- 1 -
Table of contents
1 Introduction........................................................................................................................ 2
1.1 Notation and symbols......................................................................................................... 2
1.2 Intended use....................................................................................................................... 2
1.3 System requirements.......................................................................................................... 2
1.4 License terms...................................................................................................................... 3
2 Installation .......................................................................................................................... 4
2.1 Software installation........................................................................................................... 4
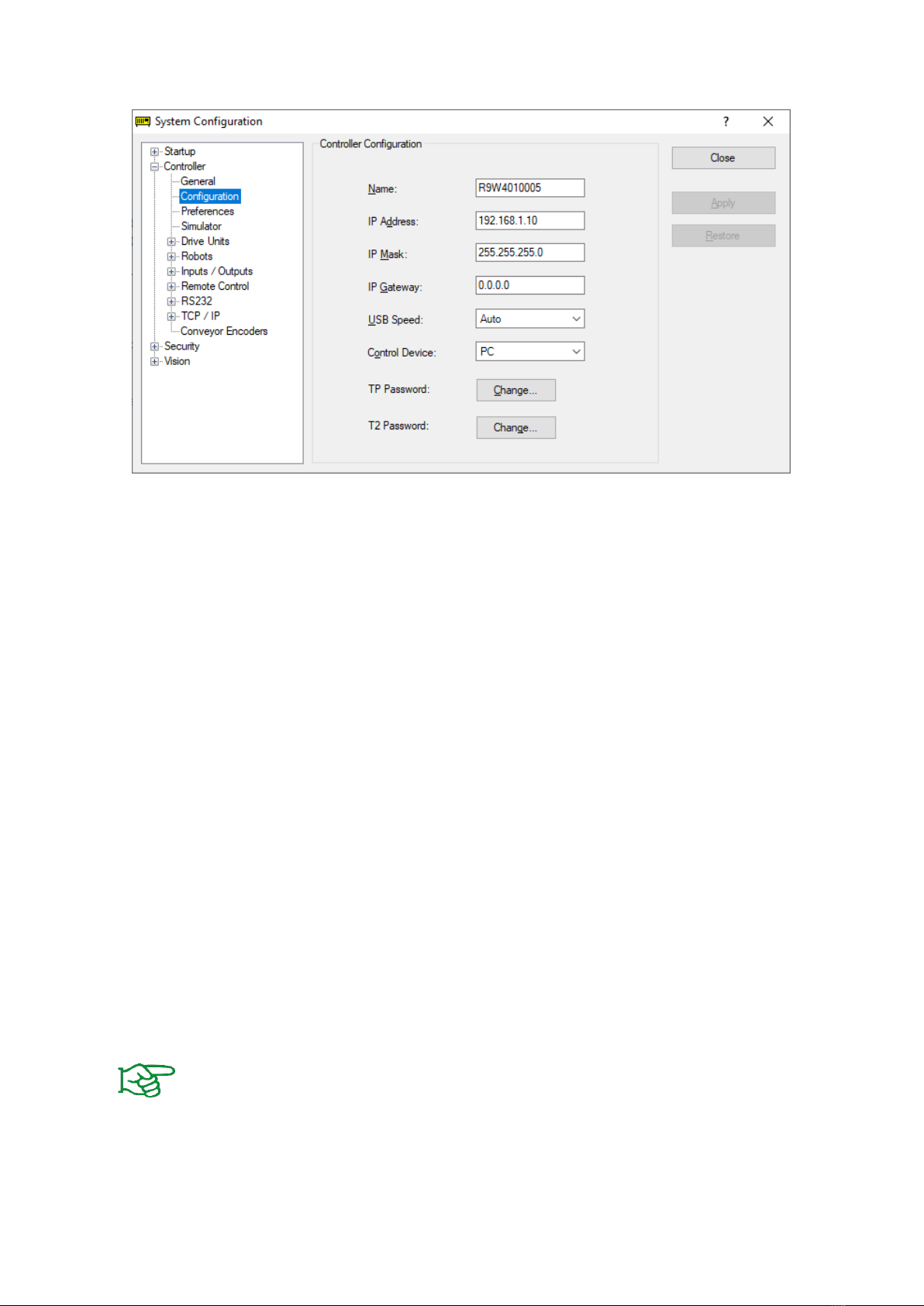
2.2 Network configuration........................................................................................................ 4
2.3 Workpiece detection and monitoring................................................................................. 5
3 Command set reference ..................................................................................................... 7
3.1 Open connection - CONNECT.............................................................................................. 8
3.2 Enable drive - ENABLE......................................................................................................... 9
3.3 Get Grip State –GET STATE .............................................................................................. 10
3.4 Read gripping state from global variable.......................................................................... 11
3.5 Disable drive - DISABLE..................................................................................................... 12
3.6 Disable drives of all modules connected –DISABLE ALL .................................................. 14
3.7 Reference gripper - HOME................................................................................................ 15
3.8 Reference multiple grippers –MHOME............................................................................ 16
3.9 Grip part - GRIP................................................................................................................. 17
3.10 Grip part with multiple grippers –MGRIP ........................................................................ 18
3.11 Release part - RELEASE ..................................................................................................... 19
3.12 Release part with multiple grippers –MRELEASE............................................................. 20
3.13 Get finger position –GET POSITION ................................................................................. 21
3.14 Control gripping force retention - PERMAGRIP................................................................ 22
3.15 Control gripping force retention for multiple grippers –MPERMAGRIP.......................... 23
3.16 Control of the LED display –LED........................................................................................ 24
4 Error Handling................................................................................................................... 25
4.1 Handle errors in GRIPLINK functions ............................................................................... 25
4.2 Handle errors in GRIPLINK background daemon.............................................................. 26