GE SAM201 User manual
Other GE Relay manuals
Popular Relay manuals by other brands

CD Automation
CD Automation REVEX 2PH 280A user manual

ABB
ABB SPAJ 142 C User manual and technical description

Ruelco
Ruelco 1S04 Operation manual

Basler
Basler V3E Z1P B2C1F instruction manual

Doepke
Doepke Dupline DSM 2 operating instructions
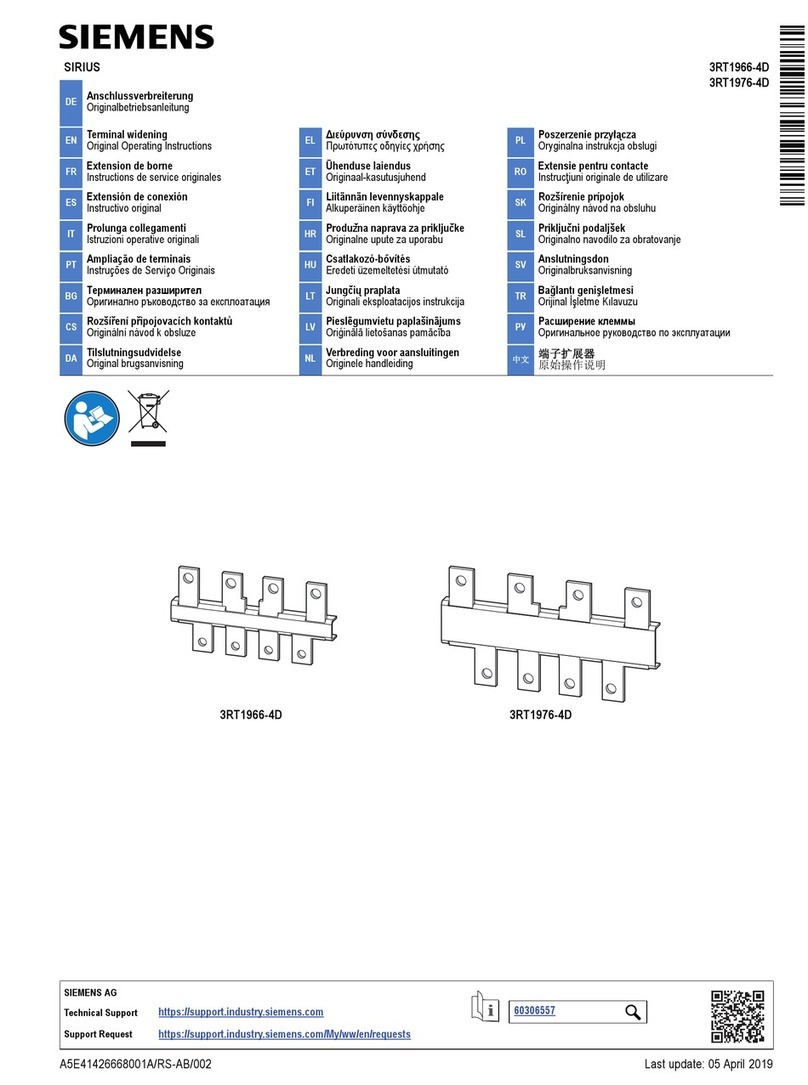
Siemens
Siemens SIRIUS 3RT1966-4D Original operating instructions