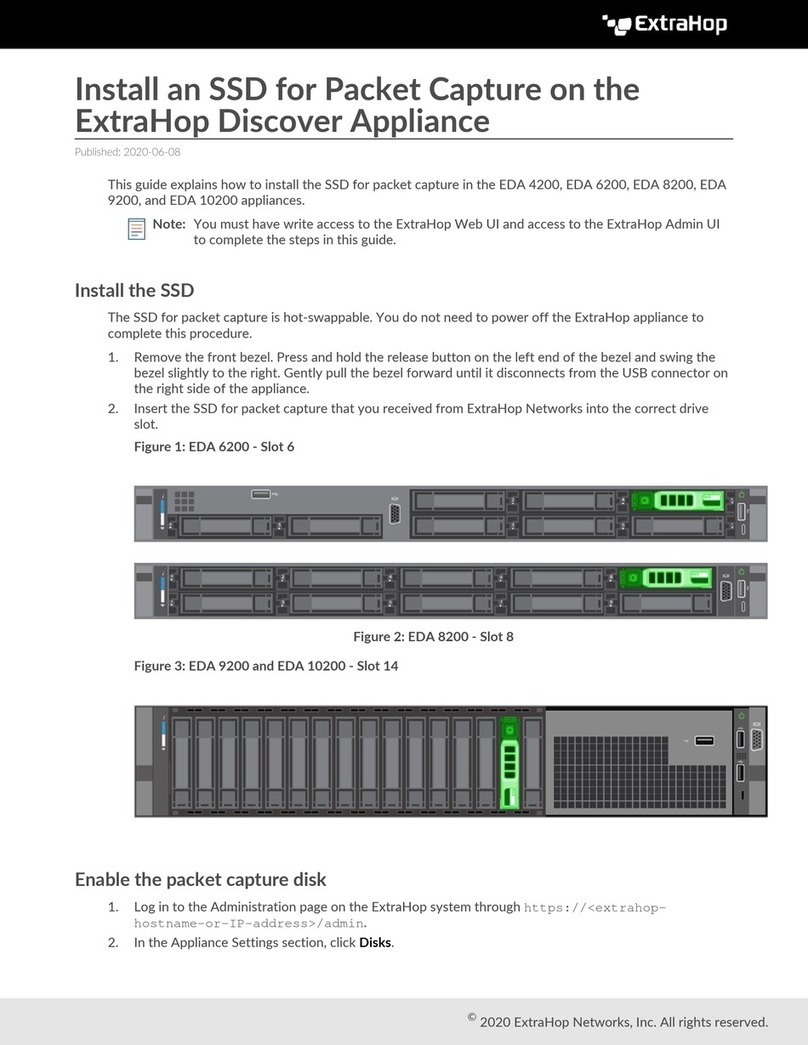
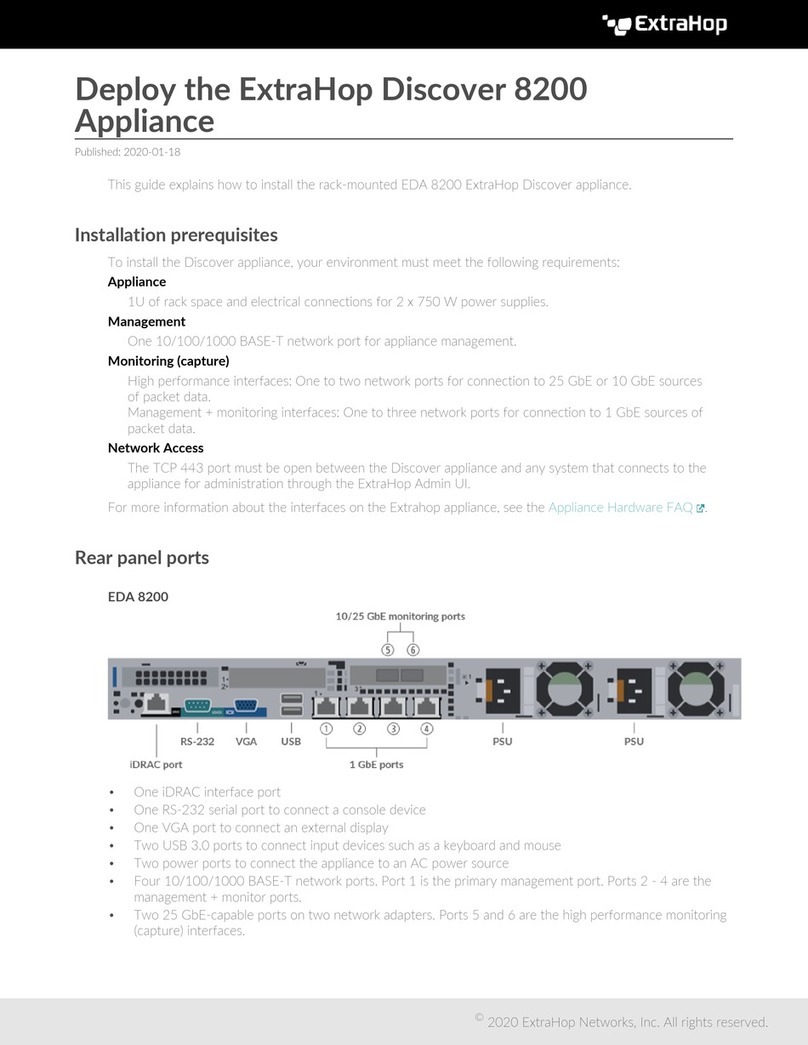
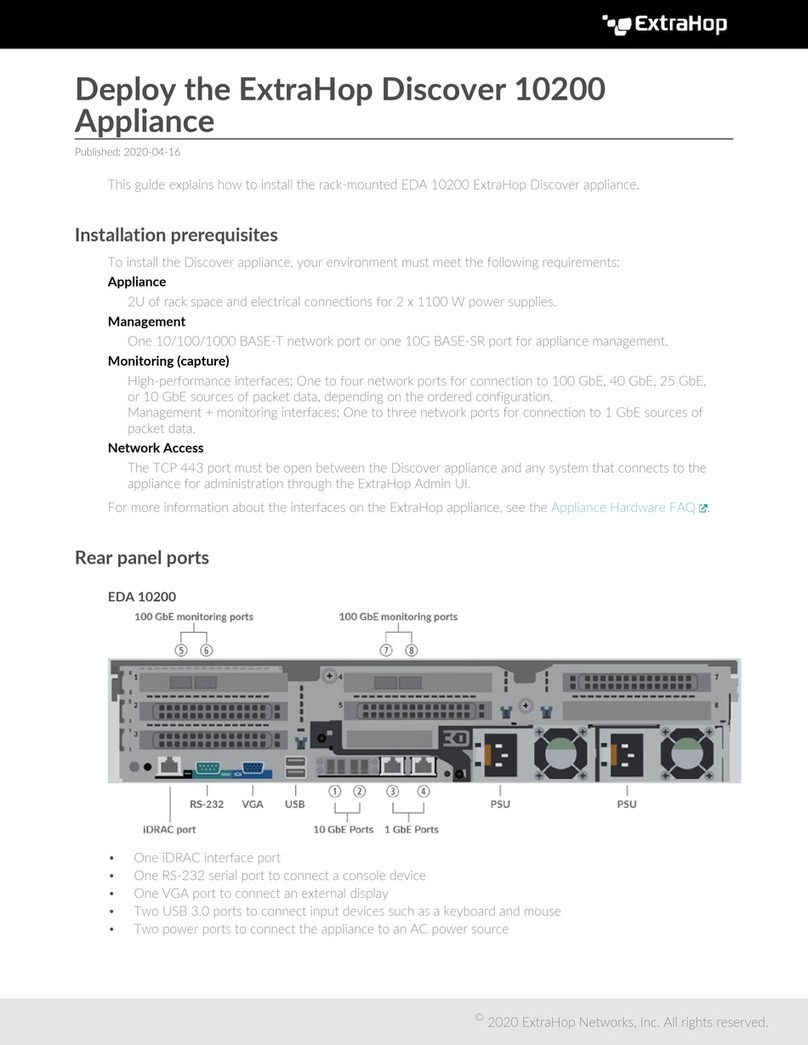
ExtraHop 8.8 ExtraHop Trace Admin UI Guide 10
Network Settings
The Network Settings section provides the following configurable network connectivity settings.
Connectivity
Configure network connections.
SSL Certificate
Generate and upload a self-signed certificate.
Notifications
Set up alert notifications through email and SNMP traps.
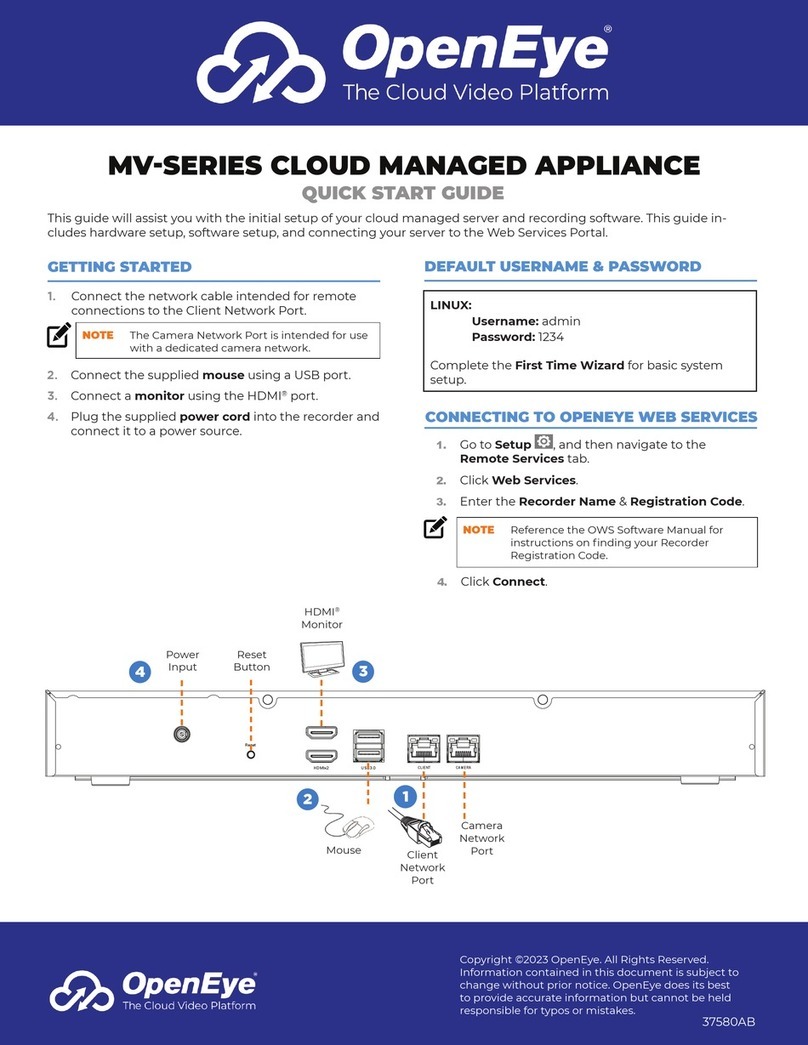
The Trace appliance has two 10/100/1000baseT network ports and four 10 GbE SFP+ network ports. By
default, the Gb3 port is configured as the management port and requires an IP address. Port 5 is the default
monitor (or capture) interface.
Before you begin configuring the network settings, verify that a network patch cable connects the
Gb3 port on the Trace appliance to the management network. For more information about installing a
Trace appliance, see the ExtraHop Trace appliance deployment guide or contact ExtraHop Support for
assistance.
For specifications, installation guides, and more information about your appliance, see the complete
ExtraHop documentation set at docs.extrahop.com .
Connect to ExtraHop Cloud Services
ExtraHop Cloud Services provides access to ExtraHop cloud-based services through an encrypted
connection. The services you are connected to are determined by your system license.
After the connection is established, information about the available services appear on the ExtraHop Cloud
Services page.
• ExtraHop Machine Learning Service enables detections for your ExtraHop system. In Reveal(x)
Enterprise, you can enable security-only or security and performance detections. In addition, you can
allow the ExtraHop Machine Learning Service to access pre-filtered, plaintext external IP addresses as
well as plaintext domains and hostnames. These settings enable the system to identify new categories
of detections and improve the accuracy of existing detections. See the Collective Threat Analysis FAQ
for more information.
• ExtraHop Update Service enables automatic updates of resources to the ExtraHop system, such as
ransomware packages.
• ExtraHop Remote Access enables you to allow ExtraHop account team members, ExtraHop Atlas
analysts, and ExtraHop Support to connect to your ExtraHop system for configuration help. If you have
signed up for the Atlas Remote Analysis service, ExtraHop analysts can perform an unbiased analysis of
your network data and report on areas in your IT infrastructure where improvements can be made. See
the Remote Access FAQ for more information about remote access users.
Before you begin
• Reveal(x) 360 systems are automatically connected to ExtraHop Cloud Services, however, you might
need to allow access through network firewalls.
• You must apply the relevant license on the ExtraHop system before you can connect to ExtraHop
Cloud Services. See the License FAQ for more information.
• You must have unlimited privileges to access Administration settings.
1. Log in to the Administration settings on the ExtraHop system through https://<extrahop-
hostname-or-IP-address>/admin.
2. In the Network Settings section, click ExtraHop Cloud Services.