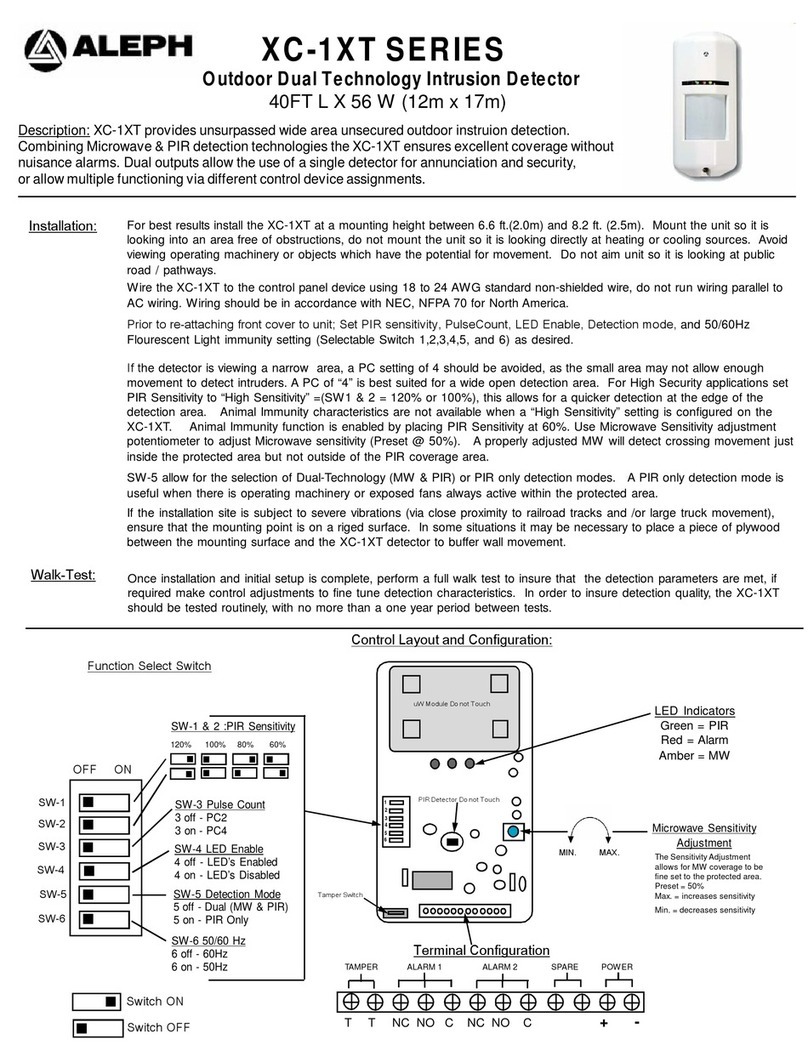
Combustible Gases Detector E2610-LEL ser Manual - Annex
Properties of gases
Acetylene
Synonyms/Trade Names: Ethine, Ethyne
Colorless flammable gas lighter that air. Mi tures with air are e plosive.
Results from the interaction of calcium carbide with water. In industrial production,
acetylene is mainly manufactured by the pyrolisis of light hydrocarbons.
Acetylene is widely used for welding and cutting of metals. The usage of acetylene
as a feedstock in chemical industry declines due to cost and environmental
considerations.
Chemical formula HC≡CH
Molar weight 26
Relative gas density (to air) 0.90
Conversion 1 ppm = 1.06 mg/m3
Boiling point -84 °C
Low e plosive limit (LEL), % vol in air 2.3* (2.5**)
Upper e plosive limit (UEL), % vol in air 100
Odour Odourless or with a faint ethereal
smell if pure. Commercial grade may
have garlic-like smell due to
impurities.
Hazards Highly flammable.
Gas/air mi tures are e plosive.
Forms e plosive acetylide
compounds with copper, mercury,
silver & brasses (containing more
than 66% copper).
Asphy iant. Non-to ic, but, when
generated from calcium carbide, it
can contain to ic impurities such as
traces of phosphine and arsine.
E posure limits (NIOSH) REL C 2662 mg/m3 /2500 ppm
Butane
Butane is colorless flammable gas heavier than air. The term “butane” is used for
any one of two structural isomers (n-butane or isobutane, with unbranched and
branched chain respectively) or for their mi ture.
Occurs in light petroleum fractions.
Butane is used mainly as a fuel and as a feedstock in organic synthesis. It is
applied also as a propellant in aerosol sprays and may be used as ozone-friendly
refrigerant.
Mi tures of butane with propane and other hydrocarbons are referred to as LPG
(liquefied petroleum gas).
Chemical formula n-butane iso-butane
CH3CH2CH2CH3 CH3CH(CH3)CH3
Molar weight 58
Relative gas density (to air) 2.0
Conversion 1 ppm = 2.38 mg/m3
Boiling point -0.56 °C −11.7 °C
Low e plosive limit (LEL), % vol in air 1.4* (1.6**) 1.5* (1.8**)
Upper e plosive limit (UEL), % vol in air 8.4 9.6
Odour gasoline-like odour
Hazards Highly flammable.
Inhalation of butane can cause
euphoria, drowsiness, narcosis,
asphy ia, cardiac arrhythmia,
fluctuations in blood pressure and
temporary memory loss, when abused
directly from a highly pressurised
container, and can result in death from
asphy iation and ventricular fibrillation.
E posure limits (NIOSH) TWA 1900 mg/m3
/800 ppm
not established
Hydrogen
Colorless, odorless flammable gas much lighter that air. Mi tures with air are
e plosive.
Results from the interaction of acids, bases and water with active metals and from
electrolysis of aqueous solutions. In industrial production, the main source of
hydrogen are hydrocarbons.
Chemical formula H2
Molar weight 2
Relative gas density (to air) 0.07
Conversion 1 ppm = 0.0818 mg/m3
Boiling point −252.88 °C
Low e plosive limit (LEL), % vol in air 4.0
Upper e plosive limit (UEL), % vol in air 75
Odour Odourless
Hazards Flammable, forms e plosive mi tures
with air.
Asphy iant.
E posure limits not established
Methane
Synonyms: Marsh Gas, Natural Gas, Carbon tetrahydride, Hydrogen carbide
Colourless flammable gas, main component of the natural gas, marsh gases.
Methane results from bacterial decomposition of plant and animal matter (landfill
gas).
Methane is widely used as a fuel and chemical feedstock.
Chemical formula CH4
Molar weight 16
Relative gas density (to air) 0.55
Conversion 1 ppm = 0.65 mg/m3
Boiling point −161.49 °C
Low e plosive limit (LEL), % vol in air 4.4* (5.0**)
Upper e plosive limit (UEL), % vol in air 15
Odour Odourless when pure. Methane used
in the kitchens contains odorant
Hazards Highly flammable, mi tures with air are
e plosive. Asphy iant.
E posure limits not established
Propane
Propane is colorless flammable gas heavier than air.
Occurs in light petroleum fractions.
Propane is used mainly as a fuel and as a feedstock in organic synthesis. It is
applied also as a propellant in aerosol sprays and may be used as ozone-friendly
refrigerant.
Mi tures of propane with butane and other hydrocarbons are referred to as LPG
(liquefied petroleum gas).
Chemical formula CH8CH2CH8
Molar weight 44
Relative gas density (to air) 1.55
Conversion 1 ppm =1.80 mg/m3
Boiling point −42 °C
Low e plosive limit (LEL), % vol in air 1.7* (2.1**)
Upper e plosive limit (UEL), % vol in air 9.5
Odour Odourless when pure. Commercially
available propane for fuel purposes
may contain odorant (“gas smell”).
Hazards Highly flammable, mi tures with air
are e plosive.
Asphy iant. May cause dizziness,
confusion, e citation when inhaled.
E posure limits
(NIOSH)
TWA 1800 mg/m3 /1000 ppm
IDLH 2100 ppm [10%LEL]
Terms and abbreviations
TWA: time-weighted average concentration for up to a 8-hour workday during a
40-hour workweek
STEL: 15-minute TWA e posure that should not be e ceeded at any time during a
workday
IDLH (immediately dangerous to life or health): likely to cause death or immediate
or delayed permanent adverse health effects or prevent escape from such an
environment
PEL: permissible e posure limits
REL recommended e posure limits.
A ceiling REL is designated by "C" preceding the value; unless noted otherwise,
the ceiling value should not be e ceeded at any time.
NIOSH (National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health): the United States
federal agency responsible for conducting research and making recommendations
for the prevention of work-related injury and illness.
NIOSH data are quoted in this manual where EU regulations are nor accessible.
Conversion of ppm to mg/m3 is calculated for 25°C and 1 atm.
* according to new E standards ('stirred' concentration of gas)
** according to S standard (‘still gas’ method)