND
3
In
+5VDC (+/- 5%)
4
In
GND
5
In
V_Motor (+14 to 50VDC)
6
In
GND
7
In
V_Motor (+14 to 50VDC)
8
In
GND
9
In
V_Motor (+14 to 50VDC)
10
In
GND
11
In
ENN (0 = enable driver)
12
In
Step/Dir mode: do not connect
SPI mode: TMC239 CLK signal
Analog mode:TMC239 MDBN signal
13
In
Step/Dir mode: do not connect
SPI mode: TMC239 CSN signal
Analog mode: TMC239 PHB signal
14
Out
Step/Dir mode: do not connect
SPI mode: TMC239 SDO signal
Analog mode: TMC239 ERR signal
15
-
n. c.
16
In
Step/Dir mode: do not connect
SPI mode: TMC239 SDI signal
Analog mode: TMC239 PHA signal
17
In
Reset (active low), leave open
18
In
Step In
19
In
SPE (0 = Analog mode,
1=SPI or Step/Dir mode)
20
In
Dir In
21
In
INA
22
In
SDEN: must be to 1 for Step/Dir
mode or 0 for SPI or Analog mode
23
In
INB
24
In
STEP16: Step/Dir mode only:
1 = 16 resp. 64 microsteps
0 = 8 resp. 32 microsteps
25
In
SPI mode: ANN (INA and INB provide
current reference if 0)
Step/Dir mode: do not connect
Analog Mode: TMC239 MDAN signal
26
In
USEMD: Set to 1 to use mixed decay
in Step/Dir mode
27
In
/STEP64EN: Leave open or tie to +5V
for 8 / 16 microsteps, tie to GND for
32 / 64 microstep resolution
28
In
OSC: leave open or supply external
chopper clock
29
-
n. c.
30
-
n. c.
31
-
n. c.
32
-
n. c.
33
-
n. c.
34
-
n. c.
35
-
n. c.
36
-
n. c.
37
Out
OB2
38
Out
OB2
39
Out
OB2
40
Out
OB2
41
Out
OB1
42
Out
OB1
43
Out
OB1
44
Out
OB1
45
In
RSB2
46
In
RSB2
47
In
RSB1
48
In
RSB1
49
Out
OA2
50
Out
OA2
51
Out
OA2
52
Out
OA2
53
Out
OA1
54
Out
OA1
55
Out
OA1
56
Out
OA1
57
In
RSA2
58
In
RSA2
59
In
RSA1
60
In
RSA1
61
In
GND
62
In
GND
63
-
n. c.
64
-
n. c.
65
-
n. c.
66
-
n. c.
67
-
n. c.
68
-
n. c.
Table 2.1: Pinout 68-Pin Connector

TMCM-035 Manual (V2.09 / February 27th, 2009) 7/18
Copyright © 2007-2009, TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
3Operational Ratings
The operational ratings show the intended / the characteristic range for the values and should be
used as design values. In no case shall the maximum values be exceeded.
Symbol
Parameter
Min
Typ
Max
Unit
VS
Power supply
14
50
V
V+5V
+5V DC input (max. 300mA)
4.75
5.0
5.25
V
ICOIL
Motor coil current for sine wave peak
(chopper regulated, adjustable via RSA /
RSB pins and software)
0
0.3 … 5
5
A
fCHOP
Motor chopper frequency
36.8
kHz
IS
Power supply current (per motor)
<< ICOIL
1.4 * ICOIL
A
fSTEP
Step frequency
245
kHz
tSPulse
Step pulse length
0.1
µs
tS2D
Direction hold time
2
µs
tD2S
Direction to step delay
0
µs
VANA
INx analog measurement range
0 ... 3
V
fSPI
SPI clock frequency
2
MHz
TBOARD
Recommended PCB temperature limit
+85
+105
°C
TENV
Environment temperature at rated current
(3.5A RMS), module mounted vertically
without forced cooling
-40
+40
°C
Environment temperature for up to
2.5A RMS, module mounted vertically
without forced cooling
-40
+60
°C
Table 3.1: Operational Ratings
4Functional Description
In Figure 4.1 the main parts of the TMCM-035 module are shown.
TMCM-035
high power
Driver
TMC239
5V DC
15..50V DC
Sequencer Step
Motor
MOSFET
Driver
Stage
SPI
Step/Dir
„classic“ analog
control
Figure 4.1: Main parts of the TMCM-035

TMCM-035 Manual (V2.09 / February 27th, 2009) 8/18
Copyright © 2007-2009, TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
4.1 Power Supply
The power supply for the TMCM-035 is 14V to 50V DC. The module is not protected against wrong
polarity. Also a +5VDC supply for module functionality is needed. Please use all listed pins for the
power supply inputs and ground parallel.
4.2 Motor Connection
Connect the motor to the OA and OB pins. Always use all the pins to connect the motor! Connect one
coil of the motor to the OA1 (53, 54, 55, 56) and OA2 (49, 50, 51, 52) pins and the other coil to the
OB1 (41, 42, 43, 44) and OB2 (37, 38, 39, 40) pins. Never connect or disconnect the motor while the
module is under power as this may damage the module.
M
OA1
OA2
OB1
OB2
Figure 4.2: How to connect the motor
4.3 Interfaces
The TMCM-035 has three different interfaces to fit in all applications. There is a SPI interface, a analog
interface and step / direction interface available. The classic analog interface provides very high
microstep resolutions but has compared to the SPI interface a disadvantage of poor diagnostics. SPI
on the other hand has all the diagnostics but is limited to 16x microstep resolution. Refer to 4.6.2 for
the possibility to increase microstep resolution to up to 64x for SPI.
4.3.1 SPI
The SPI interface pins of the connector are directly connected to the SPI pins of the TMC239. So, the
data that must be supplied via the SPI interface can be found in the TMC239 data sheet. The SPI data
can either be generated directly by a microcontroller or by a TMC428. To use the SPI interface you will
have to make the following connections:
Signal name
Pin number
Connection
SPE
19
High (can be left open, SPI enable)
SDEN
22
Connect to GND (to disable Step / Direction interface unit).
SDI
16
Connect to SPI bus
SDO
14
Connect to SPI bus
CSN
13
Connect to SPI bus
CLK
12
Connect to SPI bus
ANN
25
Set high (or leave open) for normal current settings or low to provide
the current reference via the INA and INB inputs (please see section
4.4.1 for details).
/STEP64EN
27
Leave open or connect to +5V to operate in 16 microstep mode, directly
using the 12 bits control shift register of the TMC239/249 (please refer to
the respective manuals)
Connect to GND for 64 microstep mode with 6 bit DAC. In this mode,
the SPI word is extended by an 8 bit shift register (see SPI table in
Figure 4.6).
Table 4.1: SPI interface connections

TMCM-035 Manual (V2.09 / February 27th, 2009) 9/18
Copyright © 2007-2009, TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
The SPI interface is mainly to be used to connect the TMCM-035 module to a TMCM-301 module. This
way, up to three TMCM-035 modules can be connected to one TMCM-301 module. The connection for
one module is shown in Table 4.2.
TMCM-035 pin number
TMCM-301 pin number
Signal name (TMCM-035)
1, 3
1, 3
+5V
2, 4, 6, 8, 10
2, 4, 6, 8, 10
GND
11
--
Enable, connect to GND
12
30
CLK
13
20
CSN
14
28
SDO
16
26
SDI
Table 4.2: Connecting a TMCM-035 to a TMCM-301
For operation with microstep resolution of 32 or 64 steps per fullstep refer to 4.6.2 Increasing
Microstep resolution with SPI interface
In SPI mode the LED on the board does not have any function and can be ignored.
4.3.2 Analog
The analog interface is mainly to be used to connect the TMCM-035 to a TMC453 chip or to a TMCM-
100 module (that contains a TMCM453 stepper motor controller chip).
The following pins are to be used in analogue mode:
Signal name
Pin number
Connection
SPE
19
Connect to GND (to enable analog interface unit)
SDEN
22
Connect to GND (to disable Step / Direction interface unit).
Enable
11
Connect to GND to enable or set high to disable the motor driver.
INA
21
Analog input which determines the current of phase A (0..3V).
INB
23
Analogue input which determines the current of phase B (0..3V).
PHA
16
Digital input which determines the polarity of phase A.
PHB
13
Digital input which determines the polarity of phase B.
MDAN
25
Set low to use mixed decay or high to use slow decay on phase A.
MDBN
12
Set low to use mixed decay or high to use slow decay on phase B.
Table 4.3: Analog interface connections
Please see Figure 4.3 for an explanation of the INA/INB/PHA/PHB signals.
Here is how to connect the TMCM-035 module to a TMCM-100 module:

TMCM-035 Manual (V2.09 / February 27th, 2009) 10/18
Copyright © 2007-2009, TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
TMCM-035 pin number
TMCM-100 pin number
Signal name (TMCM-035)
1, 3
1, 3
+5V
2, 4, 6, 8, 10
2, 4, 6, 8, 10
GND
19
--
SPE, connect to GND
11
--
Enable, connect to GND
22
--
SDEN, connect to GND
21
39
INA
23
41
INB
16
25
PHA
13
29
PHB
25, 12
--
MDAN/MDBN, connect to GND to use mixed
decay or leave open for slow decay.
Table 4.4: Connecting a TMCM-035 to a TMCM-100 (analog)
Please see section 4.4 for selecting the peak motor current.
In analog mode the LED shows the status of the module:
The LED is on when the motor is enabled and the supply voltage is high enough.
The LED is off when the motor is disabled due to pin 11 (Enable) set high or supply voltage to
low.
The LED flashes when there is an error :
Temperature too high: motor stops until temperature is acceptable (normally a few seconds)
Current too high (short circuit): motor is switched off until short circuit is corrected
Power supply too low for motor: motor is switched off, until power supply is sufficient.
Open load: motor is NOT switched off (occurs when a motor coil circuit is open or sometimes
at high velocities when the motors current limit is reached
90° 180° 270° 360°
INA
INB
PHA
PHB
Figure 4.3: Analog control

TMCM-035 Manual (V2.09 / February 27th, 2009) 11/18
Copyright © 2007-2009, TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
4.3.3 Step / Direction
To use the Step / Direction interface connect the inputs as follows:
Signal name
Pin number
Connection
SPE
19
high (+5V, can be left open alternatively)
SDEN
22
high (+5V, can be left open alternatively) , step / direction enable
STEP16
24
high for 16, low for 8 microsteps (STEP64EN is high)
high for 64, low for 32 microsteps (STEP64EN is low)
STEP64EN
27
high (can be left open) for 8/16 microsteps, low for 32/64 microsteps
available since version 2.0
USEMD
26
Set high (or leave open) to use mixed decay (recommended for most
applications), or low to use slow decay.
Step In
18
Connect your step signal here. The rising edge of the signal is a step
pulse.
Direction In
20
Connect your direction signal here.
ANN
25
Do not connect!
Table 4.5: Step / Direction interface connections
Note: Pins 12, 13, 14, 16 and 25 must not be connected in this mode!
The Step / Direction interface can also be used to connect the TMCM-035 module to a TMCM-100
module (however it results in a higher microstep resolution, if the analogue interface is used with the
TMCM-100). Here is how to do it:
TMCM-035 pin number
TMCM-100 pin number
Signal name (TMCM-035)
1, 3
1, 3
+5V
2, 4, 6, 8, 10
2, 4, 6, 8, 10
GND
11
--
Enable, connect to GND
18
20
STEP
20
19
DIR
Table 4.6: Connecting a TMCM-035 to a TMCM-100 (step / direction)
In step / direction mode the LED shows the status of the module:
The LED is on when the motor is enabled and the supply voltage is high enough.
The LED is off when the motor is disabled due to pin 11 (Enable) set high or supply voltage to
low.
The LED flashes when there is an error (please refer to chapter 4.3.2 for more information).
Step-Direction signal timing:
Step pulse
Direction
th tl
tS2D tD2S
2 steps CW CCW step
step
Figure 4.4: Step / Direction signal timing
Min
TS2D
2 µs
TD2S
0 µs
th
0.1µs

TMCM-035 Manual (V2.09 / February 27th, 2009) 12/18
Copyright © 2007-2009, TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
4.4 Current setting
The motor current setting can be selected by connecting the RSA and RSB pins to GND as shown in
the following table.
Note: In step-/direction mode the motor is without current until the first step impulse is given. The
same applies after a disable/enable cycle.
Caution: Never leave both, RSA/B1 and RSA/B2 pins, open!
peak coil current
RMS current
(microstep operation)
RSA1, RSB1
RSA2, RSB2
1.5 A
1 A
GND
open
3.4 A
2.5 A
open
GND
5.0 A
3.5 A
GND
GND
variable
peak current / 1.41
(external resistor from RSA/RSB to GND)
Table 4.7: Current setting
4.4.1 Fine current adjustment in SPI mode:
In SPI mode, the current values set via the sense resistors can be modified using the analog inputs
INA and INB. In this case the ANN input (pin 25) must be pulled low. The INA and INB inputs
supporting a voltage range of 0 to 3V can be used. Use a simple voltage divider on the 5V supply to
accomplish this, e.g. a 10K Potentiometer. A value of 2V corresponds to the currents given in the
table, i.e.
Current set value = (Value from Table 4.7) * (INA/INB-Voltage) / 2V
Please be careful with values of INA/INB > 2V since the maximum current of the module can be
exceeded (150% at 3V).
In 64 microstep mode the current adjustment via the analog inputs is limited. The voltage on INA and
INB should not exceed the range from 1.5 to 2.5 V in your application.
Following exemplary R/C filter gives an analog voltage range of about 0 to 2.1V.
Pin 2
Pin 30
Pin 32
Pin 34
Pin 36
Pin 38
Pin 40
Pin 68
TMCM-301
31
33
35
M
GND: Pin 2, 4, 6, 8
5V : Pin 1, 3
TMC249 /
TMCM-035
INB
OUTA1
OUTA2
OUTB1
OUTB2
PWM
47k
47k
470nF
INA
GND
GND
ANN
Figure 4.5: Application example for a TMCM-035 and TMCM-301 with analog current control

TMCM-035 Manual (V2.09 / February 27th, 2009) 13/18
Copyright © 2007-2009, TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
Another way of setting a different peak coil current is to connect the RSA pins to GND via an external
resistor and the RSB pin via the same size of resistor. The two resistors should be in the range
100mOhms to 1 Ohm. This possibility can also be used when the module is connected via its
analogue interface. However it is very important to use SMD resistors with low inductivity and very
short traces to GND for a stable operation in this configuration.
peak coil current
RMS current
(microstep operation)
RSA1, RSB1
RSA2, RSB2
1.0 A
0.7 A
open
each 0.22 R to GND
1.2 A
0.85 A
each 0.18R to GND
open
1.7 A
1.2 A
GND
each 1.5R to GND
2.1 A
1.5 A
GND
each 0.47R to GND
2.8 A
2.0 A
GND
each 0.15R to GND
4.2 A
3.0 A
each 0.27R to GND
GND
Table 4.8: Current fine adjustment with RSA and RSB
4.4.2 Standby current reduction for Step-/ Direction mode
In step / direction interface mode, the current control will switch to the INA and INB inputs when
there has been no step pulse for at least four seconds. Current control will switch back to the normal
value set via RSA/RSB pins when the next step pulse occurs. This way the standby current can be set
using the INA and INB pins (by applying a voltage between 0 (0%) and 2V (100%). The maximum
current while the motor is running must be set using the RSA/RSB pins.
The coil current should be reduced when the motor is standing still!
Power down current set value = Value from Table 4.7 * (INA/INB-Voltage) / 2V
4.4.3 Continuous Current restrictions / Thermal conditions
The module is designed as a microstepping module, with sine wave currents (sine and cosine) driving
both coils. The current peak of the sine wave can be as high as 5A, when the RMS current is set to
3.5A. The mean motor current (RMS) is calculated by dividing the peak current by 1.41.
The compact design of the module does not allow to continuously drive the full current unless forced
air cooling is used to keep the board temperature below 85°C, because of excessive heat generation.
On a short term basis, the board is allowed to reach 105°C, but it will shorten life time, if this occurs
in longer periods. However, since continuous maximum current operation also shortens the lifetime of
the motor, this is in most cases no restriction. The driver transistors on the module (8 transistors
labeled “4450” or similar) may heat up to 120°C at their surface - this is not critical!
The module provides a thermal protection, but this is only meant as a means against sudden
destruction, i.e. when a cooling blower fails and the module slowly overheats. The protection is not
meant to limit normal operation! It can not protect against all faults, since it is central in the TMC249
IC, and might react too slowly!
The following limits apply:
Maximum environment temperature for up to 3.5A RMS (= 5A peak) is 40°C, module mounted
vertically
Maximum environment temperature for up to 2.5A RMS (= 3.5A peak) is 60°C, module mounted
vertically
If the module is mounted horizontally, use forced air flow for current above 2.0A RMS.
The phase current should be reduced to a maximum of 70% of the above values while the motor
is standing

TMCM-035 Manual (V2.09 / February 27th, 2009) 14/18
Copyright © 2007-2009, TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
Maximum current for fullstep operation (both coils on) is 3.5A (peak value for fullstep is identical
to RMS value!)
For continuous operation above 2.5A RMS a forced cooling is mandatory. The module should not
be mounted in a horizontal position for continuous operation with coil currents above 2.5A RMS.
At a reduced supply voltage, heating will be less. The actual heat dissipation also depends on
the motor!
If the module will be operated near to these limits for extended periods of time, a measurement of
the board temperature in the final application / housing should be done in order to make sure, that
life time is not reduced by module operation near to / above the temperature limits.
4.5 Mixed decay and slow decay
When using the step / direction interface it is possible to switch to mixed decay by setting the USEMD
pin (pin 26) high or to switch to slow decay by pulling the USEMD pin low. When using the analogue
mode use the MDAN and MDBN pins to select between mixed decay and slow decay (pull
MDAN/MDBN low to use mixed decay). When using the SPI interface the mixed decay feature is
controlled by bit 11 and bit 5 of the SPI telegram (please see [TMC239] datasheet for details about the
structure of the SPI telegram).
The mixed decay setting especially at rotation velocities in the range of a few 10 steps per seconds to
several 100 steps per second improves motor behavior (less resonance). However, the actual
performance depends on the motor and mechanics. For supply voltages above 24V and for low
inductivity motors, best microstep behavior is reached when mixed decay setting is continuously on.
Mixed decay should be switched off when StallGuard operational in order to get usable results.
4.6 Microstep resolution adjustments
Step / direction and analog interface support high microstep resolutions. SPI is restricted to 16x
microstepping without external hardware additions described in [TMC236/239/246/249 FAQ] (Extending
the microstep resolution). Since hardware version V2.0 a 64 microstep resolution is possible without
additional hardware, refer to 4.6.2.
4.6.1 Microstep resolution with step / direction interface
When using the step / direction interface it is possible to select the microstep resolution of 8, 16, 32
or 64 microsteps per fullstep. The resolution is since hardware version 2.0 (some labeled TMCM-035 D)
pre-selected with Pin 27 “STEP64EN”. Pin 27 set high or left open selects low resolutions (8 or 16
microsteps), Pin 27 set low (to GND) selects high resolutions (32 or 64 microsteps). The final selection
has to be done by pin 24 “STEP16”, set high or left open the microstep resolution is either 16 or 64
depending on the setting of pin 27. Set low the microstep resolution is either 8 or 32. In former
hardware versions pin 24 sets the TMCM-035 to 8 or 16 microsteps only, and pin 27 has no function.
4.6.2 Increasing Microstep resolution with SPI interface
Even the 16 microstep version of the TMCM-035 can realize more than 16 microsteps via TMC428 SPI
control: Just program the TMC428 for 32 microstep mode. Due to the combination of two DACs driving
the two coils, this results in a resolution somewhere between 20 and 30 microsteps.

TMCM-035 Manual (V2.09 / February 27th, 2009) 15/18
Copyright © 2007-2009, TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
4.6.3 64 Microstep resolution with SPI interface since TMCM-035 V2.0
To get full 64 microsteps using the TMC428 with a user built electronics, please refer to the schematic
example in [TMC239] or [TMC249] and [TMC236/239/246/249 FAQ] (Extending the microstep resolution).
Please remark, that the lower two bits are inverted, and the values from 0 to 3 give a zero current.
This effectively results in a 60 level current resolution. A suitable microstep table is printed below.
The effect of this modified DAC behaviour is, that the TMC428 ramp-phase-dependent current scaling
function does not lead to a good result and should not be used! This could be improved by inverting
the additional DAC-Bits. Please be aware, that the module in 64 microstep mode can not be included
in SPI busses with multiple /CS lines.
For best microstep performance run the motors with mixed decay switched on continuously and
36kHz chopper.
To program the TMCM-035 for 64 microstep mode the pins 24 and 27 are used (refer to 4.6.1). It is
important to load the proper wave table as well as the proper SPI configuration. Both are available
on the TRINAMIC technical library. The following table depicts the SPI bit ordering. The bits are to be
shifted into the SPI chain from left (19) to right (0). The function of the bits is described in the
TMC239 / TMC249 manual and FAQ document.
Standard
function
Bit 12
TMC239 control word Additional 8 bits in 64 microstep mode
CB5
(MSB)
11
CB4
10
CB3
9
CB2
8
PHB
13
MXB
18
CA5
(MSB)
17
CA4
16
CA3
15
CA2
14
PHB
19
MXA
7
/CB1
6
/CB0
5
/CA1
4
/CA0
3
-
2
-
1
-
0
-
Figure 4.6: SPI word assignment in 64 microstep mode
Required TMC428 driver chain configuration for each TMCM-035 in 64 microstep mode:
0x11,0x05,0x04,0x03,0x02,0x06,0x11,0x0d,0x0c,0x0b,0x0a,0x0e,0x09,0x08,0x01,0x00,
0x10,0x10,0x10,0x30 // 4 unused bytes, last plus next motor bit
The suitable microstep table for 32 and 64 microstep with inverted LSBs (1/4 wave, like in TMC428):
0x00,0x07,0x05,0x04,0x0a,0x09,0x0f,0x0e,0x0c,0x13,0x11,0x10,0x17,0x15,0x14,0x1a,
0x19,0x18,0x1e,0x1d,0x1c,0x22,0x21,0x20,0x27,0x25,0x24,0x2b,0x2a,0x29,0x28,0x2f,
0x2e,0x2d,0x2c,0x33,0x32,0x31,0x30,0x37,0x36,0x35,0x35,0x34,0x3b,0x3a,0x3a,0x39,
0x39,0x38,0x38,0x3f,0x3f,0x3e,0x3e,0x3d,0x3d,0x3d,0x3d,0x3d,0x3c,0x3c,0x3c,0x3c
Since the wave table is modified (lower two bits, bit 0 and bit 1, are inverted), the current scaling
function of the TMC428 (IS_AGTAT, IS_ALEAT, IS_V0) should be switched off, i.e. these registers should
be set to zero (full current).
Hint for operation with TMC428 based controllers: The needs to read back the TMC249 bits for
operation of the StallGuard or for driver diagnostics. While the TMC428 can control driver chains with
up to 64 bits, it can read back a total of 48 bits only. Thus, when cascading three TMCM-035 in one
TMC428 driver chain and all modules are set to 64 microstep mode, the first 12 bits sent back from
the 60 bit long driver chain to the TMC428 can not be read back. These are all bits from the last
TMC249 in the chain, including its StallGuard bits. Thus, you should attach only two TMCM-035 in 64
microstep mode to a TMC428 based module. This brings also an advantage for the reachable motor
velocity. If you need all StallGuard bits in a three driver chain, switch at least two modules in the
chain to 16 microstep mode.

TMCM-035 Manual (V2.09 / February 27th, 2009) 16/18
Copyright © 2007-2009, TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
Example: Up to three TMCM-035 with 64 microsteps in use with a TMCM-301
Pin 2
Pin 20
Pin 22
Pin 24
Pin 26
Pin 28
Pin 30
Pin 68
TMCM-301
GND: Pin 2, 4, 6, 8
5V : Pin 1, 3
M
CSN
SDO
SDI
SCK
OUTA1
OUTA2
OUTB1
OUTB2
M
CSN
SDO
SDI
SCK
OUTA1
OUTA2
OUTB1
OUTB2
M
CSN
SDO
SDI
SCK
OUTA1
OUTA2
OUTB1
OUTB2
TMC249
TMC249
TMC249
3x TMCM-035 driver
Figure 4.7: Application with 3 TMCM-035 controlled by a TMCM-301
The microstep configuration of the three TMCM-035 drivers (digital pins 24 and 27) can be controlled
by the I/O ports of the TMCM-301, so that each driver is configured directly.
Fill in the Driver Chain and set global parameters according to Figure 4.8. CS_COMM_IND has to be
deactivated for cascaded TMCM-035 modules. LSMD defines the number of motors used (2 for 3
motors). After loading or filling in the driver chain press “Set” to program the TMCM-301.

TMCM-035 Manual (V2.09 / February 27th, 2009) 17/18
Copyright © 2007-2009, TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
Figure 4.8: Driver chain configuration for up to 3 TMCM-035 in use with TMCM-301
Now it is time to program the TMCM-301 with the following microstep table (Figure 4.9) by pressing
“Set”. Please use the 64 microstep table to get the smoothest operation.
Figure 4.9: Microstep table for 64 microsteps in use with TMCM-301
Mixed decay has to be switched on constantly, SAP 203 has to be set to 2048 for all used motors. This
values can be saved with STAP 203 to the EEPROM of the TMCM-301 for each motor.

TMCM-035 Manual (V2.09 / February 27th, 2009) 18/18
Copyright © 2007-2009, TRINAMIC Motion Control GmbH & Co. KG
5Hardware Revision
Version
Since
Description
1.0
2003
Initial version
2.0
Mar.2006
Labelled TMCM-035-D V1.0.
The module has been extended from maximum 16 to 32 and 64 microsteps
New function of connector pin 27 (activates 64 microsteps)
2.1
Jan 2007
Bord outline changes (please refer to 2.1):
second notch on each side for other type of plate holder
clearance close to the 64 pin connector to allow easier mounting.
Table 5.1: Hardware revision
6Documentation Revision
Version
Date
Author
Description
1.00
08-Jan-04
OK
Initial version
1.01
20-Apr-04
OK
Minor error corrections
1.02
01-Oct-04
OK
Address corrected
1.03
28-Oct-04
BD
Maximum step rate increased
1.04
13-Feb-04
OK
Ordering information added
2.00
20-Jun-06
BD
64 microstep version info added
2.01
14-Jul-06
HC
Major revision
2.02
21-Aug-06
HC
Additions to 64 microstep version info
2.03
29-Nov-06
BD
Comments on maximum component temperature
2.04
10-Jan-07
HC
Addition to 4.4; step-/Dir: motor currentless before first step
2.05
21-Feb-07
HC
Added 2.0mm pitch connector info
2.06
25-May-07
HC
Hardware revision and new dimensions for version 2.1 added
2.07
13-Jun-07
HC
Additions to 4.4.1 Fine current adjustment in SPI mode:
2.08
28-Nov-07
HC
Additions to errors indicated by LED in analog mode (4.3.2)
2.09
27-Feb-09
OK
Step/Dir connections (Table 4.5) corrected
Table 6.1: Documentation Revisions
7References
[TMC239] TMC239 manual (see http://www.trinamic.com)
[TMC249] TMC249 manual (see http://www.trinamic.com)
[TMC236/239/246/249 FAQ] TMC239/249 FAQ (see http://www.trinamic.com)
[TMCM-301] TMCM-301 manual (see http://www.trinamic.com)
[TMCM-100] TMCM-100 manual (see http://www.trinamic.com)
Table of contents
Other Trinamic Computer Hardware manuals

Trinamic
Trinamic TMCM-101 User manual
Trinamic
Trinamic TMCM-1633 User manual

Trinamic
Trinamic TMCL TMCM-142 Use and care manual

Trinamic
Trinamic PD 108-28-SE-485 Series User manual
Trinamic
Trinamic CANopen User manual

Trinamic
Trinamic PANdrive PD42-1- 1243-IOLINK Safety guide

Trinamic
Trinamic BB-100 User manual
Trinamic
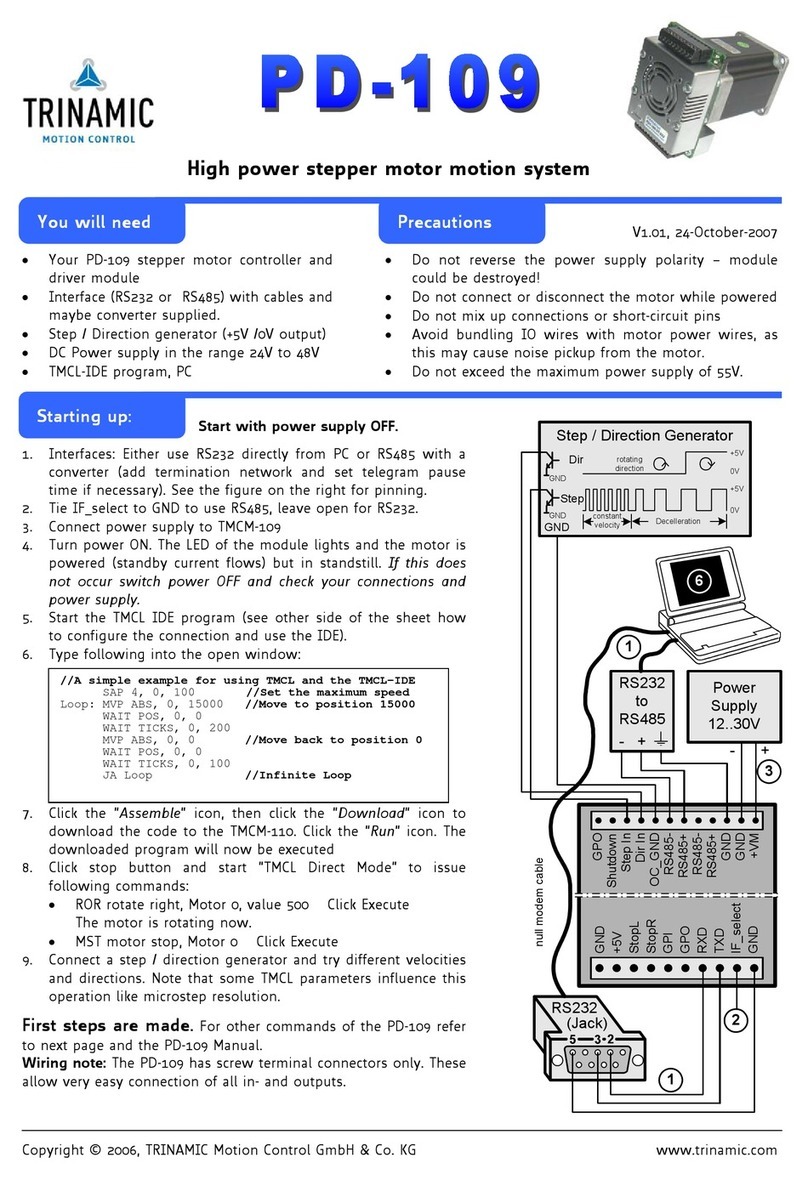
Trinamic PD-109 User manual
Trinamic
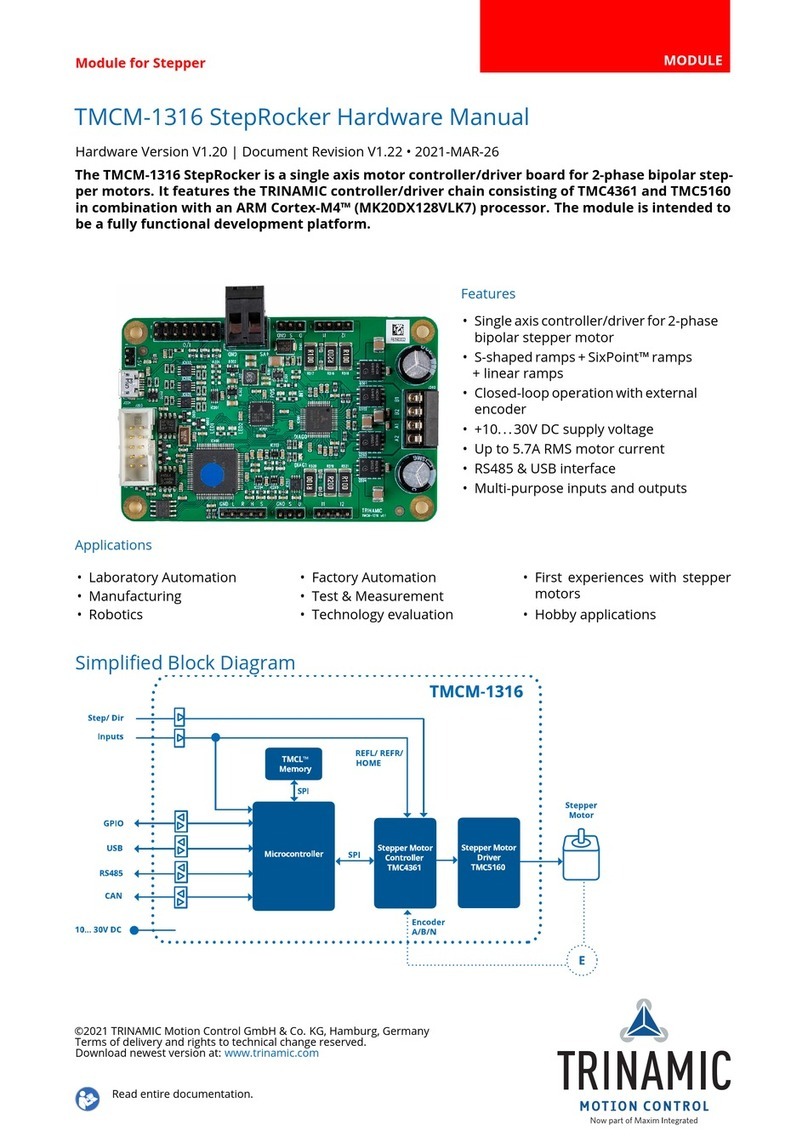
Trinamic TMCM-1316 StepRocker User manual

Trinamic
Trinamic TMCM-351 Use and care manual