bdiGDBfor BDI2000 (PowerPC 7440/7450/86xx) User Manual 2
© Copyright 1997-2015 by ABATRON AG Switzerland V 1.13
1 Introduction ................................................................................................................................. 3
1.1 BDI2000................................................................................................................................. 3
1.2 BDI Configuration ..................................................................................................................4
2 Installation ................................................................................................................................... 5
2.1 Connecting the BDI2000 to Target ........................................................................................5
2.1.1 Changing Target Processor Type ................................................................................7
2.2 Connecting the BDI2000 to Power Supply ............................................................................ 8
2.3 Status LED «MODE».............................................................................................................9
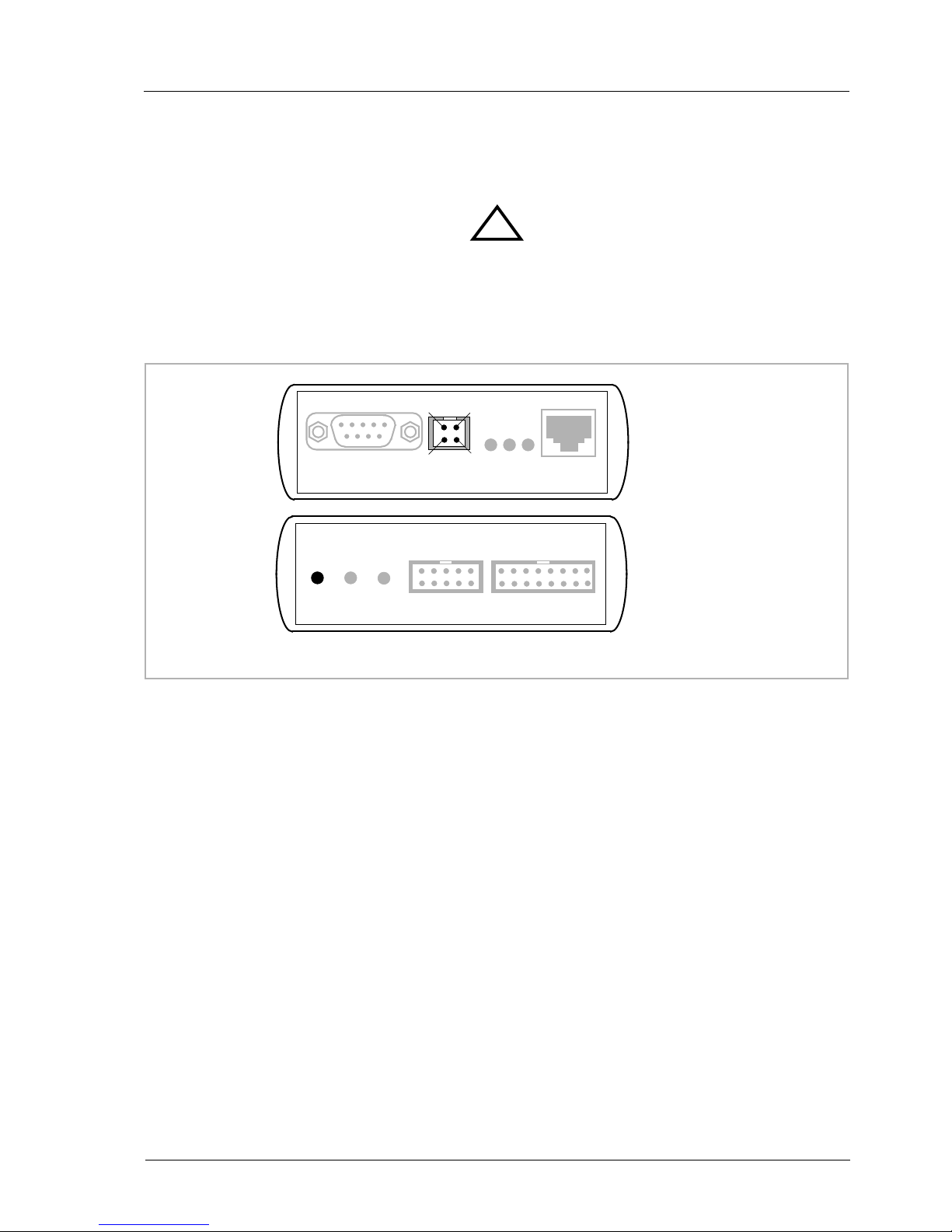
2.4 Connecting the BDI2000 to Host .........................................................................................10
2.4.1 Serial line communication ..........................................................................................10
2.4.2 Ethernet communication ............................................................................................ 11
2.5 Initial configuration of the bdiGDB system...........................................................................12
2.5.1 Configuration with a Linux / Unix host........................................................................13
2.5.2 Configuration with a Windows host ............................................................................15
2.5.3 Recover procedure.....................................................................................................16
2.6 Testing the BDI2000 to host connection..............................................................................17
2.7 TFTP server for Windows....................................................................................................17
3 Using bdiGDB ............................................................................................................................ 18
3.1 Principle of operation...........................................................................................................18
3.2 Configuration File.................................................................................................................20
3.2.1 Part [INIT]...................................................................................................................21
3.2.2 Part [TARGET] ...........................................................................................................23
3.2.3 Part [HOST]................................................................................................................ 28
3.2.4 Part [FLASH] ..............................................................................................................30
3.2.5 Part [REGS] ............................................................................................................... 34
3.3 Debugging with GDB ...........................................................................................................36
3.3.1 Target setup ...............................................................................................................36
3.3.2 Connecting to the target.............................................................................................36
3.3.3 Breakpoint Handling...................................................................................................37
3.3.4 GDB monitor command..............................................................................................37
3.3.5 Target serial I/O via BDI.............................................................................................38
3.3.6 Embedded Linux MMU Support .................................................................................39
3.4 Telnet Interface....................................................................................................................41
3.5 Dual-Core Support for MPC8641D......................................................................................43
4 Specifications ............................................................................................................................ 45
5 Environmental notice................................................................................................................ 46
6 Declaration of Conformity (CE)................................................................................................ 46
7 Warranty..................................................................................................................................... 47
Appendices
A Troubleshooting ....................................................................................................................... 48
B Maintenance .............................................................................................................................. 49
C Trademarks ............................................................................................................................... 51