Model DM-100
Model DM-100 iii
Table of Contents
1. Introduction ..................................................................................................................................................1
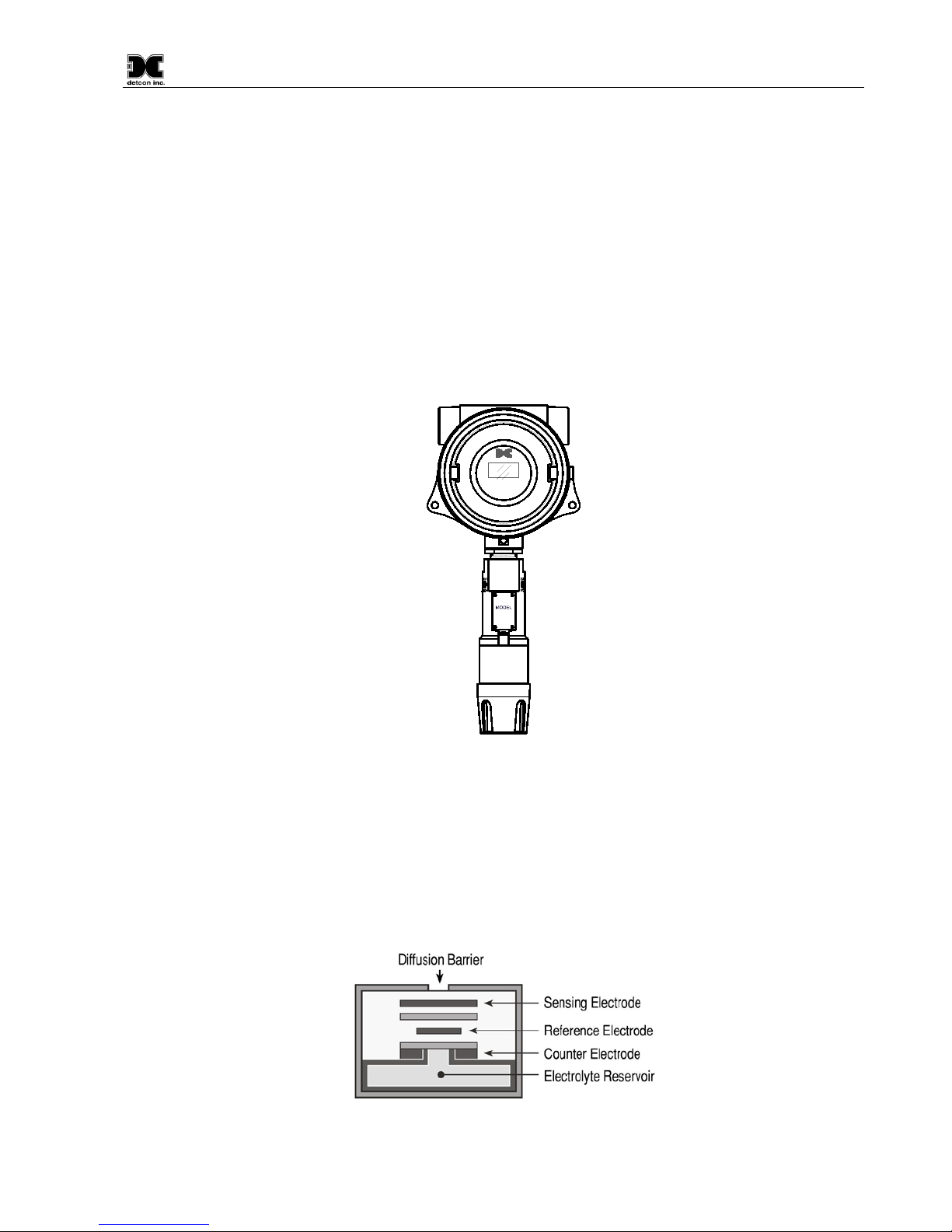
1.1 Description.......................................................................................................................................... 1
1.2 Modular Mechanical Design............................................................................................................... 2
1.3 Model 100 Standard Terminal Board (Optional)................................................................................ 4
1.4 DM-100 Display Terminal Board (Optional) ..................................................................................... 4
1.5 DM-100 Series Display (Optional)..................................................................................................... 5
1.6 Wireless Transceiver and Battery Pack (Optional)............................................................................. 5
2. Installation....................................................................................................................................................6
2.1 Hazardous Locations Installation Guidelines for Safe Use................................................................. 6
2.2 Sensor Placement................................................................................................................................ 7
2.3 Sensor Contaminants and Interference ............................................................................................... 8
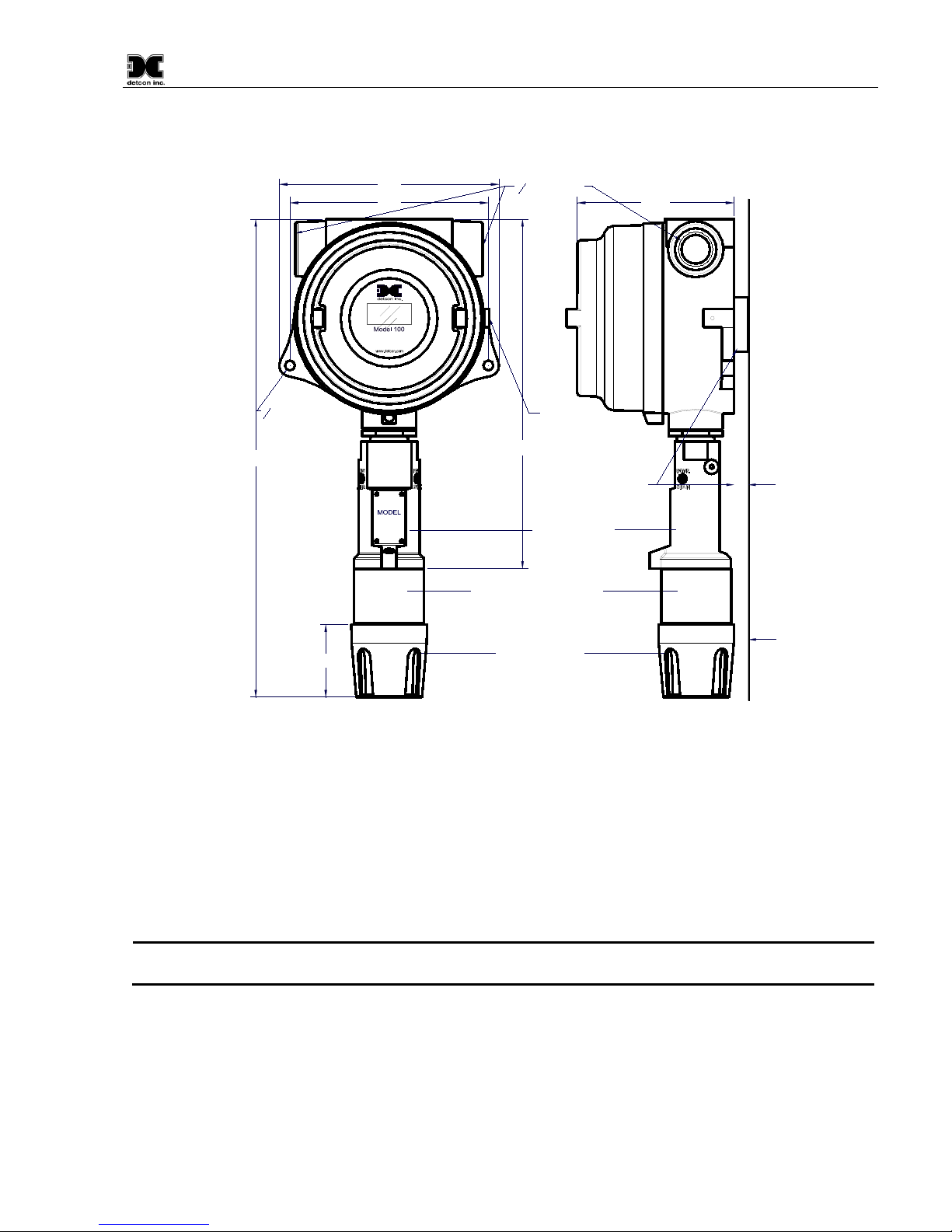
2.4 Sensor Mounting................................................................................................................................. 8
2.5 Electrical Installation.......................................................................................................................... 9
2.6 Field Wiring...................................................................................................................................... 10
2.6.1 DM-100 Display Terminal Board Settings................................................................................... 11
2.7 Initial Start Up................................................................................................................................... 11
2.7.1 Toxic Gas Sensors........................................................................................................................ 11
2.7.2 O2Deficiency Sensors.................................................................................................................. 13
3. Operation....................................................................................................................................................14
3.1 Normal Operation ............................................................................................................................. 14
3.2 Auto Span Level Adjustment............................................................................................................ 14
3.3 Calibration ........................................................................................................................................ 15
3.3.1 Zero Calibration............................................................................................................................ 15
3.3.2 Span Calibration........................................................................................................................... 17
3.4 Fault Diagnostic/Failsafe Feature ..................................................................................................... 19
4. Service and Maintenance............................................................................................................................20
4.1 Replacement of Plug-in Sensor......................................................................................................... 20
4.2 Replacement of ITM......................................................................................................................... 21
4.3 Replacement of the Model 100 Terminal Board............................................................................... 21
5. Troubleshooting Guide...............................................................................................................................23
5.1 Smart Display Error Codes............................................................................................................... 25
6. Customer Support and Service Policy........................................................................................................26
7. DM-100 Sensor Warranty ..........................................................................................................................27
8. Appendix ....................................................................................................................................................28
8.1 Specifications.................................................................................................................................... 28
8.2 Sensor Specific Data......................................................................................................................... 29
8.3 Interference Table............................................................................................................................. 31
8.4 Proper Application and Maintenance of Acrylonitrile Sensor.......................................................... 37
8.5 Intrinsically Safe Installation Guidelines, Control Drawing #3993.................................................. 38
8.6 Spare Parts, Sensor Accessories, Calibration Equipment................................................................. 39
8.7 Revision Log..................................................................................................................................... 40