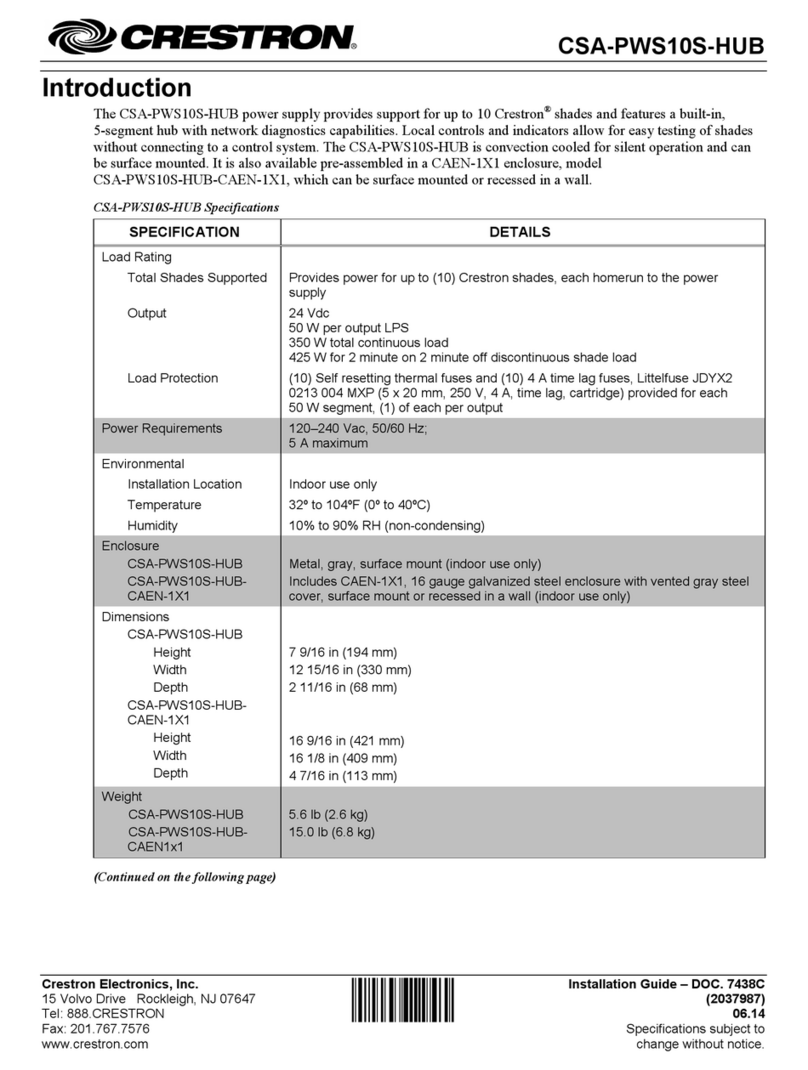
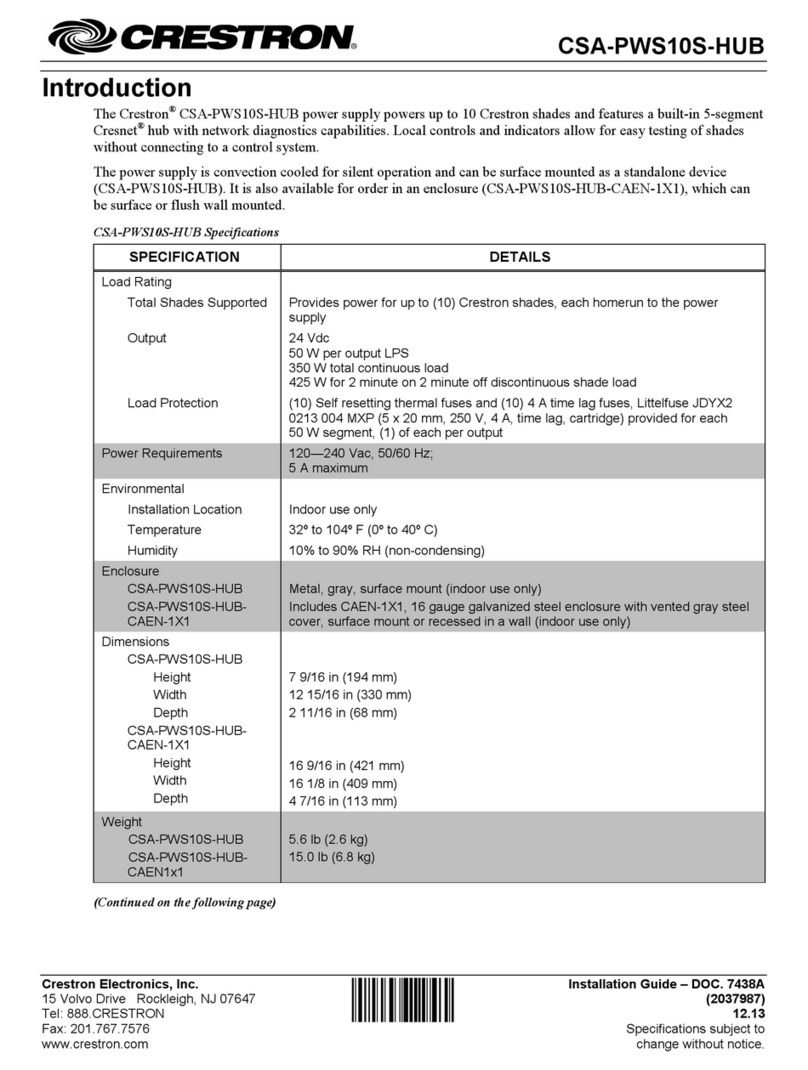
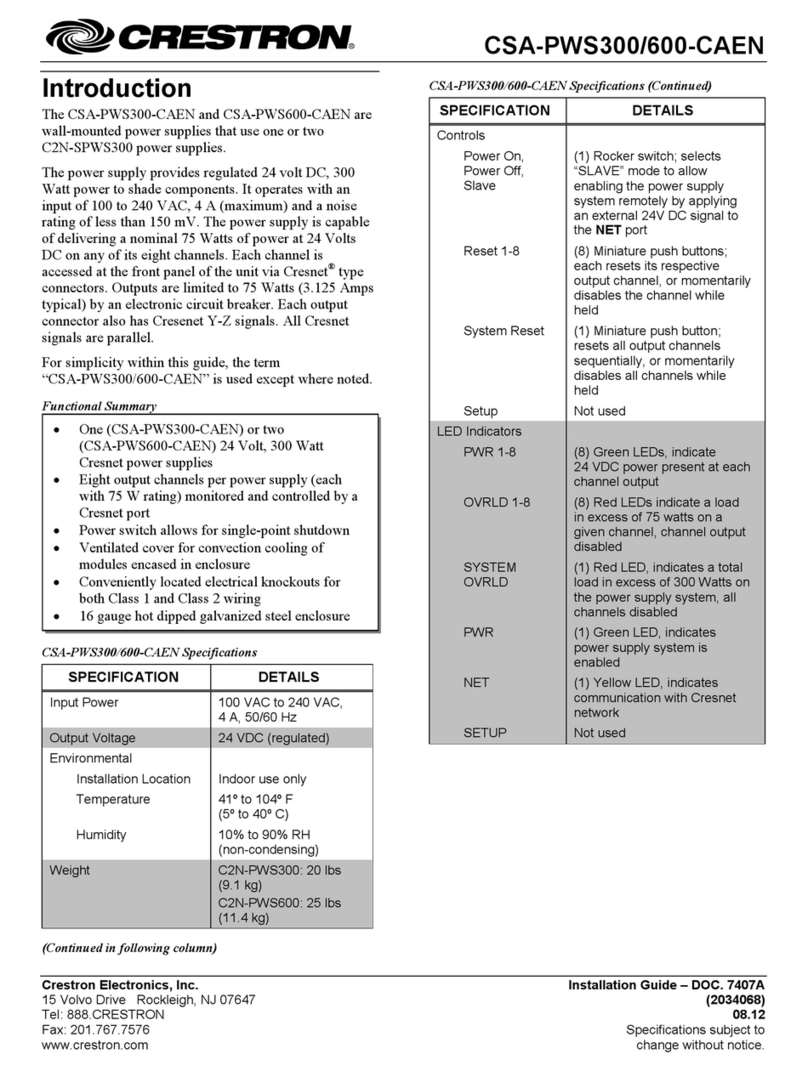
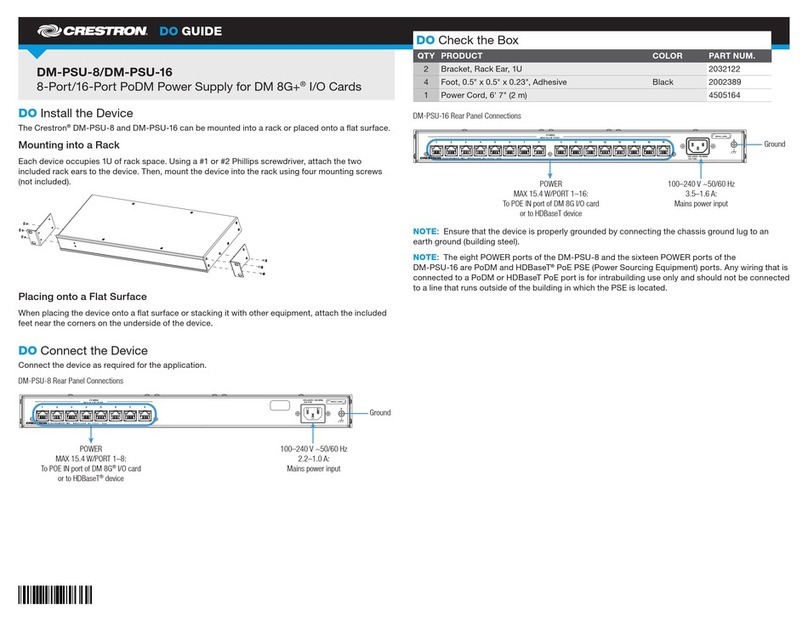
Crestron CNPWS-75 System Power Supply
Operations Guide - DOC. 8091A System Power Supply: CNPWS-75 •• 3
Setup
System Requirements
A CNPWS-75 is necessary to supply power to modular "card cage" control systems
(i.e., CNRACKX and CNRACKX-DP) via the central processing unit. An additional
CNPWS-75 may also be required in a Cresnet system managed by an integrated
control system (i.e., CNMSX) if the power requirements of the system components
are greater than the internal 75-watt power supply of the control system.
To determine the number of CNPWS-75s necessary to power all Cresnet components
in a particular Cresnet system, the total system power requirement must be
calculated. This is accomplished by adding the power requirements of all system
components. Refer to the leading specifications of each component for individual
power requirements. The total system power requirements should include the control
system, all cards in the control system, any expansion racks and associated cards,
and any network units. Once the total system power requirement is calculated, the
number of CNPWS-75s used should be selected such that their combined output
wattage meets or exceeds the total system power requirement.
Another important system factor to consider is the fact that a single network unit
cannot be powered by two different CNPWS-75s. In other words, one CNPWS-75,
which is not being used to its full capacity, cannot contribute its unused power to
'help' another CNPWS-75 power the network units connected to it. For example,
suppose a system consists of a CNRACKX (cards included) with a power
requirement of 20 watts and three wired panels, each with a power requirement of 20
watts. The total system power requirement is 80 watts. The first CNPWS-75 could
power the CNRACKX and two wired panels for a total of 60 watts. A second
CNPWS-75 could power the remaining wired panel for a total of 20 watts.
Network Wiring
NOTE: When making wire connections, refer to the latest revision of the Cresnet
Network Interconnect Drawing (Doc. 5411). The document can be obtained from the
Downloads page (CABLES and MANUAL Libraries) of the Crestron website
(www. crestron.com). Search for the CRESNET.PDF files.
When calculating the wire gauge for a particular network run, the length of the run
and the power requirement of each network unit to be connected must be taken into
consideration. If network units are to be daisy chained on the run, the load factor of
each network unit to be daisy chained must be added together to determine the load
factor of the entire chain. The length of the run in feet and the load factor of the run
should be used in the following resistance equation to calculate the value on the right
side of the equation.
Resistance Equation
R = Resistance (refer to table below).
L = Length of run (or chain) in feet.
LF = Load factor of entire run (or chain).
R < L x LF
40,000 Where:
The required wire gauge should be chosen such that the resistance value is less than
the value calculated in the resistance equation. Refer to the table after this paragraph.