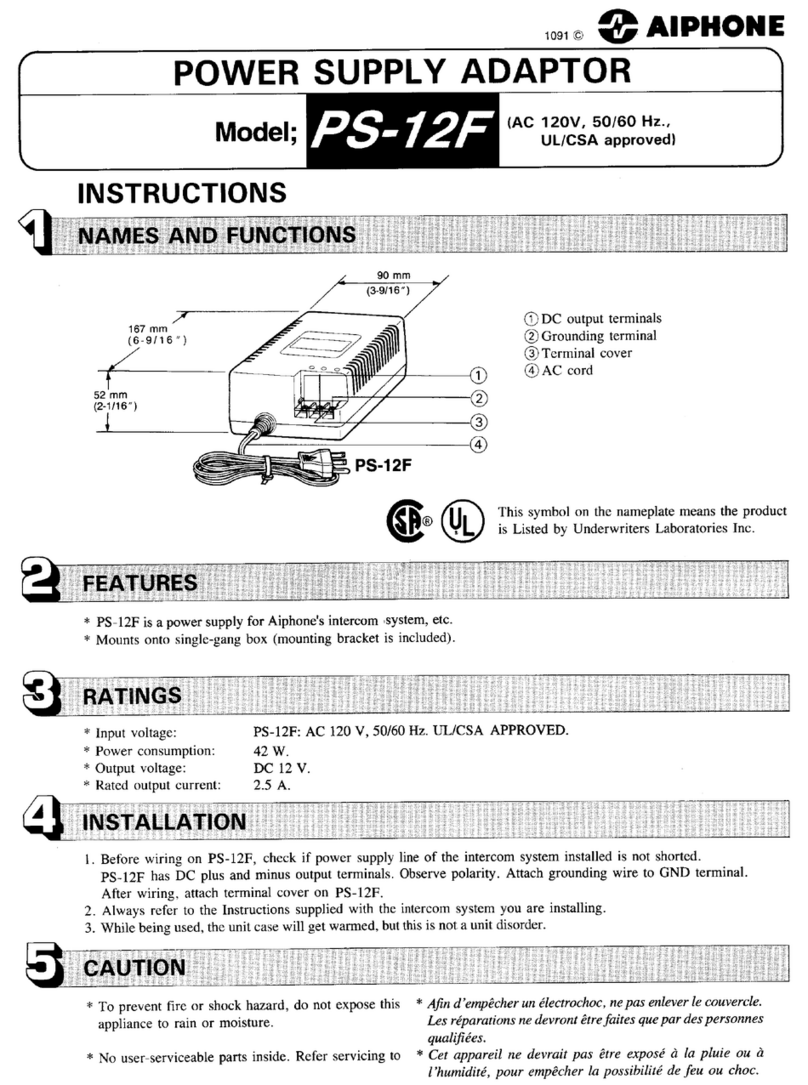
DR-135 / DR-435MkII
Service Manual
CONTENTS
SPECIFICATIONS
General..................................................................... 2
Transmitter ................................................................ 2
Receiver ................................................................... 2
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
1) Receiver System DR-135 ..................................... 3, 4
2) Transmitter System DR-135 ...................................... 5
3) PLL Synthesizer Circuit DR-135 ........................... 5, 6
4) Receiver System DR-435 ..................................... 6, 7
5) Transmitter System DR-435 ...................................... 8
6) PLL Synthesizer Circuit DR-435 ........................... 8, 9
7) CPU and Peripheral Circuit ................................. 9, 10
8) Power Supply Circuit............................................... 10
9) M38267M8L272GP (XA0851)........................... 11~13
SEMICONDUCTOR DATA
1) M5218AFP (XA0068).............................................. 14
2) NJM7808FA (XA0102) ............................................ 14
3) TC4S66F (XA0115) ................................................ 14
4) BU4052BF (XA0236) .............................................. 15
5) TA75S01F (XA0332) ............................................... 15
6) TC4W53FU (XA0348)............................................. 15
7) TA31136FN (XA0404)............................................. 16
8) LA4425A (XA0410)................................................. 16
9) M67746 (XA0412) .................................................. 17
10) M57788M (XA0077A) ............................................. 18
11) NJM2902V (XA0596).............................................. 19
12) 24LC32AT (XA0604) ............................................... 19
13) S-80845ALMP (XA0620) ........................................ 19
14) TK10931V (XA0666)......................................... 20, 21
15) L88MS05TLL (XA0675) .......................................... 22
16) M64076AGP (XA0915) ........................................... 23
17) Transistor, Diode and LED Outline Drawing ............ 24
18) LCD Connection (TTR3626UPFDHN) .................... 25
EXPLODED VIEW
1) Top and Front View ................................................. 26
2) Bottom View............................................................ 27
3) LCD Assembly........................................................ 28
PARTS LIST
CPU Unit .......................................................... 29, 30
MAIN Unit DR-135 ............................................ 30~33
MAIN Unit DR-435 ............................................ 33~36
VCO Unit DR-435 ................................................... 36
Mechanical Parts .............................................. 36, 37
Packing Parts.......................................................... 37
ACCESSORIES...................................................... 37
ACCESSORIES (SCREW SET).............................. 37
TNC (EJ41U) .......................................................... 38
TNC (EJ41U) Packing Parts ................................... 39
DR-135 ADJUSTMENT
1) Adjustment Spot .................................................... 40
2) VCO and RX Adjustment Specification ................... 41
3) Tx Adjustment Specification.................................... 41
4) Rx Test Specification............................................... 42
5) Tx Test Specification ............................................... 43
DR-435 ADJUSTMENT
1) Adjustment Spot .................................................... 44
2) VCO and RX Adjustment Specification ................... 45
3) Tx Adjustment Specification.................................... 46
4) Rx Test Specification............................................... 47
5) Tx Test Specification ............................................... 48
PC BOARD VIEW
1) CPU Unit Side A ..................................................... 49
2) CPU Unit Side B ..................................................... 49
3) MAIN Unit Side A DR-135 (UP0467A) .................... 50
4) MAIN Unit Side B DR-135 (UP0467A) .................... 50
5) MAIN Unit Side A DR-435 (UP0468A) .................... 51
6) MAIN Unit Side B DR-435 (UP0468A) .................... 51
7) TNC Unit Side A (UP0402) (option) ........................ 52
8) TNC Unit Side B (UP0402) (option) ........................ 52
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM
1) CPU Unit DR-135 / DR-435 .................................... 53
2) MAIN Unit DR-135 .................................................. 54
3) MAIN Unit DR-435 .................................................. 55
4) TNC Unit (option).................................................... 56
BLOCK DIAGRAM
1) DR-135 ................................................................... 57
2) DR-435 ................................................................... 58
ALINCO,INC.