1
2019/01/22
Series Temperature Controller Instruction Sheet
Thank you very much for choosing Delta DTE series temperature controller. Please read this instruction sheet carefully before using your
DTE to ensure proper operation. Keep this instruction sheet handy for quick reference.
Warning
DANGER! CAUTION! ELECTRIC SHOCK!
DTE is an OPEN-TYPE device and therefore should be installed in an enclosure free of airborne dust, humidity, electric shock
and vibration. The enclosure should prevent non-maintenance staff from operating the device (e.g. key or specific tools are
required for opening the enclosure) in case danger and damage on the device may occur.
1. Prevent dust or metallic debris from falling into the device and cause malfunctions. DO NOT modify or uninstall the circuit board of DTE
without being permitted. DO NOT use empty terminals.
2. Keep away from high-voltage and high-frequency environment during the installation in case of interference. Prevent using the device in
premises which contain:
(a) dust or corrosive gas; (b) high humidity and high radiation; (c) shock and vibration.
3. The power has to be switched off when wiring or changing the temperature sensor.
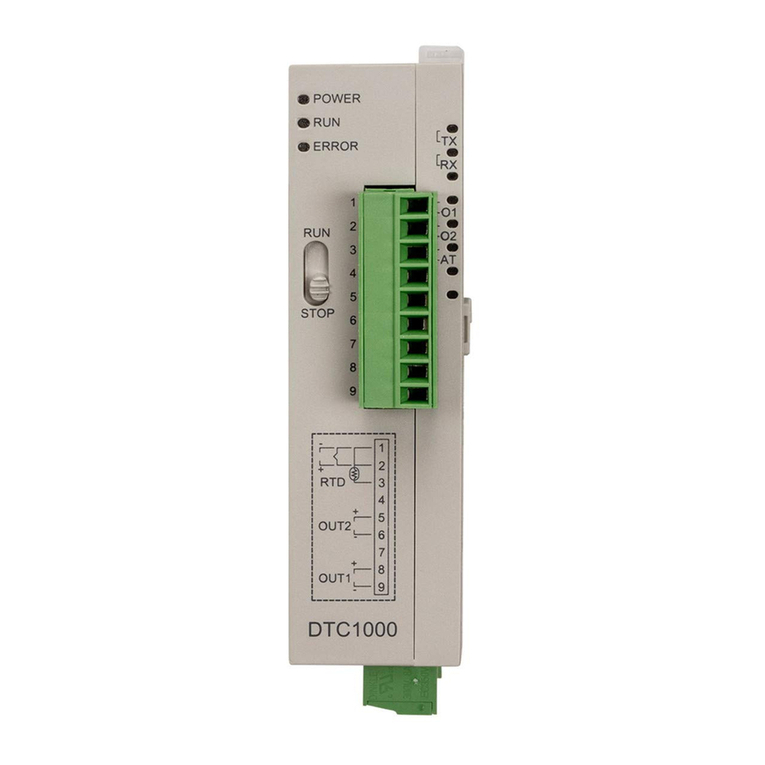
4. When installing the circuit board of the accessory, please make sure the power of the main unit is switched off and insert the accessory
into the correct slot on the main unit.
5. Make sure to use compensation wire which matches the thermocouple or platinum resistance when extending or connecting the
thermocouple or platinum resistance.
6. Keep the wire as short as possible when wiring a sensor to the controller. Separate the power cable and load wire in order to prevent
interference and induced noise.
7. Make sure the power cables and signal device are installed correctly before switching on the power; otherwise serious damage may
occur.
8. DO NOT touch the terminal or repair the device when the power is on; otherwise an electric shock may occur.
9. Please wait for 1 minute after the power is switched off to allow the capacitor to discharge and DO NOT touch the internal wiring within
this period.
10. DO NOT touch the internal terminal when DTE is either switched on or off in case you may damage the circuit.
11. Please place DTE with other heating objects (e.g. power supply) within proper distance while installing DTE.
Ordering Information
Series name DTE: Delta E series temperature controller
1 Device type 1: main unit 2: accessory
2 3 - 4 0T: 4-channel TC
0P: 3-channel PT
0T: 4 - channel TC
0P: 3 - channel PT
0V: 4 channels of voltage pulse output
0C: 4 channels of linear current output
0R: 4 channels of relay output
0L: 4 channels of linear voltage output
DS: Display and setup module
CT: 4 channels of current transformer sensors
0D: 8-channel EVENT input
Functions & Electrical Specifications
Power input 24 VDC, isolated switching power supply
Voltage range 90 to 110% rated voltage
Power consumption Max. 10 W + 3 W × number of DTC2000 controllers connected in parallel (Max. 7)
Input sensor Thermocouple: K, J, T, E, N, R, S, B, L, U, TXK
Platinum resistance: Pt100, JPt100, Cu50, Ni120
Sampling cycle Thermocouple or platinum resistance: 1.0 second/all input
Control method PID, PID programmable, manual, ON/OFF
Output accessories
(optional)
Relay output: SPST, Max. 250 VAC load, 3A resistive load
Voltage pulse output: 12 VDC, Max. 40 mA current output
Current output: DC 4 to 20 mA output (resistive load < 500 Ω); for OUT1 and OUT2 only