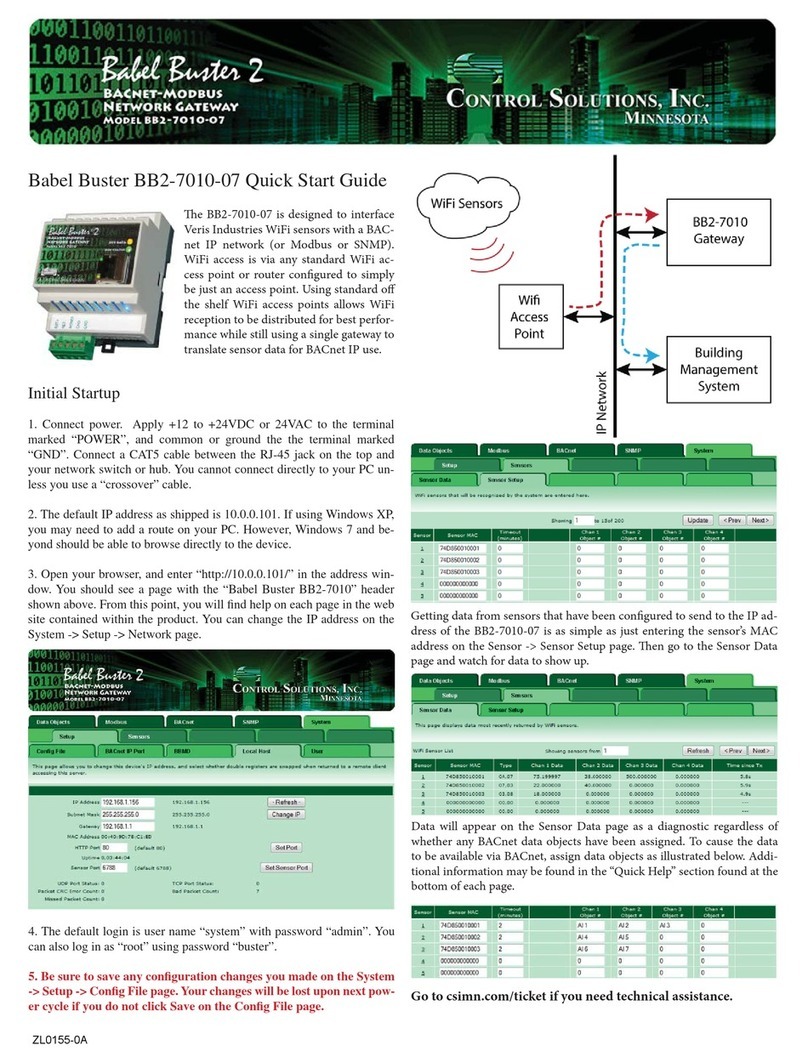
BB2-7030 User Guide – Rev. 1.0 Page iii
Contents
1. Introduction ..................................................................................................................................................... 1
2. Connecting the BB2-7030 for the First Time.................................................................................................. 3
3. Minimum BB2-7030 Gateway/Router Setup .................................................................................................. 6
4. Using the BB2-7030 as a BACnet Router....................................................................................................... 9
5. Using the BB2-7030 as a BACnet Server ..................................................................................................... 12
6. Using the BB2-7030 as a BACnet Client ...................................................................................................... 16
7. Using the BB2-7030 as an MS/TP to BACnet IP gateway ........................................................................... 25
8. Configuring the BB2-7030-01 as a Modbus TCP Server.............................................................................. 26
9. Configuring the BB2-7030-01 as a Modbus TCP Client............................................................................... 30
10. Using the BB2-7030-01 as a BACnet to Modbus TCP Gateway................................................................ 39
11. Using the BB2-7030-02 as an SNMP Server (Agent)................................................................................. 40
12. Using the BB2-7030-02 as an SNMP Client (Manager) ............................................................................. 44
13. Using the BB2-7030-02 as a BACnet to SNMP Gateway .......................................................................... 52
14. Using the BB2-7030 Proxy Support............................................................................................................ 53
15. Using the BB2-7030 BBMD Support and WAN Routing...........................................................................55
16. Miscellaneous System Setup ....................................................................................................................... 60
17. Hardware Guide........................................................................................................................................... 62
18. Trouble Shooting......................................................................................................................................... 64
19. BACnet Object Properties ........................................................................................................................... 65
19.1Data Object Properties (Analog, Binary, Multi-state)....................................................................... 65
19.2Device Object Properties................................................................................................................... 66
20. Modbus Slave Register Mapping ................................................................................................................ 68
20.1Using the BB2-7030 as a Modbus TCP Slave................................................................................... 68
20.2Modbus Registers Accessible with BB2-7030 as a Slave ................................................................. 68
20.3Modbus Function Codes Recognized by BB2-7030 .........................................................................69
History:
Rev 1.0 – Initial release