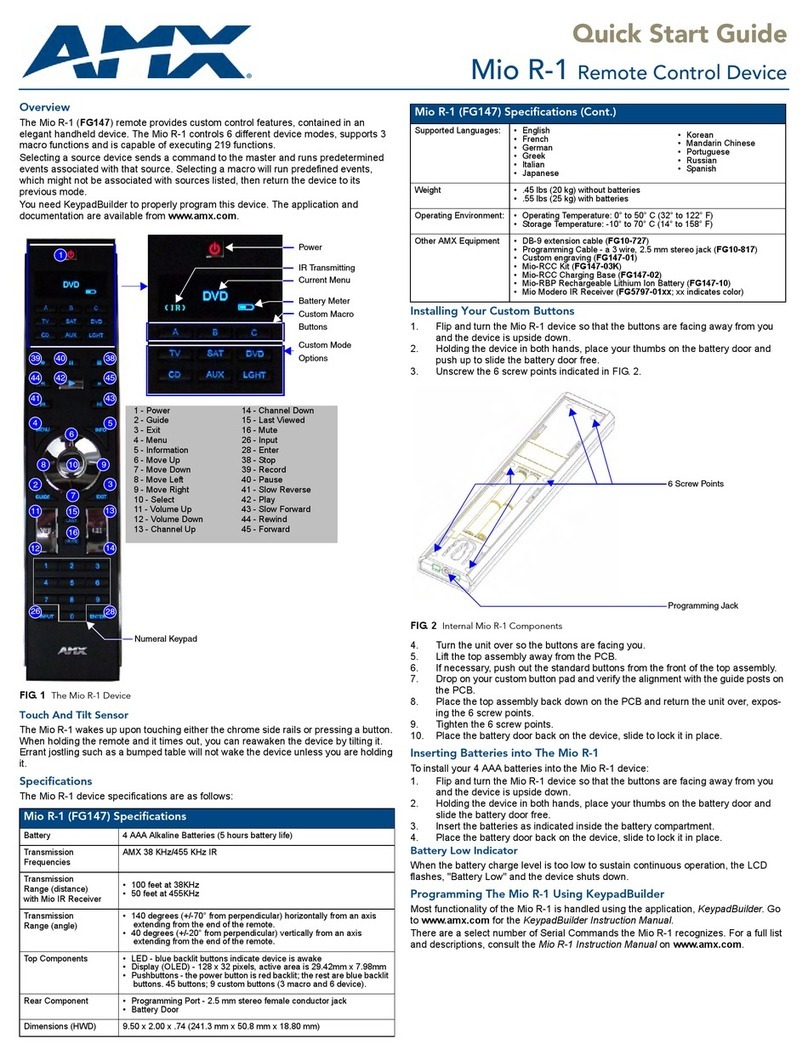
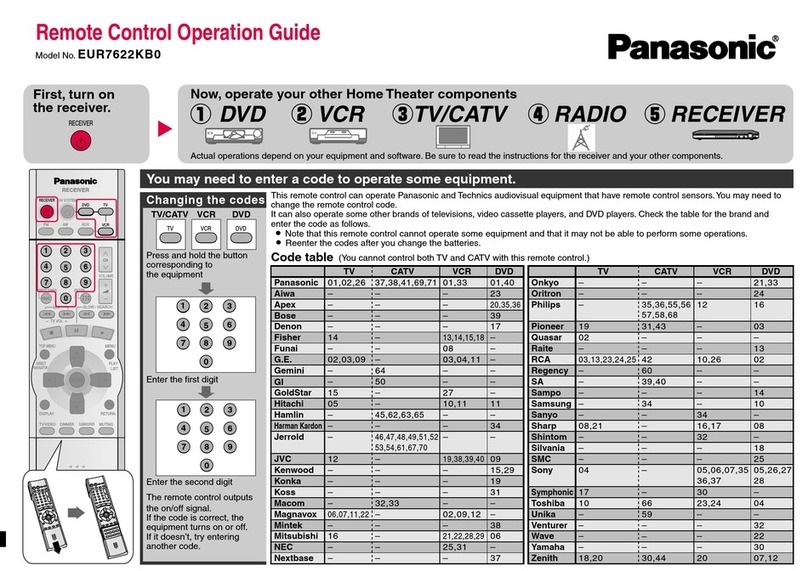
For full warranty information, refer to the AMX Instruction Manual(s) associated with your Product(s).
9/07
©2007 AMX. All rights reserved. AMX and the AMX logo are registered trademarks of AMX.
AMX reserves the right to alter specifications without notice at any time.
3000 RESEARCH DRIVE, RICHARDSON, TX 75082 • 800.222.0193 • fax 469.624.7153 • technical support 800.932.6993 • www.amx.com
93-5791-03 REV: A
Note: “RSSI” and “SNR” are terms that technically are associated with the
80211G wireless protocol (as opposed to ZigBee). However, most
mapping software applications (including NetStumbler) use these terms
generically across all protocols, including ZigBee.
If the site survey indicates that your ZigBee devices are communicating
outside of these guidelines, consider relocating one or more ZigBee APs
to improve signal quality.
When installing a Gateway or Repeater, do not deviate from the site
survey unless absolutely necessary.
If you have no choice but to install a Gateway or Repeater in a place other
than the most optimal location, resurvey the site again and note any dead
spots in the coverage area.
• Bluetooth-enabled devices, such as laptop computers and PDAs,
may cause issues with performance if operating in close proximity to
ZigBee Gateways or Repeaters. This issue is particularly severe if
the ZigBee device is relatively distant from the ZigBee AP with which
it is communicating.
• 2.4 GHz wireless telephones have also been noted to cause similar
interference.
Site Survey Tools - More Information
Free mapping software applications (particularly NetStumbler) are
supported via an extensive online community. There are many FAQs and
user forums to help you get started. The better you understand these
tools, the more successful your ZigBee installation is likely to be. Keep in
mind that these tools are also valuable for troubleshooting wireless
networks.
Temperature and Humidity
When conducting the site survey, consider the maximum and minimum
temperature and humidity under which the device(s) will function.
Installing ZigBee APs in areas subject to heat buildup in excess of
specifications (for instance, in attics or eaves) is not recommended.
Materials tending to absorb moisture from the air (wood, concrete, and
heavy cardboard, among others) may also tend to block wireless
transmissions.
Test for signal blockage during particularly humid conditions if possible.
Avoid Potential Sources of Signal Blockage
Don't place ZigBee Gateways or Repeaters behind metallized or metal-
bracketed objects, such as mirrors, windows, or equipment racks. Check
the wall and ceiling composition for possible range fall off.
Materials That May Affect Signals
Metal, walls, and floors can affect wireless signals. The closer your
Gateway or Repeater is to these obstructions, the more severe the
potential for blockage and/or reflection becomes, very likely resulting in
some degree of signal degradation.
Note: The depth or thickness of the blocking material may also affect
wireless connections.
While not all-inclusive, a list of common construction and fabrication
materials and their potential for adversely affecting wireless signals is
provided in the following table:
For instance, installing a ZigBee Gateway within an equipment rack may
produce a multipath signal as a result of signal reflections as well as
blockage. Multipath signals result in poor connectivity and slower reaction
times. For this reason, make sure to install the Gateway in as accessible a
location as possible to prevent or at least minimize multipath signals.
Place Gateways and Repeaters as High as Possible
All ZigBee APs should be placed as high as possible, according to the
location that offers the greatest amount of coverage, within a room to
guarantee maximum connectivity.
Placing a ZigBee AP close to the ground increases the likelihood of
interference from furnishings, support structures, and other objects within
an area.
ZigBee APs are best placed five feet (1.52 m) above the ground or
floor for maximum coverage.
Note: Locales containing large groups of people should have all ZiGbee
APs well above the average height of the people inside.
Don’t Saturate the RF Environment
Too many Gateways and receivers, whether ZigBee or WiFi, are worse
than not enough.
Always be careful not to saturate the local RF environment.
Don’t Place Gateways and Repeaters Within 5’ of
Each Other
Don't put receivers of any type within five feet (1.52 m) of each other. This
includes not only ZigBee Gateways and Repeaters, but also any other RF
transmitting devices such as WiFi access points and wireless phone base
stations.
Proper Channel Selection
When reserving channels to be used for a particular ZigBee PAN ID, use
ones that are not already in use by other ZigBee or WiFi devices. This
includes specifying channels that may overlap channels already in use.
For instance, if channel 21 is already taken for a WiFi network ID, try not
to use channels 20 or 22 for a ZigBee PAN ID.
For best results, do not use the same channel for different ZigBee PANs.
Don’t Use Gateways as Repeaters
Since each wireless Gateway has a unique PAN ID, devices cannot roam
between Gateways. If you need to extend coverage over a large area,
always use Repeaters to expand that coverage.
Setting up multiple Gateways within an area will NOT expand a particular
ZigBee network, even if the Gateways are all connected to the same
master.
Additional Sources of Information
• For more information on the ZigBee wireless protocol, please refer to
the ZigBee Alliance site at www.zigbee.org.
• To download the latest (free) version of NetStumbler software for
performing site surveys, go to www.netstumbler.com.
Additional information on using NetStumbler is available at
NetStumbler.org Forums (http://www.netstumbler.org/).
• To download the latest (free) version of Chanalyzer spectrum
analyzer software for performing site surveys, go to
http://www.metageek.net/products/chanalyzer.
Low potential:
Wood
Plaster
Synthetic materials (plastic, Lucite, fabric, composites)
Glass (window or other clear glass)
Medium potential:
Water
Brick or cinder block
Marble or other soft stone
High potential:
Paper rolls and heavy corrugated cardboard
Concrete
Granite or other hard stone
Bulletproof glass
Mirrors and smoked or tinted glass
Ferrous and nonferrous metal
FIG. 3 Proper placement of ZigBee APs