Deif PPU 300 Quick start guide

DEIF A/S · Frisenborgvej 33 · DK-7800 Skive · Tel.: +45 9614 9614 · Fax: +45 9614 9615 · info@deif.com · www.deif.com
DEIF A/S · Frisenborgvej 33 · DK-7800 Skive · Tel.: +45 9614 9614 · Fax: +45 9614 9615 · info@deif.com · www.deif.com
DEIF A/S · Frisenborgvej 33 · DK-7800 Skive · Tel.: +45 9614 9614 · Fax: +45 9614 9615 · info@deif.com · www.deif.com
COMMISSIONING GUIDELINES
Paralleling and Protection Unit
PPU 300
Document no.: 4189341106B

1. Introduction
1.1 About the Commissioning guidelines......................................................................................................................................................................................6
1.1.1 General purpose.............................................................................................................................................................................................................................6
1.1.2 Intended users of the Commissioning guidelines.................................................................................................................................................. 6
1.1.3 Switchboard panel examples................................................................................................................................................................................................6
1.1.4 Software versions.......................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 8
1.1.5 Technical support...........................................................................................................................................................................................................................8
1.1.6 List of technical documentation for PPU 300............................................................................................................................................................8
1.2 Warnings and safety................................................................................................................................................................................................................................ 9
1.2.1 Safety during installation and operation ...................................................................................................................................................................... 9
1.2.2 Design, drawings and FAT test.........................................................................................................................................................................................10
1.2.3 Hot commissioning and retrofits...................................................................................................................................................................................... 10
1.2.4 Controller power supply..........................................................................................................................................................................................................11
1.2.5 Connect the controller protective earth.......................................................................................................................................................................11
1.2.6 Switchboard control...................................................................................................................................................................................................................11
1.2.7 Factory settings ...........................................................................................................................................................................................................................11
1.2.8 Remote-controlled starts........................................................................................................................................................................................................11
1.2.9 Electrostatic discharge ...........................................................................................................................................................................................................11
1.2.10 Do not manually override active alarm actions..................................................................................................................................................... 11
1.3 Legal information.....................................................................................................................................................................................................................................12
1.3.1 Third party equipment............................................................................................................................................................................................................. 12
1.3.2 Warranty............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................ 12
1.3.3 Open source software............................................................................................................................................................................................................. 12
1.3.4 Trademarks..................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 12
1.3.5 Copyright...........................................................................................................................................................................................................................................12
1.3.6 Disclaimer ....................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 13
2. Preparation for commissioning
2.1 Tools.................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 14
2.1.1 Tools required................................................................................................................................................................................................................................ 14
2.2 Software........................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 15
2.2.1 Downloading and installing PICUS................................................................................................................................................................................15
2.3 Information.................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 15
2.3.1 System drawings.........................................................................................................................................................................................................................15
2.3.2 IO setup and parameter configuration.........................................................................................................................................................................16
2.3.3 AC protections...............................................................................................................................................................................................................................16
2.3.4 Transformer information.........................................................................................................................................................................................................16
2.3.5 Breaker information...................................................................................................................................................................................................................16
2.3.6 Governor information............................................................................................................................................................................................................... 16
2.3.7 AVR information........................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 17
3. Controller checks
3.1 BEFORE connecting the controller power supply.....................................................................................................................................................18
3.1.1 Disable the breakers ...............................................................................................................................................................................................................18
3.1.2 Disable the engine start......................................................................................................................................................................................................... 18
3.1.3 Activate switchboard control...............................................................................................................................................................................................18
3.2 Checking each controller..................................................................................................................................................................................................................18
3.2.1 Connecting the controller power supply.....................................................................................................................................................................18
3.2.2 Checking the controller LEDs............................................................................................................................................................................................ 18
3.3 Ethernet communication...................................................................................................................................................................................................................19
3.3.1 Plug and play connections in the network................................................................................................................................................................19
PPU 300 Commissioning guidelines 4189341106 UK
www.deif.com
Page 2 of 75

3.3.2 Non-plug and play connections in the network.....................................................................................................................................................20
3.3.3 Configuring a switch (optional)......................................................................................................................................................................................... 20
3.3.4 Checking the Ethernet connections.............................................................................................................................................................................. 23
3.4 Checking each display unit............................................................................................................................................................................................................ 23
3.4.1 Display unit...................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 23
3.5 Firmware update.......................................................................................................................................................................................................................................25
3.5.1 Connecting to a controller with PICUS....................................................................................................................................................................... 25
3.5.2 Downloading firmware.............................................................................................................................................................................................................25
3.5.3 Installing controller firmware ............................................................................................................................................................................................. 26
3.5.4 Installing display unit firmware..........................................................................................................................................................................................27
3.6 Safety..................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................27
3.6.1 Checking the Emergency stop..........................................................................................................................................................................................27
3.6.2 Checking the protection parameters............................................................................................................................................................................ 28
3.6.3 Checking the parameters......................................................................................................................................................................................................29
4. System checks
4.1 Working through the alarms.......................................................................................................................................................................................................... 30
4.1.1 Using the controllers to check the system................................................................................................................................................................30
4.1.2 Testing the controller AC alarms..................................................................................................................................................................................... 30
5. Equipment checks
5.1 Genset................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................31
5.1.1 Important information...............................................................................................................................................................................................................31
5.1.2 Starting the engine for the first time..............................................................................................................................................................................31
5.1.3 Setting the governor................................................................................................................................................................................................................. 31
5.1.4 Setting the AVR............................................................................................................................................................................................................................ 32
5.1.5 Testing the switchboard GOV and AVR controls.................................................................................................................................................33
5.1.6 Testing the overspeed protection....................................................................................................................................................................................34
5.2 Breaker..............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................35
5.2.1 Checking the phase sequence......................................................................................................................................................................................... 35
5.2.2 Checking the voltage across the breaker when synchronised..................................................................................................................36
5.2.3 Checking breaker open and close wiring..................................................................................................................................................................38
5.3 Synchronisation and de-loading................................................................................................................................................................................................38
5.3.1 Checking synchronisation.................................................................................................................................................................................................... 38
5.3.2 Checking de-loading.................................................................................................................................................................................................................39
5.4 Droop.................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................. 39
5.4.1 Controller types............................................................................................................................................................................................................................ 39
5.4.2 Introduction to droop................................................................................................................................................................................................................ 39
5.4.3 Checking the system stability by running under switchboard control.................................................................................................. 40
5.4.4 Measuring speed droop......................................................................................................................................................................................................... 41
5.4.5 Adjusting speed droop............................................................................................................................................................................................................ 42
5.4.6 Measuring voltage droop.......................................................................................................................................................................................................42
5.4.7 Adjusting voltage droop..........................................................................................................................................................................................................44
6. Tune regulators
6.1 Introduction...................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................45
6.1.1 Controller types............................................................................................................................................................................................................................ 45
6.1.2 Introduction to regulation.......................................................................................................................................................................................................45
6.1.3 Optimum regulation...................................................................................................................................................................................................................46
PPU 300 Commissioning guidelines 4189341106 UK
www.deif.com Page 3 of 75

6.2 Relay-controlled regulators............................................................................................................................................................................................................47
6.2.1 Checking the control range................................................................................................................................................................................................. 47
6.2.2 Setting up relay-controlled regulators..........................................................................................................................................................................48
6.2.3 Tuning P regulators................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 48
6.3 Analogue-controlled regulators..................................................................................................................................................................................................50
6.3.1 Setting up analogue-controlled regulators............................................................................................................................................................... 50
6.3.2 External resistor for GOV/AVR......................................................................................................................................................................................... 50
6.3.3 Checking the control range................................................................................................................................................................................................. 50
6.3.4 Tuning PID regulators..............................................................................................................................................................................................................51
6.4 Tuning governor regulators............................................................................................................................................................................................................53
6.4.1 Tuning for frequency regulation....................................................................................................................................................................................... 53
6.4.2 Tuning for frequency synchronisation..........................................................................................................................................................................53
6.4.3 Tuning for phase synchronisation...................................................................................................................................................................................54
6.4.4 Tuning for power regulation................................................................................................................................................................................................ 54
6.4.5 Tuning for power load sharing...........................................................................................................................................................................................54
6.5 Tuning AVR regulators........................................................................................................................................................................................................................ 55
6.5.1 Tuning for voltage regulation..............................................................................................................................................................................................55
6.5.2 Tuning for reactive power regulation............................................................................................................................................................................ 55
6.5.3 Tuning for reactive power load sharing...................................................................................................................................................................... 56
7. System testing
7.1 GENSET controller................................................................................................................................................................................................................................. 57
7.1.1 Basic GENSET controller tests........................................................................................................................................................................................ 57
7.1.2 GENSET controller functions.............................................................................................................................................................................................58
7.2 SHAFT generator controller........................................................................................................................................................................................................... 59
7.2.1 Basic SHAFT generator controller tests.................................................................................................................................................................... 59
7.2.2 SHAFT generator controller functions.........................................................................................................................................................................60
7.3 SHORE connection controller...................................................................................................................................................................................................... 60
7.3.1 Basic SHORE connection controller tests................................................................................................................................................................60
7.3.2 SHORE connection controller functions.................................................................................................................................................................... 61
7.4 BUS TIE breaker controller............................................................................................................................................................................................................. 61
7.4.1 Basic BUS TIE breaker controller tests......................................................................................................................................................................61
7.4.2 BUS TIE breaker controller functions.......................................................................................................................................................................... 62
7.5 Customised functions and sequences.................................................................................................................................................................................62
7.5.1 Testing CustomLogic................................................................................................................................................................................................................62
7.6 PLC....................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 63
7.6.1 Testing the PLC............................................................................................................................................................................................................................63
7.7 Failure scenarios......................................................................................................................................................................................................................................63
7.7.1 Testing blackout close............................................................................................................................................................................................................. 63
8. Final commissioning actions
8.1 Update the documentation..............................................................................................................................................................................................................64
8.1.1 Backing up the controller information.......................................................................................................................................................................... 64
8.1.2 Finalising the operator's manual......................................................................................................................................................................................65
8.1.3 Finalising the commissioning report............................................................................................................................................................................. 65
8.1.4 Commissioning checklist.......................................................................................................................................................................................................65
9. Troubleshooting
9.1 Regulators......................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................67
9.1.1 Troubleshooting relay-controlled governors............................................................................................................................................................67
PPU 300 Commissioning guidelines 4189341106 UK
www.deif.com
Page 4 of 75

9.1.2 Troubleshooting analogue-controlled governors (mA signal).................................................................................................................... 68
9.2 Alarms................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................69
9.2.1 Troubleshooting alarms..........................................................................................................................................................................................................69
9.3 Terminals.........................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................69
9.3.1 Troubleshooting terminal damage..................................................................................................................................................................................69
9.3.2 Troubleshooting the MPU input........................................................................................................................................................................................69
10. Glossary
10.1 Terms and abbreviations...................................................................................................................................................................................................................70
10.1.1 Terms and abbreviations....................................................................................................................................................................................................... 70
10.2 Units.....................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................73
10.2.1 Units......................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................73
10.3 Symbols............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................75
10.3.1 Symbols for notes.......................................................................................................................................................................................................................75
10.3.2 Mathematical symbols.............................................................................................................................................................................................................75
PPU 300 Commissioning guidelines 4189341106 UK
www.deif.com Page 5 of 75

1. Introduction
1.1 About the Commissioning guidelines
1.1.1 General purpose
The commissioning guidelines provide information for a thorough, safe and effective commissioning of controller(s), within the
system.
DANGER!
Commissioning is the most risky period of operation. Commissioning errors can lead to personal injury or
death, or equipment damage. These guidelines cannot anticipate or include every possible commissioning
problem. Commissioning must therefore be done thoughtfully, systematically and carefully by qualified and
experienced personnel.
DANGER!
DEIF does not accept any responsibility for wiring errors.
DANGER!
The controllers interface to third party equipment. DEIF does not accept any responsibility for the operation
of third party equipment.
INFO
The commissioning guidelines provide information about checking third-party equipment, for example, the
switchboard wiring. This information is provided to help ensure a successful commissioning of the entire system.
However, DEIF does not accept any responsibility for the operation of third party equipment.
1.1.2 Intended users of the Commissioning guidelines
The commissioning guidelines are primarily for the person who commissions the controller.
DANGER!
To prevent personal injury and/or damage to equipment, you must read these Commissioning guidelines
before connecting the controller to a power supply.
The commissioning guidelines can be useful to the designers working with the controller during the design process.
Operators may find the commissioning guidelines useful for troubleshooting.
1.1.3 Switchboard panel examples
The PPU 300 can be used for a wide range of applications. As the example below shows, in addition to the controller display
unit, a complex application like a tanker's switchboard panel typically includes extra voltage, current, frequency and
synchronisation indicators, as well as manual operation buttons and switches. These indicators and switches are useful
during commissioning.
However, for example, a yacht switchboard panel might consist of only a controller display unit. The commissioning must be
adapted accordingly. There is no substitute for carefully thinking through each commissioning step, based on the actual
system.
PPU 300 Commissioning guidelines 4189341106 UK
www.deif.com
Page 6 of 75

Figure 1.1 Switchboard example for a controller in a complex application
Log on LogAlarm Live data
Configure Tools Info
A
200
0
400 600 1200 kW
0
-100
200
600
400
V
200
0
400 600 Hz
45
50
55
Figure 1.2 Switchboard example for controller in a simple application
Log on LogAlarm Live data
Configure Tools Info
PPU 300 Commissioning guidelines 4189341106 UK
www.deif.com Page 7 of 75

1.1.4 Software versions
The information in this document corresponds to the following software versions.
Table 1.1 Software versions
Software Details Version
PCM APPL Controller application 1.0.0.x
DU APPL Display unit application 1.0.5.x
PICUS PC software 1.0.3.x
1.1.5 Technical support
You can read about service and support options on the DEIF website, www.deif.com. You can also find contact details on the
DEIF website.
You have the following options if you need technical support:
• Help: The display unit includes context-sensitive help.
• Technical documentation: Download all the product technical documentation from the DEIF website:
www.deif.com/documentation
• Training: DEIF regularly offers training courses at the DEIF offices worldwide.
• Support: DEIF offers 24-hour support. See www.deif.com for contact details. There may be a DEIF subsidiary located near
you. You can also e-mail [email protected].
• Service: DEIF engineers can help with design, commissioning, operating and optimisation.
1.1.6 List of technical documentation for PPU 300
Document Contents
Data sheet
• System description and functions
• Controller applications, functions, hardware and protections
• Technical specifications
• Hardware modules, display unit, and accessories
• Ordering information
Quick start guide
• Mounting
• Connecting wiring
• PICUS (PC software)
◦ Download and install
◦ Controller configuration
• Display unit overview
PPU 300 Commissioning guidelines 4189341106 UK
www.deif.com
Page 8 of 75

Document Contents
Designer's handbook
• Principles
• General controller sequences, functions and protections
• GENSET controller
• Protections and alarms
• AC configuration and nominal settings
• Breaker and synchronisation
• Regulation
• Load sharing
• Hardware characteristics
• PICUS (including permissions)
• CustomLogic
• Modbus
Installation instructions
• Tools and materials
• Mounting
• Minimum wiring for the controller
• Wiring for hardware module terminals
• Wiring for controller functions
• Wiring communication
• Wiring the display unit
Commissioning guidelines
• Tools, software and information required
• Controller, system and equipment checks
• Regulator tuning
• System testing
• Troubleshooting
Operator's manual
• Controller equipment (push-buttons and LEDs)
• Operating the system
• Alarms and log
• Using the display unit
• Troubleshooting and maintenance
PICUS manual Using PICUS and CustomLogic
Modbus tables
• Modbus address list
◦ PLC addresses
◦ Corresponding controller functions
• Descriptions for function codes, function groups
1.2 Warnings and safety
1.2.1 Safety during installation and operation
Installing and operating the equipment may require work with dangerous currents and voltages. The installation must only be
carried out by authorised personnel who understand the risks involved in working with electrical equipment.
PPU 300 Commissioning guidelines 4189341106 UK
www.deif.com Page 9 of 75

DANGER!
Hazardous live currents and voltages. Do not touch any terminals, especially the AC measurement inputs
and the relay terminals. Touching the terminals could lead to injury or death.
1.2.2 Design, drawings and FAT test
These commissioning guidelines assume that all of these tasks are completed before the commissioning:
1. Control system design
• System single-line drawing created and broadcast to the controllers
• Controllers allocated and configured for their unique controller ID
• I/O configuration created and written to each controller
• Parameters created and written to each controller
• Optional: CustomLogic created and written to each controller
2. System and switchboard drawings completed
3. Factory acceptance test (FAT) completed
1.2.3 Hot commissioning and retrofits
These commissioning guidelines assume that the system is not live and that the system is new.
Hot commissioning
Hot commissioning is possible, that is, you can commission the controller(s) as part of a live system. However, in addition the
normal commissioning risks, the live system itself presents challenges and risks that must be anticipated and mitigated.
DANGER!
For a hot commissioning, qualified and experienced personnel must carefully consider the effect of each
commissioning step. Mistakes may cause death, personal injury, and/or damage to equipment.
Retrofits
Retrofits are possible, that is, you can use the controllers to replace the controllers in an existing system. This may involve
commissioning just one controller at a time, and/or hot commissioning. However, in addition the normal commissioning risks,
the existing system, and, in the case of hot commissioning, the live system, present challenges and risks that must be
anticipated and mitigated.
DANGER!
For retrofits, qualified and experienced personnel must carefully consider the effect of each commissioning
step. Mistakes may cause death, personal injury, and/or damage to equipment.
DANGER!
For hot commissioning and retrofits, good communication is essential. Respect all limitations from the
system owner or operator. Always check before touching or changing any existing wiring.
INFO
During a retrofit, you can use switchboard control and the switchboard GOV up, GOV down, AVR up and AVR down
controls to transfer the load to the first new controller as it is commissioned. Once two or more new controllers are
commissioned, you can use the load sharing parameters to transfer the load to the new controllers.
PPU 300 Commissioning guidelines 4189341106 UK
www.deif.com
Page 10 of 75

1.2.4 Controller power supply
If the controller has no power supply, it is OFF and does not provide any protection. The controller cannot enforce any trips,
shutdowns or latches when it is off. The controller does not provide any control or load sharing. All the controller relays de-
energise.
The controller must have a reliable power supply (including a backup power supply). In addition, the switchboard design must
ensure that the system is sufficiently protected if the controller power supply fails.
1.2.5 Connect the controller protective earth
You must ground the controller rack to create a protective earth.
DANGER!
Failure to ground the controller rack could lead to injury or death.
1.2.6 Switchboard control
Under Switchboard control, the operator controls and operates the equipment from the switchboard. When switchboard
control is activated:
• If an alarm situation arises, and the alarm action requires a trip and/or shutdown, then the controller trips the breaker and/or
shuts down the engine.
• The controller DOES NOT accept operator commands.
• The controller cannot and DOES NOT prevent any manual operator actions.
The switchboard design must therefore ensure that the system is sufficiently protected when the controller is under
switchboard control.
1.2.7 Factory settings
The controller is delivered pre-programmed from the factory with a set of default settings. These settings are based on typical
values and may not be correct for your system. You must therefore check all parameters before using the controller.
1.2.8 Remote-controlled starts
The gensets can be started by remote signals (for example, by using an Ethernet connection, or a digital input). A remote
start could lead to personal injury. The genset design, layout, and maintenance procedures must take this into account.
1.2.9 Electrostatic discharge
You must protect the equipment terminals from electrostatic discharge when not installed in a grounded rack. Electrostatic
discharge can damage the terminals.
1.2.10 Do not manually override active alarm actions
DANGER!
Do not use switchboard or manual control to override the alarm action of an active alarm.
PPU 300 Commissioning guidelines 4189341106 UK
www.deif.com Page 11 of 75

An alarm may be active because it is latched, or because the alarm condition is still present. If the alarm action is manually
overridden, a latched alarm does not do its alarm action again. In this situation, the latched alarm does not provide protection.
Latched Over-current alarm example
The controller trips a breaker because of over-current. The operator then manually (that is, not using the controller)
closes the breaker while the Over-current alarm is still latched.
If another over-current situation arises, the controller does not trip the breaker again. The controller regards the
original Over-current latched alarm as still active, and does not provide protection.
1.3 Legal information
1.3.1 Third party equipment
DEIF takes no responsibility for the installation or operation of any third party equipment, including the genset. Contact the
genset company if you have any doubt about how to install or operate the genset.
1.3.2 Warranty
CAUTION
The rack may only be opened to remove, replace, and/or add a hardware module. The procedure in the Installation
instructions must be followed. If the rack is opened for any other reason, and/or the procedure is not followed, then
the warranty is void.
CAUTION
If the display unit is opened, then the warranty is void.
1.3.3 Open source software
This product contains open source software licensed under, for example, the GNU General Public License (GNU GPL) and
GNU Lesser Public License (GNU LGPL). The source code for this software can be obtained by contacting DEIF at
[email protected]. DEIF reserves the right to charge for the cost of the service.
1.3.4 Trademarks
DEIF, power in control and the DEIF logo are trademarks of DEIF A/S.
Modbus is a registered trademark of Schneider Automation Inc.
Windows is a registered trademark of Microsoft Corporation in the United States and other countries.
All trademarks are the properties of their respective owners.
1.3.5 Copyright
© Copyright DEIF A/S 2017. All rights reserved.
PPU 300 Commissioning guidelines 4189341106 UK
www.deif.com
Page 12 of 75

1.3.6 Disclaimer
DEIF A/S reserves the right to change any of the contents of this document without prior notice.
The English version of this document always contains the most recent and up-to-date information about the product. DEIF
does not take responsibility for the accuracy of translations, and translations might not be updated at the same time as the
English document. If there is a discrepancy, the English version prevails.
PPU 300 Commissioning guidelines 4189341106 UK
www.deif.com Page 13 of 75

2. Preparation for commissioning
2.1 Tools
2.1.1 Tools required
The following tools are required for commissioning:
Tool Used to
Safety equipment Personal protection, according to local standards and requirements
Computer Run PICUS
Ethernet cable Connect the computer to the controller
PICUS
(The DEIF utility software)
• Draw the single-line drawing
• Configure the I/Os
• Configure the parameters
• Create CustomLogic
• Monitor operation (Live data and Supervision)
Bonjour
Network discovery of controllers on the DEIF network
INFO
Please refer to Apple's support page for Bonjour, regarding information and
downloading. http://www.apple.com/support/bonjour/
See the PICUS manual for the system requirements to run PICUS.
DEIF supporters and other commissioning technicians have found these tools useful during controller commissioning:
Tool Used to
Multimeter, with accessories and
spare batteries
Check wiring
Measure the duty cycle for MPU and PWM terminals
Phase sequence meter Check the phase sequence
Synchroscope Check the synchronisation
Process meter Provide a 25 mA current signal for testing analogue-controlled regulators and wiring
Mirror or camera Look into the areas above and below the rack
Torch (US: Flashlight) Look at Ethernet cable wiring
Wire stripper, pliers and cutters Change wiring
Trim cable ties
Screwdrivers
Change wiring
Swap hardware modules
See Preparing for the installation, Tools in the Installation instructions for more
information.
PPU 300 Commissioning guidelines 4189341106 UK
www.deif.com
Page 14 of 75

Tool Used to
Active load bank(s)*
Measure speed droop
Tune governors
Fully test generation capacity
Reactive load bank(s)*
Measure voltage droop
Tune AVRs
Fully test generation capacity
*Note: Load banks are optional. They are only required if the loads available during commissioning are small compared to the
generation capacity.
INFO
The controller's analogue output, to control the governor or AVR, can be selected to be either voltage or current.
You therefore do not need a set of resistors to convert a current output to a voltage output.
2.2 Software
2.2.1 Downloading and installing PICUS
Downloading PICUS
1. Visit: http://www.deif.com/software.
2. Scroll to Software download and choose Multi-line 300, PICUS ver. 1.x.x software.
3. Submit your email address to receive a download link.
4. Follow the link to download PICUS.
Installing PICUS
1. Launch the PICUS installer from your computer.
2. Follow the instructions in the installer program.
See the PICUS manual for further information on how to download and install PICUS.
CAUTION
You must install Bonjour, if you do not already have this installed on your computer. This service is used for the
network detection on the DEIF network. PICUS uses Bonjour to detect all controllers that are connected to the same
network. No additional configuration is required.
2.3 Information
2.3.1 System drawings
The following drawings must be available:
PPU 300 Commissioning guidelines 4189341106 UK
www.deif.com Page 15 of 75

Drawing Used to
Single-line diagram Set up or check the single-line diagram in PICUS
Detailed drawings Configure the inputs and outputs in PICUS
2.3.2 IO setup and parameter configuration
The following information must be available:
Information Used to
Analogue input and output characteristics* Check and/or configure the analogue inputs and outputs in PICUS
Functions specification Check and/or configure the parameters in PICUS
Optional: Logic specification Check and/or configure the CustomLogic in PICUS
*Note: For example, for an oil pressure sensor with a resistance output, you need the relationship between the resistance
output and the oil pressure.
2.3.3 AC protections
To avoid delays during commissioning, ensure that the list of protections for each controller is available, as required by the
class society and/or shipowner.
2.3.4 Transformer information
To avoid delays during commissioning, ensure that configuration information is available for each current transformer, voltage
transformer and step-up transformer in the system.
2.3.5 Breaker information
To avoid delays during commissioning, ensure that the manufacturer's information is available for each breaker that the
controllers will control. This information should include:
• The breaker type.
• Breaker characteristics, especially the breaker closing time. Other breaker characteristics are also useful, like the spring
loading time for a compact breaker.
2.3.6 Governor information
To avoid delays during commissioning, ensure that the manufacturer's information is available for each governor that the
controllers will regulate. This information should include:
• Instructions on setting the governor initial speed.
• Instructions on setting the governor control range.
• Governor characteristics. For example, for a relay controlled governor: The effect of the number of pulses and the pulse
length.
• The speed droop, and how to adjust it.
PPU 300 Commissioning guidelines 4189341106 UK
www.deif.com
Page 16 of 75

2.3.7 AVR information
To avoid delays during commissioning, ensure that the manufacturer's information is available for each AVR that the
controllers will regulate. This information should include:
• Instructions on setting the AVR initial voltage.
• Instructions on setting the AVR control range.
• AVR characteristics. For example, for a relay controlled AVR: The effect of the number of pulses and the pulse length.
• The voltage droop, and how to adjust it.
PPU 300 Commissioning guidelines 4189341106 UK
www.deif.com Page 17 of 75

3. Controller checks
3.1 BEFORE connecting the controller power supply
3.1.1 Disable the breakers
Disconnect or disable the breakers BEFORE connecting the controller power supply.
Do not enable the breakers until AFTER the wiring and controller operation are thoroughly tested.
DANGER!
Unintended breaker closing can cause deadly and/or dangerous situations.
3.1.2 Disable the engine start
Disconnect or disable or block the engine start (the crank, and, if present, the run coil) BEFORE connecting the controller
power supply.
Do not enable the engine start until AFTER the wiring and controller operation are thoroughly tested.
DANGER!
Unintended engine starts can cause deadly and/or dangerous situations.
3.1.3 Activate switchboard control
Activate switchboard control before connecting the controller power supply. This prevents unwanted controller actions before
the system is ready.
CAUTION
A combination of wiring and/or configuration errors can create a dangerous situation even under switchboard
control. Therefore, the breakers and engine start MUST also be disabled.
Activating and deactivating switchboard control
DEIF recommends that you put the controller under switchboard control at several points during commissioning. These are
called Activate switchboard control and Deactivate switchboard control respectively.
3.2 Checking each controller
3.2.1 Connecting the controller power supply
If the breakers and engine start are disabled, and switchboard control is activated, then you can connect the controller power
supply.
3.2.2 Checking the controller LEDs
When the controller is powered on, check that the controller the LEDs are as expected:
PPU 300 Commissioning guidelines 4189341106 UK
www.deif.com
Page 18 of 75
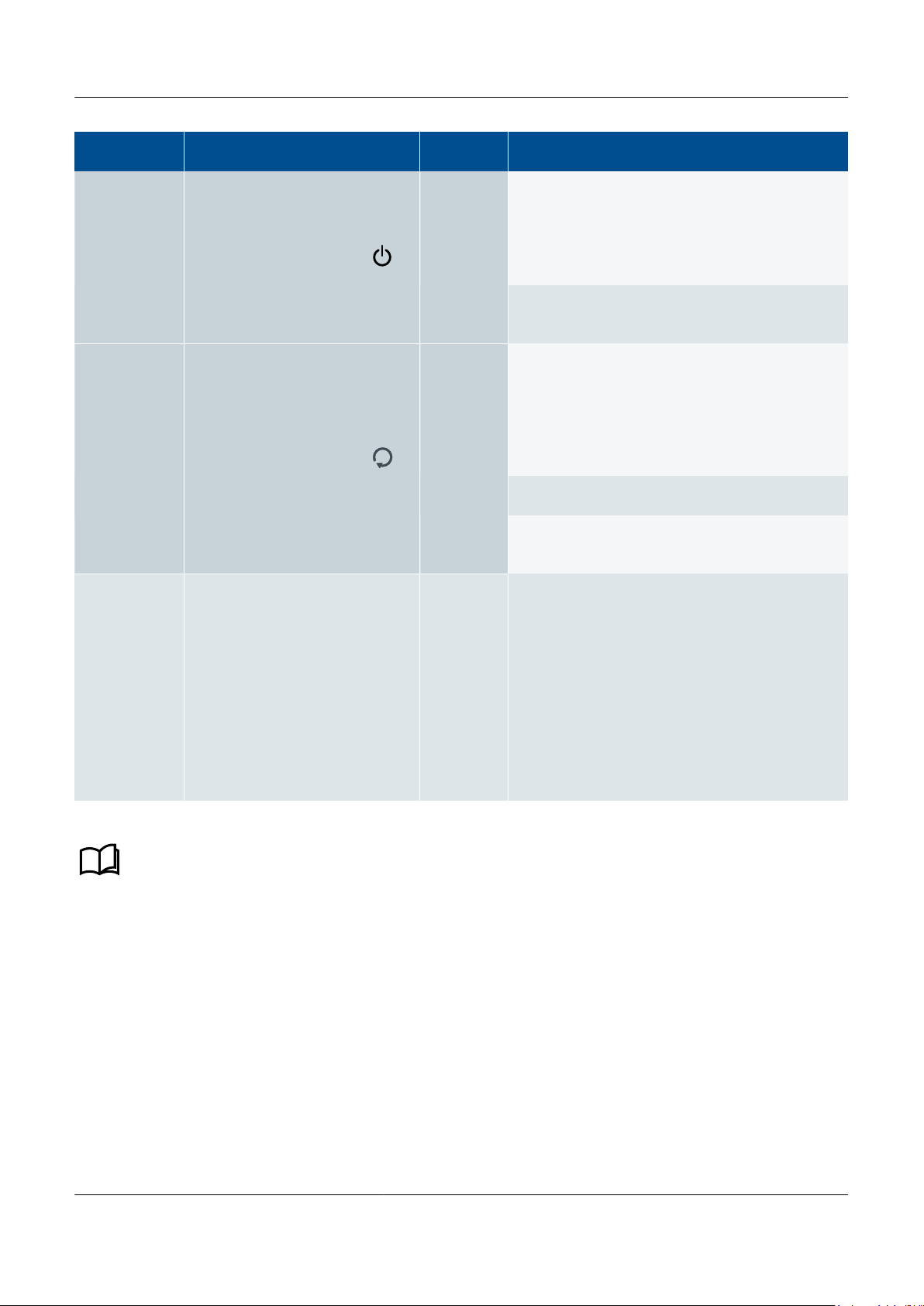
LED Location Expected
state Unexpected state and action
PSM3.1 Power On the front plate of PSM3.1 Green
Red
Wait for the self-check and/or software update to
complete.
If necessary, use the hardware module self-check
LEDs to find and replace the defective hardware
module(s).
Off
Check the controller power supply.
If necessary, replace the power supply module.
PCM3.1 Self-
check OK On the front plate of PCM3.1 Green
Red (flashing slowly)
One or more hardware module self-check is not OK.
Wait for the self-check and/or software update to
complete.
If necessary, use the hardware module self-check
LEDs to find and replace the defective hardware
module(s).
Green (flashing)
The software update has failed to apply correctly.
Off
There is no power from the rack's backplane.
If necessary, replace the rack and/or the PCM3.1.
Hardware
module self-
checks
At the top of the hardware modules,
inside the rack frame.
Do not check these LEDs unless
the PSM3.1 Power LED or the
PCM3.1 Self-check OK LED shows
that there is a defective hardware
module.
These LEDs may be hidden by
wiring, or invisible due to too much
ambient light.
Off
One or more LEDs are lit
Wait for the self-check and/or software update to
complete.
If necessary, replace the defective hardware
module(s).
See Controller equipment, Controller rack in the Operator's manual for more information.
3.3 Ethernet communication
3.3.1 Plug and play connections in the network
The network is plug and play for the following connections:
• Display unit connected to a controller.
• Controllers connected to each other (for example, in a line or a ring).
• Any controller connected to a computer running PICUS.
PPU 300 Commissioning guidelines 4189341106 UK
www.deif.com Page 19 of 75

• A single controller connected to a SCADA server.
• Modbus connected to a controller.
When the controller power is on, the controller automatically checks for other equipment on the network.
3.3.2 Non-plug and play connections in the network
The network supports non-plug and play equipment, if it has the correct configuration.
Non-plug and play connections include:
• Controllers that are connected using a switch to a SCADA server or AMS. A technician with network expertise must
configure the switch.
• Controllers with a redundant connection to a SCADA server or AMS.
See Hardware characteristics and configuration, DEIF Ethernet network in the Designer's handbook for
further information.
3.3.3 Configuring a switch (optional)
A switch can be used with the Ethernet connections to connect a third party system, for example, SCADA or AMS.
CAUTION
The switch must be marine-approved. The switch must also support (and be enabled for) Rapid Spanning Tree
Protocol (RSTP).
PPU 300 Commissioning guidelines 4189341106 UK
www.deif.com
Page 20 of 75
Other manuals for PPU 300
3
Table of contents
Other Deif Protection Device manuals