Seametrics INW CT2X User manual

PROUDLY
MADE
IN THE
USA
C
e
r
t
i
f
i
e
d
C
o
m
p
a
n
y
ISO
9001:2008
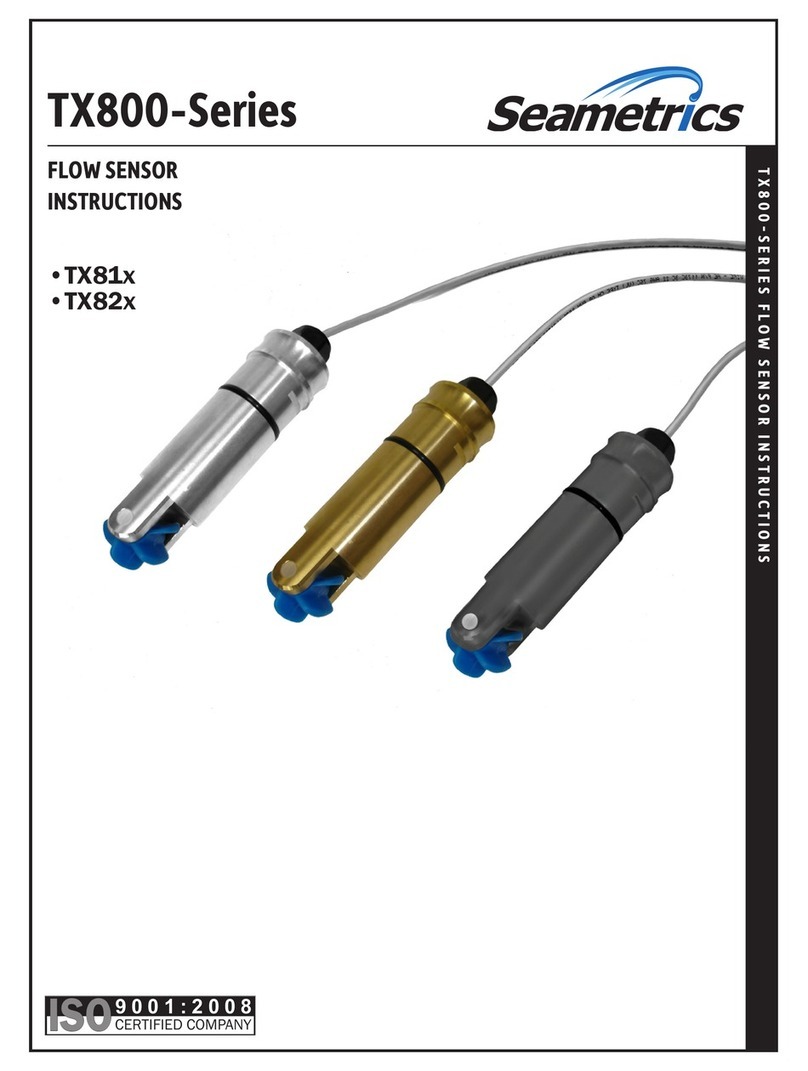
INW CT2X
Conductivity Smart Sensor
and Data Logger Instructions
For PSIG
sensors, refer
to page 21
regarding
desiccant
use!

CT2X INSTRUCTIONS
Seametrics • 253.872.0284 Page 2 inwusa.com

CT2X INSTRUCTIONS
Seametrics • 253.872.0284 Page 3 inwusa.com
General Information
General Information ...................................................................................................................................................Page 4
Dimensions ....................................................................................................................................................................Page 4
Specications ................................................................................................................................................................Page 5
Initial Inspection and Handling..............................................................................................................................Page 6
Do’s and Don’ts ............................................................................................................................................................Page 6
Installation
Connecting External Power......................................................................................................................................Page 7
Connecting a CT2X to a Computer.......................................................................................................................Page 7
Cable Wiring..................................................................................................................................................................Page 8
Installing Aqua4Plus or Aqua4Plus Lite Software ...........................................................................................Page 8
Using Without Aqua4Plus or Aqua4Plus Lite Software ................................................................................Page 9
Installing the Sensor...................................................................................................................................................Page 9
Desiccant Use................................................................................................................................................................Page 9
Grounding Issues.........................................................................................................................................................Page 9
Settings and Calibration
General Settings and Calibration Information .................................................................................................Page 10
Conductivity Channel.................................................................................................................................................Page 10
Pressure Channel .........................................................................................................................................................Page 12
Depth/Submergence........................................................................................................................................Page 13
Depth-to-Water..................................................................................................................................................Page 13
Elevation Above Sea Level..............................................................................................................................Page 14
Staff Gauge...........................................................................................................................................................Page 14
Operation
Collecting Data with Aqua4Plus and Aqua4Plus Lite ....................................................................................Page 15
Real Time Monitor.......................................................................................................................................................Page 15
Setting up Data Recording.......................................................................................................................................Page 15
Retrieving Data.............................................................................................................................................................Page 15
Viewing Data .................................................................................................................................................................Page 15
Exporting Data..............................................................................................................................................................Page 16
A Word about Units....................................................................................................................................................Page 16
Direct Read Modbus/SDI-12
Setting Units for Direct Read ..................................................................................................................................Page 16
Power Consideration..................................................................................................................................................Page 17
Reading via Modbus RTU.........................................................................................................................................Page 17
Reading via SDI-12......................................................................................................................................................Page 18
Maintenance
Desiccant Tubes............................................................................................................................................................Page 21
Removing Debris from End Cone..........................................................................................................................Page 21
Sensor/Cable/End Connections .............................................................................................................................Page 21
Changing Batteries......................................................................................................................................................Page 22
Troubleshooting
Problems/Probable Causes/Things to Try..........................................................................................................Page 25
TABLE OF CONTENTS
IF USING ALKALINE BATTERIES—PREVENT BATTERY LEAKAGE!
CT2X sensors are typically shipped with lithium batteries. If, however, you are
using alkaline batteries, be aware that under some circumstances alkaline
batteries can leak, causing damage to the sensor. To prevent leakage, the
following is recommended. (Does not apply to lithium batteries.)
• Change the batteries at least every 12 months.
• If the sensor will not be deployed for 3 months or more, remove the
batteries.

CT2X INSTRUCTIONS
Seametrics • 253.872.0284 Page 4 inwusa.com
GENERAL INFORMATION
The INW CT2X Smart Sensor is a microprocessor-based
submersible conductivity/temperature sensor with built-
in data logging. This device stores thousands of records
of conductivity, temperature, salinity, and total dissolved
solids (TDS). The CT2X is also available with a depth/level
option giving added functionality in the same sensor
housing.
The CT2X incorporates 4-pole electrode cell measurement
technology for conductivity, salinity, and TDS. This
technology reduces fringe eld interference errors,
lessens inaccuracy caused by polarization effects, and
lowers contact resistance problems. Four-pole electrode
technology also allows users to work with one electrode
over a wide range of conductivity. The conductivity element
is constructed of epoxy/graphite, making it extremely
durable for use in rugged eld conditions. To clean, simply
scrub with a small brush.
Depth and level is measured with an extremely rugged
and stable piezo-electric, media isolated pressure element
and compensated for temperature using INW’s proprietary
calibration methodology. Temperature is measured using a
borosilicate glass encapsulated thermistor.
The CT2X is powered internally with two AA batteries.
Alternately it can be powered with an external auxiliary
power supply for data intensive applications. Several
CT2Xs, or a combination of CT2Xs and other INW Smart
Sensors, can be networked together and controlled from
one location, either directly from a single computer or via
INW’s Wireless Data Collection System.
While most will use the CT2X with our free, easy-to-use
Aqua4Plus Lite or Aqua4Plus software, it is by no means
limited to that software. You can use your own Modbus®
RTU or SDI-12 software or logging equipment to read
measurements, thus tying into your existing systems and
data bases.
Dimensions
15.44” (39.2 cm)
11.64” (29.6 cm)
Diameter
0.75” (1.9 cm)
0.28” (0.7 cm)
0.28” (0.7 cm)
Cableless
0.25” (0.6 cm)
Shorter
Battery Version
Non-Battery Version
with Pressure:
1.5” (3.8 cm)
Longer
CT2X INSTRUCTIONS
Seametrics • 253.872.0284 Page 5 inwusa.com
Specications*
GENERAL INFORMATION
Housing & Cable Weight 1.0 lb (0.5 kg)
Body Material Acetal & 316 stainless or titanium
Wire Seal
Material Fluoropolymer and PTFE
Cable Submersible: polyurethane, polyethylene, or ETFE (4 lb/100 ft, 1.8 kg/30 m)
Desiccant 1-3 mm indicating silica gel
Field Connector Standard
Temperature Operating Range Recommended: -5˚ to 40˚C (23˚ to 104˚F) Requires freeze protection kit if using pressure option in water
below freezing.
Storage Range Without batteries: -40˚ to 80˚C (-40˚ to 176˚F)
Power Internal Battery Two lithium ‘AA’ batteries - Expected battery life: 12 months at 15 minute polling interval (may vary due
to environmental factors)
Auxiliary Nominal: 12 Vdc, Range: 9–16 Vdc
Communication RS485 Modbus® RTU (output = 32-bit IEEE oating point), SDI-12 (ver. 1.3) - ASCII
Logging Memory 4MB - 349,000 records
Logging Types Variable, user-dened, proled
Logging Rates 4x/sec maximum, no minimum
Baud Rates 9600, 19200, 38400
Software Complimentary Aqua4Plus and Aqua4Plus Lite
Networking 32 available addresses per junction (Address range: 1 to 255)
File Formats .a4d and .csv (also .xls in Windows 8 and earlier)
Output Channels Temperature Depth/Level¹ Conductivity
Element Borosilicate glass
encapsulated thermistor
30K ohm thermistor
Silicon strain gauge transducer
316 stainless or Hastelloy Epoxy/Graphite - 4-pole
Accuracy ±0.25˚C ±0.05% FSO (typical, static)
±0.1% FSO (maximum, static)
(B.F.S.L. 20˚C)
Static: ±0.5% of measured value
(0–100,000 µS/cm)
Resolution 0.1˚C 0.0034% FS (typical) (32 bit internal) 0.1 µS/cm, 0.001
mS/cm, 0.1 mg/L (TDS), 0.001 PSU
Units Celsius, Fahrenheit, Kelvin PSI, FtH₂O, inH₂O, mmH₂O, mH₂O,
inH₂O, cmHg, mmHg, Bars, Bars, kPa µS/cm, mS/cm, mg/L, PSU
Range -5˚ to 40˚C (23˚ to 104˚F) Gauge:
PSI: 1³, 5, 15, 30, 50, 100, 300
FtH₂O: 2.3³, 12, 35, 69, 115, 231, 692
mH₂O: 0.7³, 3.5, 10.5, 21, 35, 70, 210
Absolute4:
PSI: 30, 50, 100, 300
FtH₂O: 35, 81, 196, 658
mH₂O: 10, 24, 59, 200
Conductivity²: 0–300,000 µS/cm
TDS: 4.9-147,000 mg/L
Salinity: 2-42 PSU
Compensated --- 0˚ to 40˚C (32˚ to 104˚F) Thermal: None, Linear, or nLFn
Warmup Time --- --- 200 msec
Max operating pressure 1.1 x full scale
Over pressure protection 3x full scale up to 100psi—for > 300psi (650 ft or 200 m), contact Seametrics
Burst pressure 550 psi (approx. 2000 ft or 600 m)
Environmental IP68, NEMA 6P
*Specications subject to change. Please consult our web site for the most current data (inwusa.com).
Modbus is a registered trademark of Schneider Electric. Pyrex is a registered trademark of Corning Incorporated.
1 Higher pressure ranges available upon request
2 Accuracy reduced at levels <10 µS/cm and >100,000 µS/cm
3 ±0.25% accuracy FSO (max) at this range
4 Depth range for absolute sensors has 14.7 PSI subtracted to give actual depth allowed.
Table of contents
Other Seametrics Accessories manuals

Seametrics
Seametrics DO2 User manual

Seametrics
Seametrics IP800 Series User manual

Seametrics
Seametrics PT2X-BV User manual

Seametrics
Seametrics EX80 Series User manual

Seametrics
Seametrics PT2X User manual

Seametrics
Seametrics LevelSCOUT User manual

Seametrics
Seametrics INW LevelSCOUT User manual
Seametrics
Seametrics CT2X User manual

Seametrics
Seametrics TX81 Series User manual

Seametrics
Seametrics INW PT2X User manual