6 INTRODUCTION SMARTSENSOR V USER GUIDE
SmartSensor V Package
A typical sensor package contains the following items:
10.525 GHz SmartSensor V radar trac sensor
SmartSensor mounting kit
SmartSensor 8-conductor cable
SmartSensor Manager soware
SmartSensor V User Guide
Note
Check the packing slip for actual contents. If any of these items are missing, note
the serial number located on the back of the sensor and contact your distributor.
Additional products may be purchased through your distributor. e following optional
items are not included unless specically ordered (check packing list for actual inventory):
Click 200 surge protector – Prevents electrical surges conducted along underground
cables from damaging the sensor and/or cabinet equipment.
Click 201/202/204 AC to DC converter – A Click 201 provides 1 A of power and is ca-
pable of powering a single sensor; a Click 202 provides 2 A and can power two sensors;
a Click 204 provides 4 A and can power four sensors.
Click 210 circuit breaker – Interrupts power during overload conditions and provides
a convenient way to turn power on and o for the entire system.
Click 230 AC surge protector – Helps protect equipment from current surges on the
power lines.
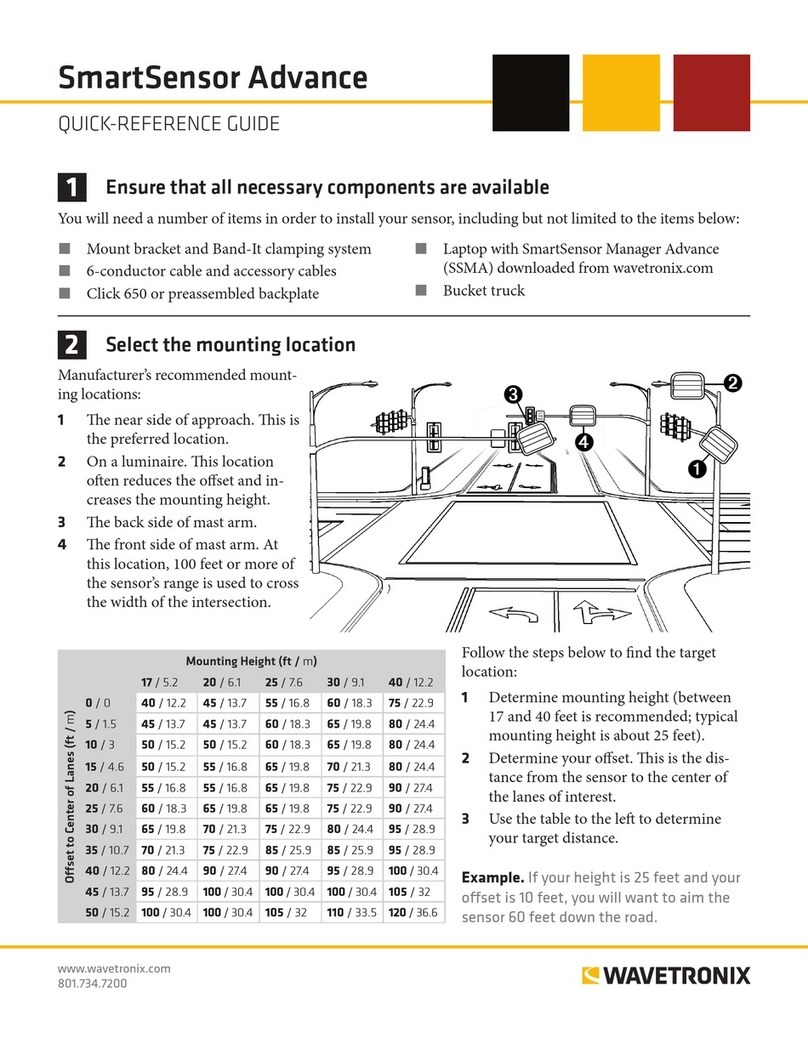
Selecting a Mounting Location
Consider the following guidelines when selecting a mounting location:
Lane Coverage – Sensor mounting locations should be selected so that all monitored
lanes are within 10 to 200 . (3 to 61 m) and run parallel with each other. If more than
eight lanes need to be simultaneously monitored, consider using multiple sensors or
the SmartSensor HD, which can monitor up to 10 lanes simultaneously.
Parallel Lanes – When the sensor is used to collect both mainline and ramp data, the
pole position should be selected so that the on and o ramp lanes run parallel with the
mainline. If lanes are not parallel, installation of multiple SmartSensor units should be
considered to achieve the sensor’s ±2° side-to-side angle requirement.
Sensors on the Same Pole – When multiple sensors are mounted on the same pole,
they will not be subject to interference if they are congured to operating using dif-
ferent RF channels and are separated vertically by a few feet. e higher sensor would
typically be used for the lanes further from the pole in order to minimize occlusion.