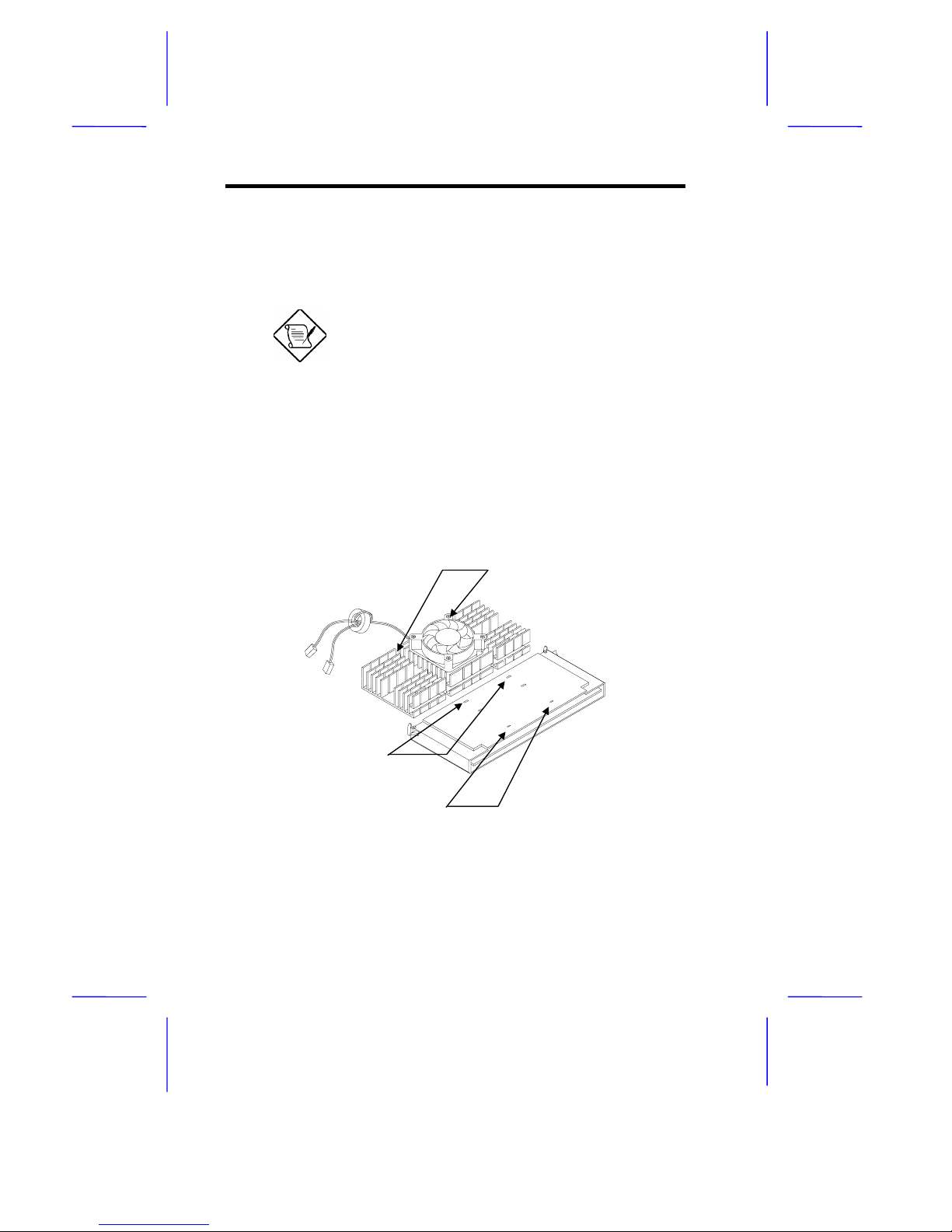
1-2 User’s Guide
A 50-pin Fast SCSI (Small Computer System Interface) and a 68-pin
Wide SCSI comes with the system board to connect SCSI devices.
Wide SCSI supports 32-bit transfers while fast SCSI uses a 16-bit bus
that doubles the clock rate to support data rates of 40 Mb/s.
The M19A system board also supports the USB (Universal Serial Bus)
connector, and other standard features such as two UART NS16C550
serial ports, one enhanced parallel port with Enhanced Parallel Port
(EPP)/Extended Capabilities Port (ECP) feature, a diskette drive
interface, and two embedded hard disk interfaces. The board also
includes a built-in 10/100 Mb/s Intel 82558 LAN chip that supports
Wake-On-LAN (WOL).
The system supports the power-management function that conforms
to the power-saving standards of the U.S. Environmental Protection
Agency (EPA) Energy Star program. It also offers the Plug-and-Play
feature. This feature saves the user from configuration troubles, thus
making the system more user-friendly. The system board supports two
optional features, ASM Pro and Remote Diagnostic
Management (RDM), that allow better server management. The ASM
Pro detects problems in CPU thermal condition, CPU working voltage
detection (±12V/±5V/3.3V/1.5V), and PCI bus utilization calculation. It
also detects if the CPU fan or the chassis fan malfunctions. RDM
allows execution of the RDM diagnostic program from a remote RDM
station to fix detected problems or to reboot the system.
The system is fully compatible with MS-DOS V6.X, DOS/V, IBM OS/2
Warp, Novell Netware, Novel SFT III, SCO UNIX, Windows NT and
Windows 95 operating systems.