Location
For best operating characteristics and longest unit life,
take care in selecting an installation site. Avoid
locations exposed to high humidity, dust, high ambient
temperature, or corrosive fumes. Moisture can
condense on electrical components, causing corrosion
or shorting of circuits (especially when dirt is also
present).
Adequate air circulation is needed at all times in order to
assure proper operation. Provide a minimum of 6
inches of free air space at the sides of the unit.
Make sure that ventilation openings are not obstructed.
Always remove the charger shipping skid from the unit
before installation. The charger must be installed over
a noncombustible surface such as concrete or metal.
Keep the charging area clear of all combustible material
such as wood, paper, and cloth. When moving the
charger after the packing skid and box have been
removed, make sure that lifting forks do not damage the
charger panels or cables.
WARNING: SPARKS OR MOLTEN METAL
falling through open bottom can cause fire or
explosion.
•Install over noncombustible material such as
concrete or metal.
•Keep charging area clear of combustible
material.
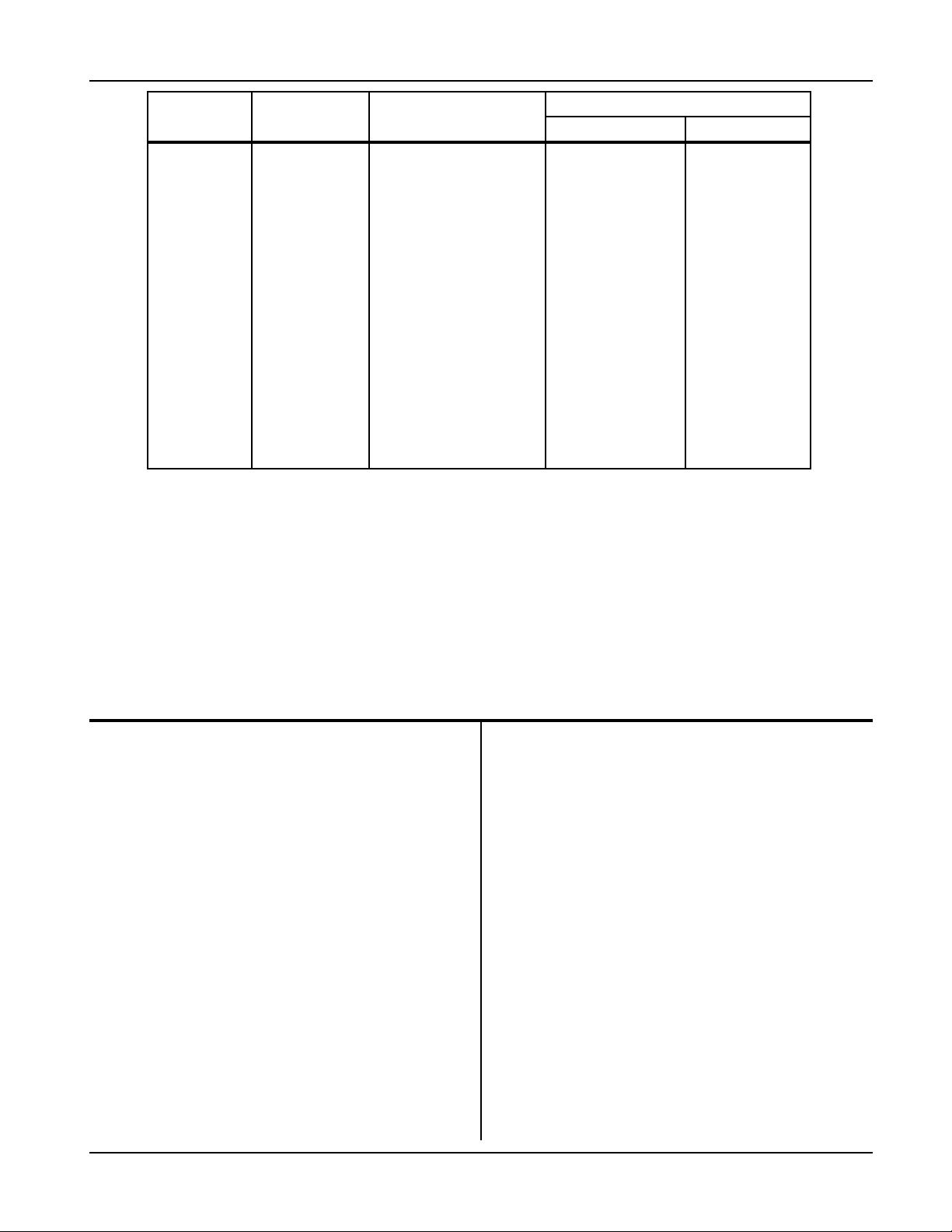
Environmental Characteristics
Operating Characteristics 0°C to 40°C
(32°F to 104°F)
Operating Altitude To 2000 Meters
(6562 Feet)
Operating Humidity 80% up to 31°c,
decreasing to 50% at
40°C, non-condensing
80% up to 88°F
decreasing to 50% at
104°F, non-condensing
Grounding
The frame of the power source must be grounded for
personnel safety. Where grounding is mandatory under
state or local codes, it is the responsibility of the user to
comply with all applicable rules and regulations. Where
no state or local codes exist, it is recommended that
the National Electrical Code be followed.
In addition to the usual function of protecting personnel
against the hazard of electrical shock due to fault in the
equipment, grounding serves to discharge the static
electrical charges which tend to build up on the
surfaces of equipment. These static charges can cause
painful shock to personnel, and can lead to the errone-
ous conclusion that an electrical fault exists in the
equipment.
If a charger is to be connected to the AC power supply
with a flexible jacketed cable, one having a separate
grounding conductor should be used. When included in
cable assembly, grounding conductor will be green,
green with a yellow stripe, or bare. When connecting
input power to charger (as instructed in Line
Connection to Battery Charger section of this manual),
connect grounding conductor to equipment grounding
terminal (stud with a green nut and a cup washer and
identified by symbol ), taking care to make a good
electrical connection. Connect other end of grounding
conductor to the system ground.
If, for any reason, an input cable which does not include
a grounding conductor is used, the equipment must be
grounded with separate conductor. Minimum size and
color coding requirements must be in accordance with
any applicable state or local code, or the National
Electrical Code.
If metallic armored cable or conduit is used, the metal
sheathing or conduit must be effectively grounded as
required by state or local code, or the National
Electrical Code.
If a system ground is not available, the charger frame
must be connected to a driven ground rod (at least 8 ft
[2438 mm] long), or to a water pipe that enters the
ground not more than 10 ft (3048 mm) from the charger.
A grounding conductor must be connected to the rod or
pipe in a manner that will assure a
permanent and effective ground. The conductor must
be sized in accordance with any applicable state or
local code, or by the National Electrical Code. If in
doubt, use the same size conductor as is used for the
conductors supplying power to the charger.
WARNING: ELECTRIC SHOCK
HAZARD – Under no circumstance
should you use a grounding
conductor with a current carrying
capacity less than the ampere
rating shown in Table 4-1.
April 26, 2007 4-1
193111-075
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION