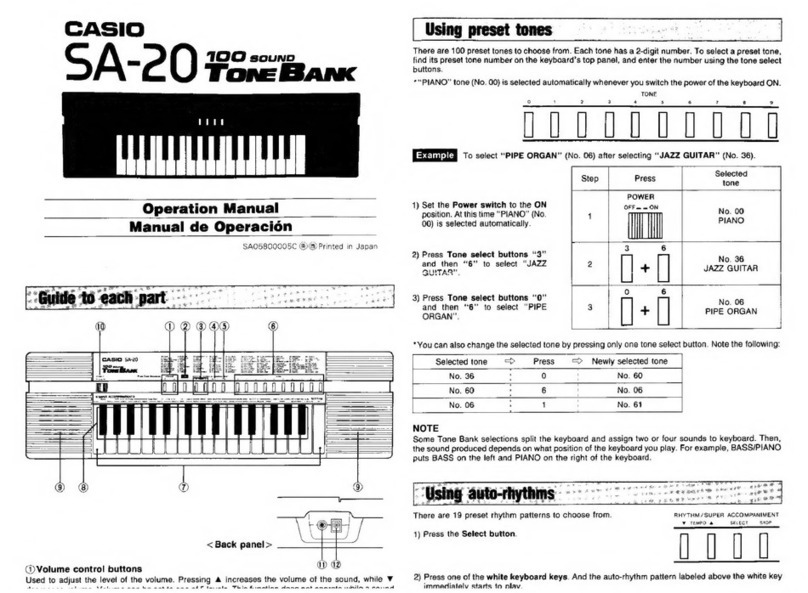
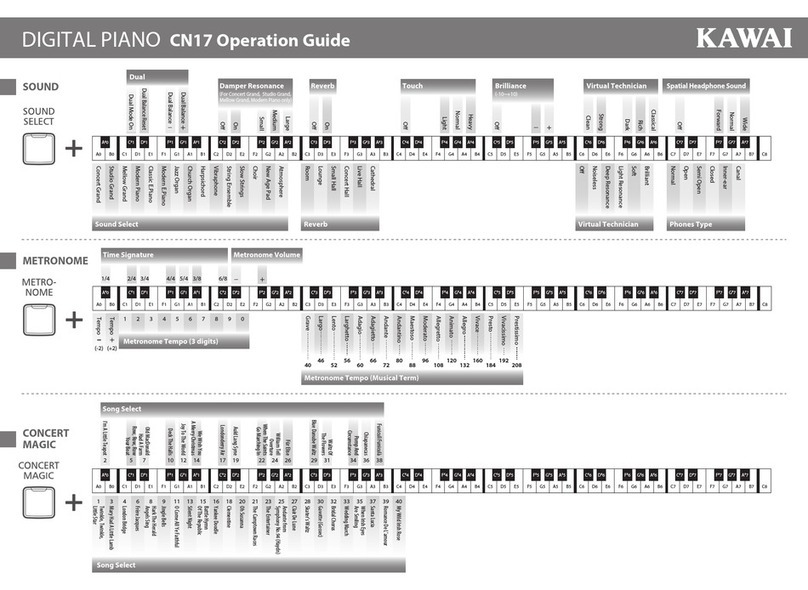
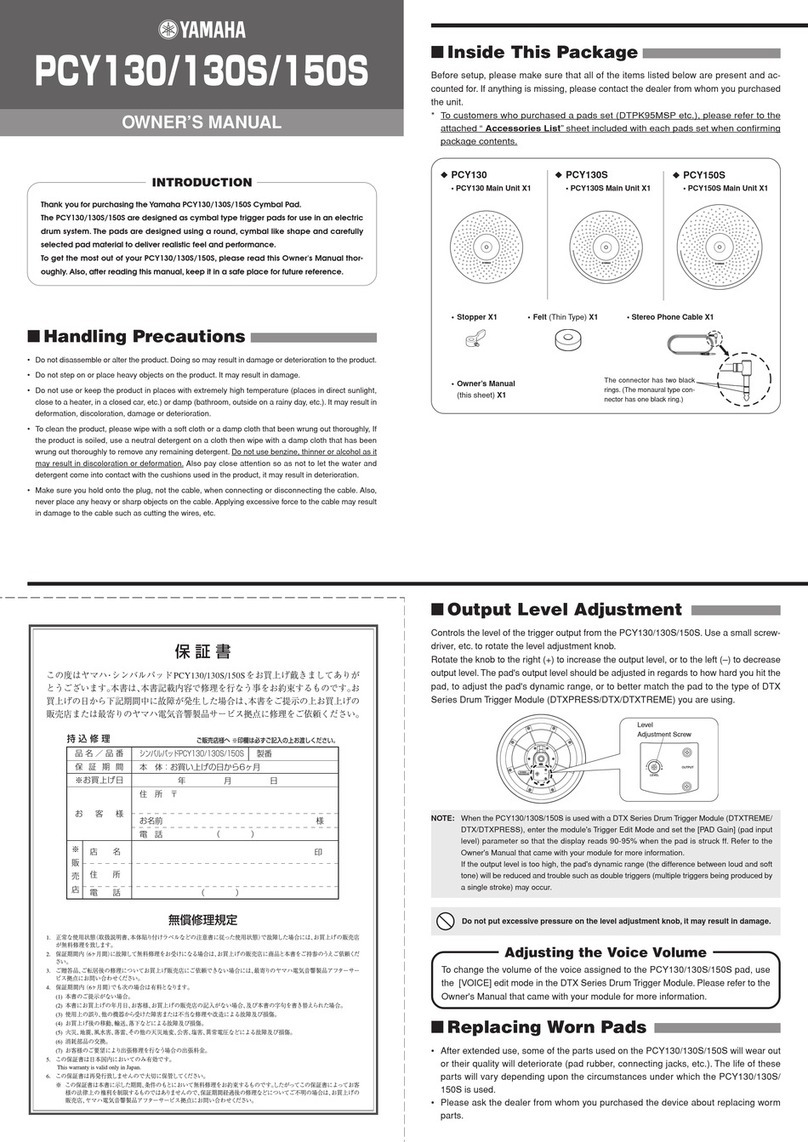
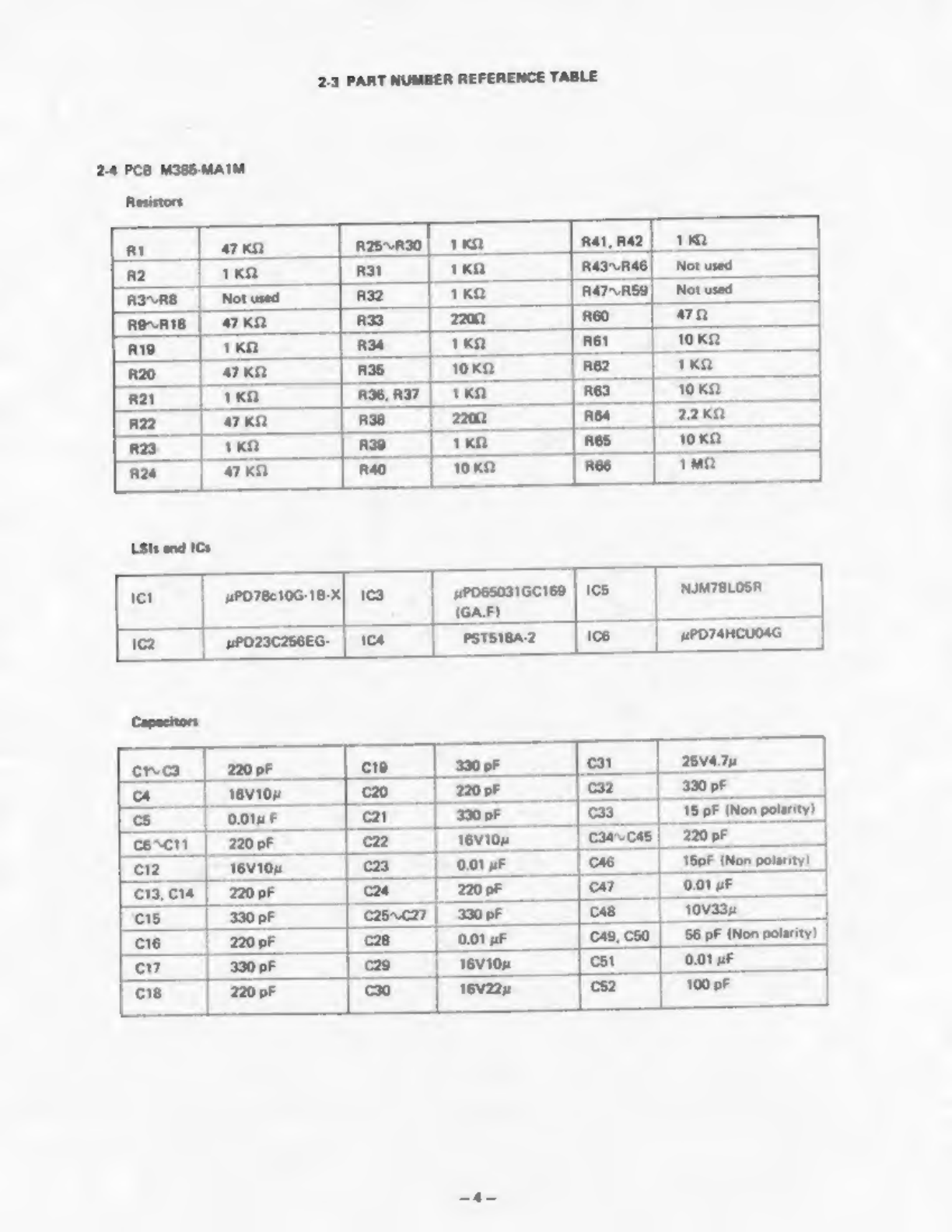
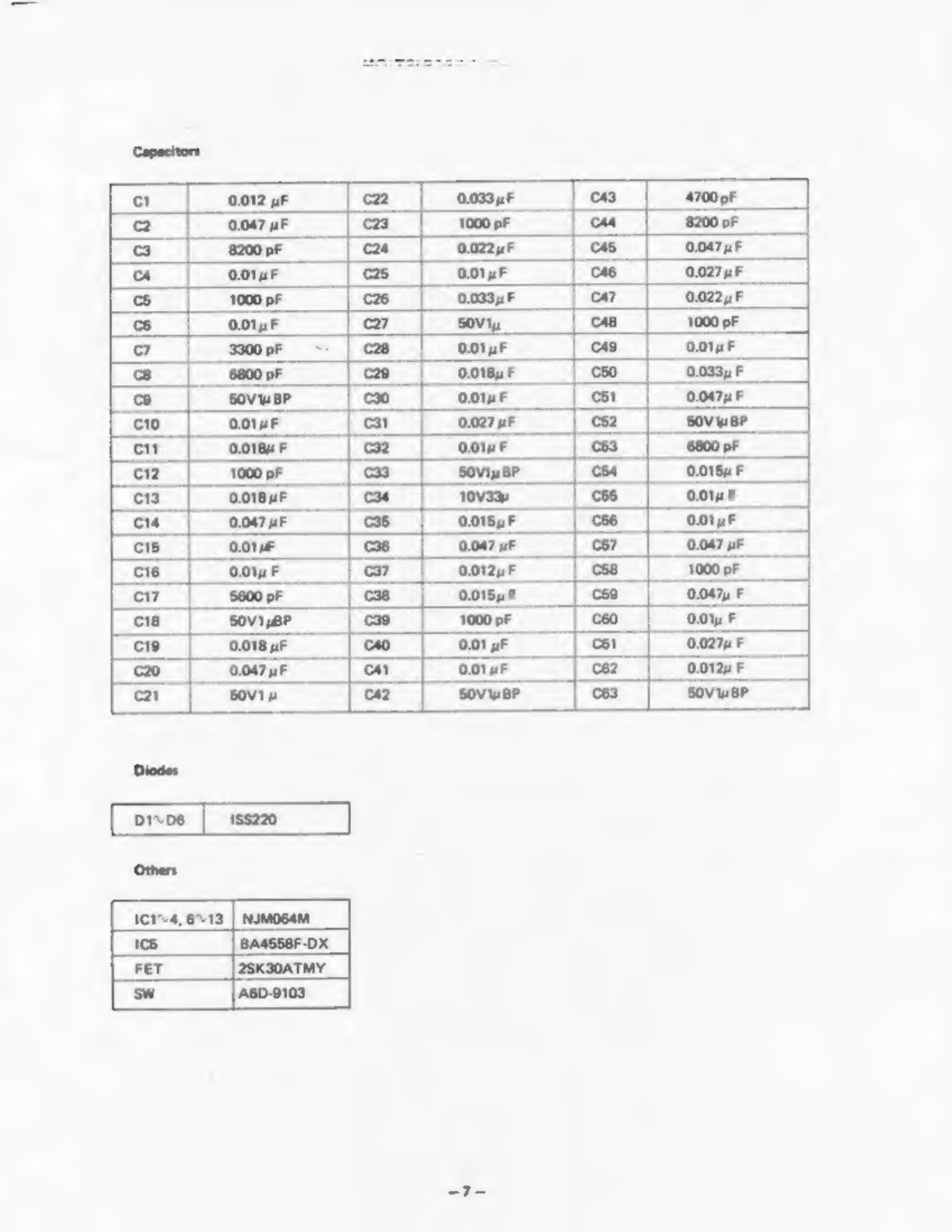
Casio MG-500 Troubleshooting guide
Other Casio Musical Instrument manuals

Casio
Casio LD-80 User manual

Casio
Casio CTK-3400SK User manual

Casio
Casio Aculaser M2 User manual

Casio
Casio AP-20 User manual

Casio
Casio SK-5 - SERVICE Troubleshooting guide
Casio
Casio SA-21 User manual

Casio
Casio Privia PX-S1000 Instruction Manual

Casio
Casio Privia PX-S6000 User manual

Casio
Casio Privia PX-720 User manual

Casio
Casio CELVIANO GP-400 User manual

Casio
Casio PX-S5000 User manual

Casio
Casio SongBank SA-35 User manual

Casio
Casio CTK-1300ES User manual

Casio
Casio CDP-S360 User manual

Casio
Casio Privia PX-700 Installation instructions

Casio
Casio Privia PX-S1000 User manual

Casio
Casio CGP-700 User manual

Casio
Casio CTK6000 User manual

Casio
Casio DG-20 Troubleshooting guide

Casio
Casio Celviano AP-60R User manual