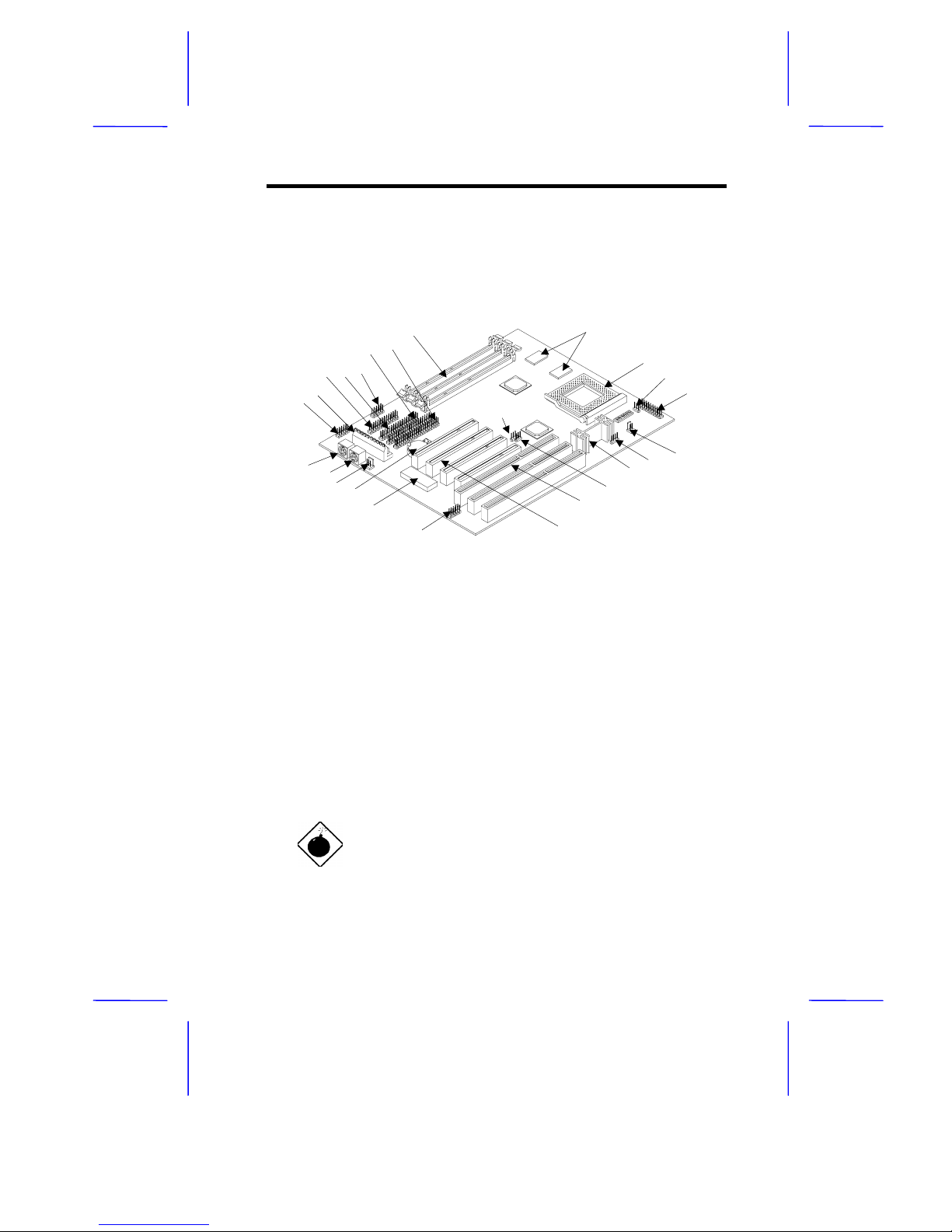
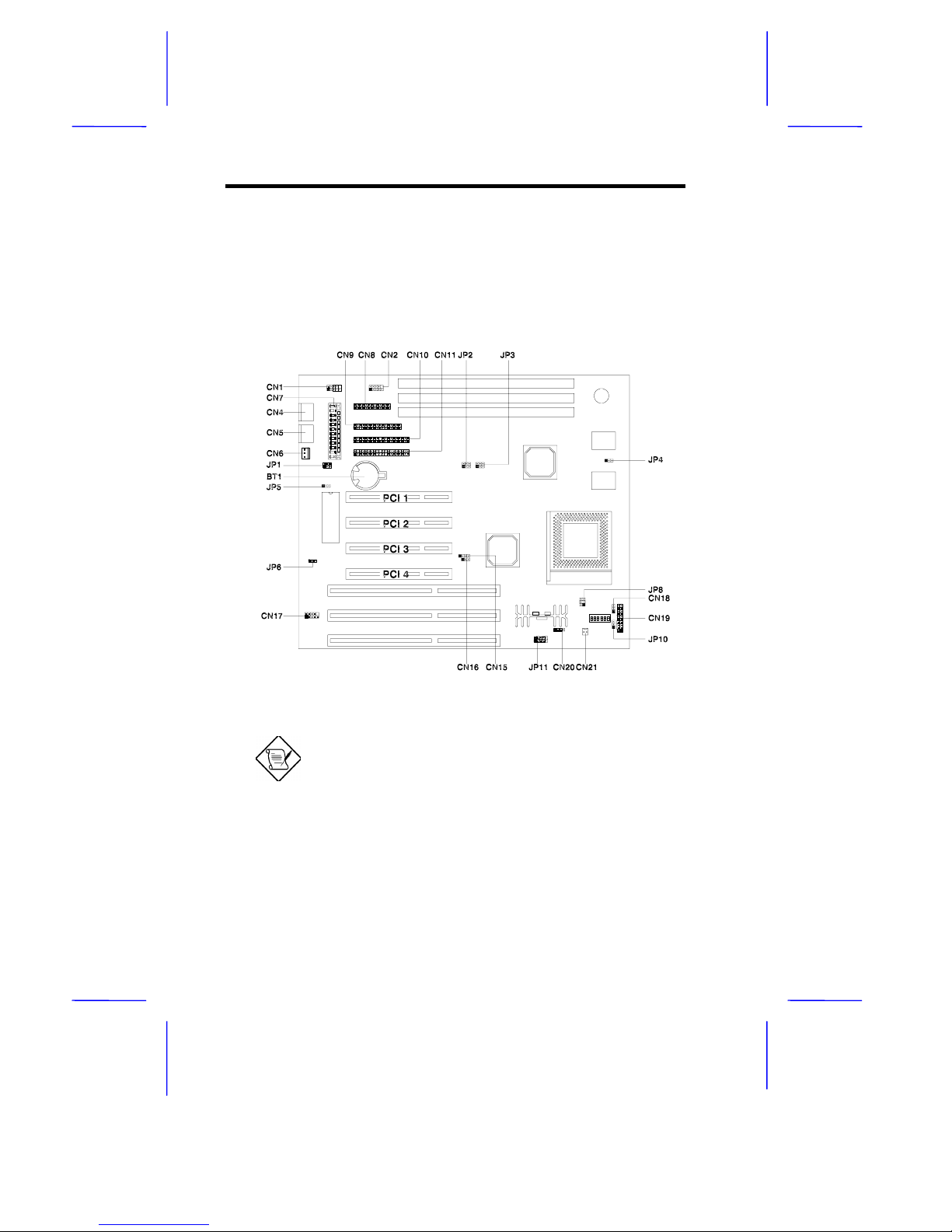
System Board 1-9
1.5 Installation Precautions
Before you install any system component, we recommend that you
read the following sections. These sections contain important ESD
precautions, pre- and post installation instructions.
1.5.1 ESD Precautions
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) can damage your processor, disk drives,
expansion boards, and other components. Always observe the
following precautions before you install a system component.
1. Do not remove a component from its protective packaging until
you are ready to install it.
2. Wear a wrist grounding strap and attach it to a metal part of the
system unit before handling components. If a wrist strap is not
available, maintain contact with the system unit throughout any
procedure requiring ESD protection.
1.5.2 Pre-installation Instructions
Always observe the following before you install a system component:
1. Turn off the system power and all the peripherals connected to
the unit before opening it.
2. Open the system according to the instructions in the housing
installation manual.
3. Follow the ESD precautions in section 1.5.1 before handling a
system component.
4. Remove any expansion boards or peripherals that block access
to the DIMM sockets or CPU socket.
5. See the following sections for specific instructions on the
component you wish to install.