2
Contents
1. Application Notices........................................................................................................................................... 3
1.1. About the User Manual..............................................................................................................................3
1.2. Safety Precautions..................................................................................................................................... 3
1.3. Printing Consumables................................................................................................................................ 3
1.4. Environment requirements........................................................................................................................4
2. Introduction to the Printer................................................................................................................................4
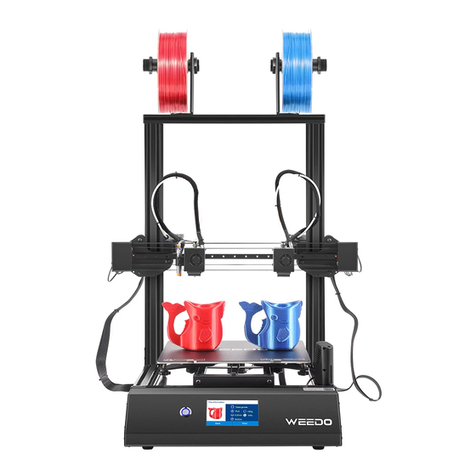
2.1 Appearance Introduction............................................................................................................................4
2.2 Technical Parameters..................................................................................................................................5
3. Install the software of the printer.....................................................................................................................6
3.1 Install Wiibuilder software..........................................................................................................................6
3.2 Wiibuilder Instructions for advanced settings............................................................................................7
4. Print the first model......................................................................................................................................222
4.1. Connect the power supply.....................................................................................................................222
4.2 Loading the filament............................................................................................................................... 222
4.3 Printing preparation................................................................................................................................233
4.4 Printing Mode......................................................................................................................................... 233
4.5 Removing Model....................................................................................................................................... 23
5. Details of the Printing Operation....................................................................................................................24
5.1 Operation Panel Setting............................................................................................................................24
5.1.1 Introduction of the Operation Panel..................................................................................................... 24
5.1.2 Operation Panel Menu........................................................................................................................25
5.1.3 Common operations of the control panel.......................................................................................... 25
5.1.4 Printer Preheat....................................................................................................................................................................26
5.1.5 Debuggung of Printing Function...................................................................................................................................26
5.1.6 Filament Replacement.....................................................................................................................................................27
5.1.7 Printer Jog Bebugging.......................................................................................................................................................27
5.1.9. Auto Home............................................................................................................................................ 29
5.1.10. Stop printing/Pause printing...............................................................................................................30
5.1.11. Adjust the temperature...................................................................................................................... 31
6. Daily Repair and Maintenance.......................................................................................................................... 31
6.1. Printer Daily Maintenance Guide.............................................................................................................31
6.1.1.Clean and replace the nozzle ...........................................................................................................31
6.1.2 Replacing the tape of the glass plate.....................................................................................................32
7. Optical Shaft and Screw Rod Maintenance..............................................................................................................34
8.Printing Nozzle Maintenance and Replacement.......................................................................................................35