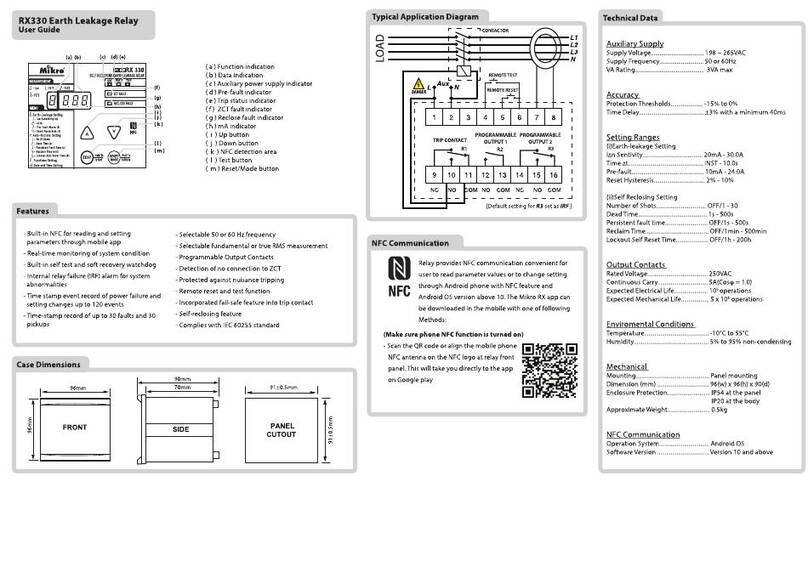
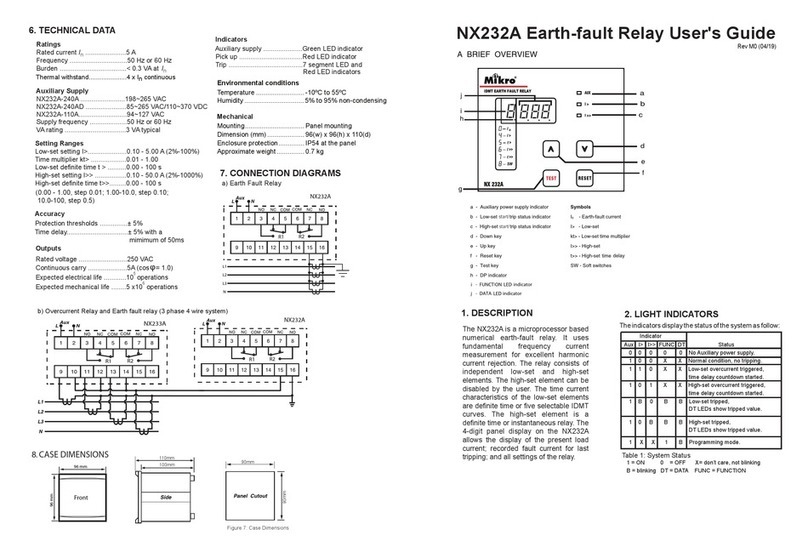
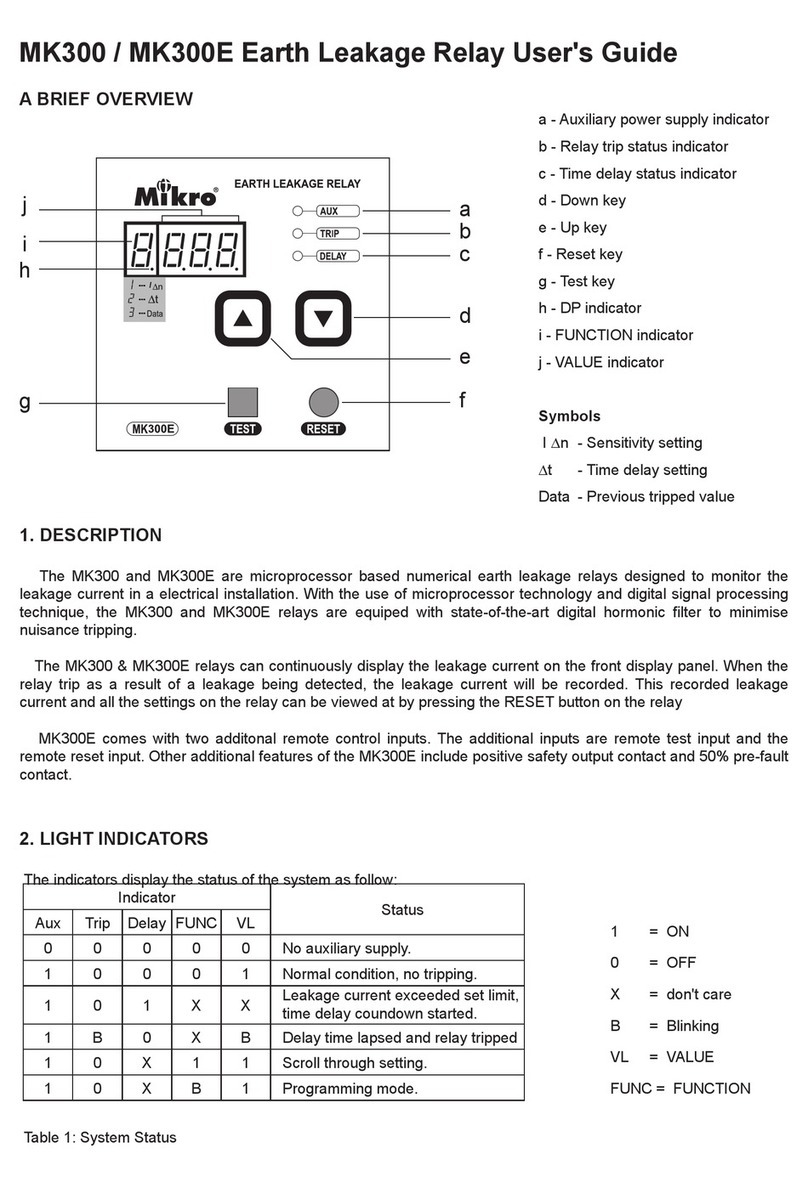
Mikro MPR500 User manual

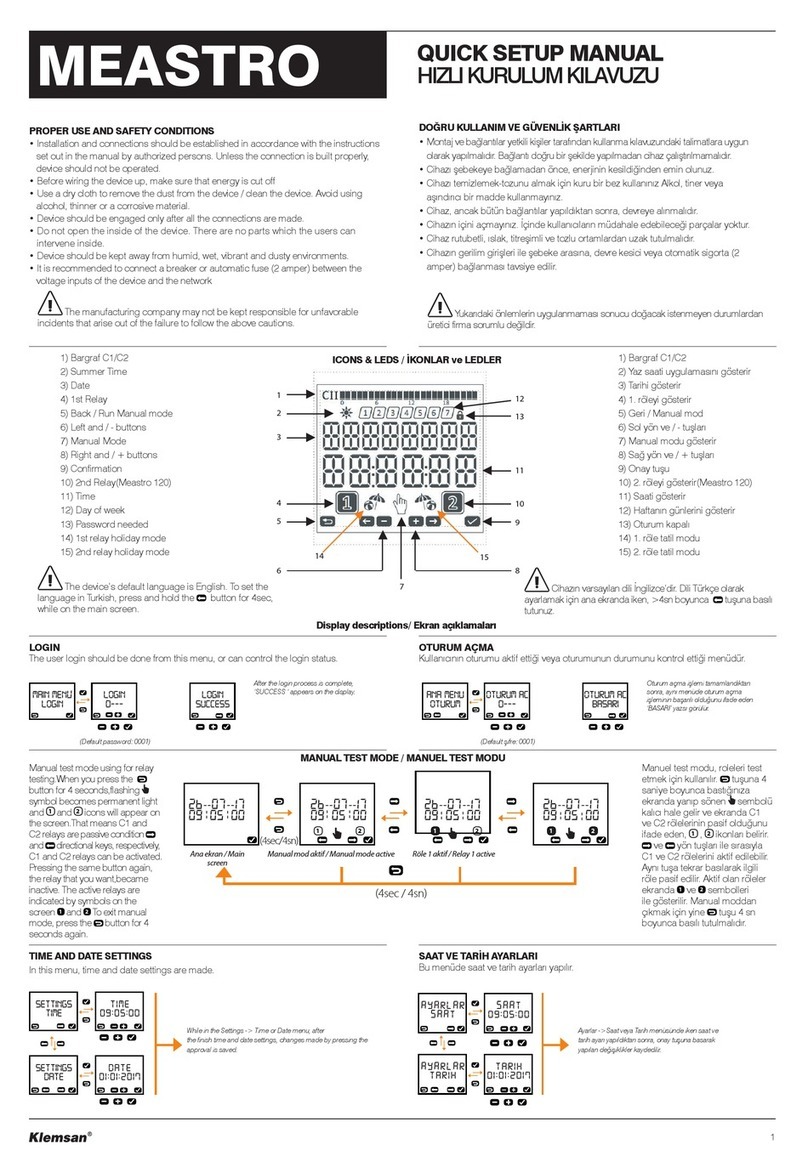
MPR500 Motor Protection Relay User's Guide
Brief Overview
a
b
c
d
e
f
g
h
a – Run LED
b – Trip/Pickup LED
c – Thermal LED
d – Down key
e – Up key
f – Reset/Mode key
g – Test key
h – Data LED
i – Function LED
1. General Description
MPR500 is a motor protection relay that combines
thermal overload, short circuit, undercurrent, unbalance,
phase loss, phase sequence, lock/stall rotor and earth
fault protections.
MPR500 incorporates a 4-digit LED indicator which
allows direct numerical readout of set values, actual
measured value and system indication.
MPR500 has 2 relay outputs (R1 and R2). R1 is On
under normal operating condition to allow motor running,
and off during tripping. R2 is programmable to give signal
in various conditions.
A programmable binary input is provided to perform
various operations upon binary input triggering.
2. Display
2.1 Current and Thermal Capacity Display
During power up, when the relay is not under tripping
condition, the display shows current in ampere or
thermal capacity %. The Function LED indicates which
parameter is being displayed. The Data LED showing
value.
Press “UP” or “DOWN” to scroll through the parameters.
1
Motor
Protection
Relay
t
>>
I
<<
t
<<
t
6X
t
Start
I
o
>>
t
o
>>
CT
t
Stall
I
B
t
SW
I
>>
I
S
>>
i
Symbols
t6X – Thermal overload time constant
I>> – Short circuit/High set Overcurrent
t>> – Short circuit/High set Overcurrent
delay time
I< – Undercurrent
t< – Undercurrent delay time
– Unbalance
t – Unbalance delay time
I0> – Earth fault
t0> – Earth fault delay time
IS>> – Prolonged starting/stall rotor
tStart – Prolonged starting delay time
tStall – Stall rotor delay time
IB – Base/full load current
CT – External current transformer ratio
SW – Soft switch
IL1
IL2
IL3
I0
Thermal
Figure 1: Front panel overview
Figure 2: Current and thermal capacity display
For current more than 1000A, a dot is shown behind
least significant digit. Eg: 1.25. = 1.25kA
IL1 - Phase 1 current
IL2 - Phase 2 current
IL3 - Phase 3 current
I0- Zero sequence/Earth fault current
Thermal % - Thermal capacity % (Thermal overload trip-
ping at 100%)
During Thermal capacity display, thermal capacity can be
cleared to 0% by pressing "UP" and "DOWN" simultane-
ously for longer than 1.5 seconds.
Warning: Clearing thermal capacity effectively reset
to cold start condition, user is not encouraged to
clear thermal capacity unless it is sure that motor is
cool enough to run/start within its thermal limit.
V1.3

2.2 Auto Scroll
When auto scroll is enabled, the display scrolls between
currents and thermal reading every 10 seconds. To
toggle auto scroll mode, press "UP" and "DOWN"
simultaneously.
2.3 LED Display
a) Run LED
Run LED shows the motor status. Refer to 3.2.1 Motor
Starting.
2
Off
Motor stopping
Blink
Motor starting
On
Motor running
b) Trip LED
Trip LED is normally off. During tripping pickup, where
tripping delay is counting down, Trip LED blinks. Trip
LED on during tripping.
Off
Normal
Blink
Pickup
On
Tripping
c) Thermal LED
Thermal LED blinks when motor current is more than
105% of IB. Thermal LED on during thermal overload
tripping, and when thermal capacity is more than 40%
after overload tripping (in which R1 is off, motor not
allowed to start)
Off
Normal
Blink
Thermal overload warning
On Thermal overload tripping
3. Settings and Protection Features
3.1 Setting Display
When the relay is not under tripping condition, pressing
"RESET/MODE" will scroll through various settings.
Function LED showing number or alphabet to indicate
which setting is being view as shown in Figure 3. Table 1
gives description of each setting.
Tip: To quickly jump back to current/thermal display
during setting display, press and hold "RESET/MODE"
for 1.5 second.
1 t6X Thermal overload time constant
Current/Thermal Display
3 t>> Short circuit delay time
4 I<< Undercurrent
5 t<< Undercurrent delay time
2 I>> Short circuit
b t Start >> Prolonged starting delay
time
7 t Unbalance delay
time
A IS>> Prolonged starting / stalled rotor
8 I0>> Earth fault
6 Unbalance
9 t0>> Earth fault delay time
Tripping History
c t >> Stalled rotor delay
time
d IB
Base/full load current
E External CT ratio
F1 Auto/Manual Reset
F2 Binary input
F3 Relay 2 function
Stall
Figure 3: Display mode when pressing
Reset/Mode
F4 Phase Sequence/ Phase Loss option
F5 Frequency
Thermal LED will on if after thermal trip and user press reset but thermal % still > 40%
Thermal capacity high, R1 off

3.2 Programming Setting
Step 1: Press "RESET/MODE" until the Function LED shows the required setting.
Step 2: Press "UP" and "DOWN" simultaneously toenter programming mode.
The Function LED blinks to indicate the relay is in programming mode.
Step 3: Press "UP" or "DOWN" to change the value.
Step 4: To save the new value, press "UP" and "DOWN" simultaneously again. Programming mode exits,
function LED stop blinking.
To exit programming mode without saving, press "RESET/MODE" once
3
Setting
Function
Setting Range
Description
1
t6X Thermal overload
time constant
1-40s. In steps of 0.1s
for 1-10s, in steps of
1s for 10-40s.
Time constant for thermal overload
2
I>> Short circuit
off, 2-12 x IB. In steps
of 1 x IB
Short circuit setting in multiples of IB
3
t>> Short circuit delay
time
0-25s. In steps of 0.1s
for 0-10s, in steps of
1s for 10-25s
Delay time for short circuit
4
I<< Undercurrent
off, 20-90% of IB. In
steps of 1%
Undercurrent setting in % of IB
5
t<< Undercurrent delay
time
0-60s. In steps of 0.1s
for 0-10s, in steps of
1s in 10-60s.
Delay time for undercurrent
6
Unbalance
off, 10-50%. In steps
of 1%
Phase unbalance setting in %
7
t Unbalance delay
time
0-25s. In steps of 0.1s
for 0-10s, in steps of
1s for 10-25s.
Delay time for phase unbalance
8
I0>> Earth fault
off, 10-60% of IB. In
steps of 1%
Earth fault setting in % of IB
9
t0>> Earth fault delay
time
0-25s. In steps of 0.1s
for 0-10s, in steps of
1s for 10-25s.
Delay time for earth fault
A
IS>> Prolonged starting
/stalled rotor
off, 2-12 x IB. In steps
of 0.1 x IB
Prolonged starting/stalled rotor setting in
multiples of IB
b
tStart >> Prolonged
starting delay
time
0-60s. In steps of 0.1s
for 0-10s, in steps of
1s for 10-60s.
Delay time for prolonged starting
c
tStall>> Stalled rotor
delay time
0-60s. In steps of 0.1s
for 0-10s, in steps of
1s for 10-60s.
Delay time for stalled rotor
d
IBBase/full load current
2-10A
Base/full load current of motor
E
1-800:1
External CT ratio. 1=direct.
F1
Auto/Manual Reset
0 - Manual reset
1- Auto reset
Manual or auto reset of tripping
Thermal overload is always auto reset
F2
Binary input
0 - Block relay 1
1 - Reset tripping
2 - Instant tripping
Setting for binary input
F3
Relay 2 function
0 - On any tripping
1 - On thermal tripping
2 - On thermal
warning
Relay 2 function
Table 1: Description of settings
External CT ratio
F4 Phase sequence (PS)/
phase loss (PL) option
0 - PS and PL off
1 - PS on
2 - PL on
3 - PL and PS on
Phase sequence and phase loss option
F5 Frequency 50 or 60Hz Nominal value of network frequency

3.2.1 Motor Status
Run LED shows the motor status. Upon power on the
relay, if there is no tripping, Relay 1 turns on.
If motor current is more than 1.1 x IB, motor is
considered starting, Run LED blinks. If motor current is
less than 1.05 x IB, motor is running, Run LED on. Motor
is stopping when motor current drops below 0.1 x IB.
If motor starts abnormally for longer than 60s, Run LED
stops blinking and turns off, Relay 1 also turns off. This
condition reset when motor current drops below 0.1 x IB.
3.2.2 Thermal Overload
The protection is based on mathematical model of motor
thermal image. The thermal capacity is calculated
continuously when motor is starting, overloading or even
after tripping. Tripping takes place when the thermal
capacity of the motor reaches 100%. This could happen
when the motor current is higher than 1.05 x IB. After
tripping a new start is not allowed until the motor cools
down to less than 40% of thermal capacity. Thermal
capacity can be cleared to 0% by pressing "UP" and
"DOWN" simultaneously for longer than 1.5 seconds
during thermal capacity display.
Warning: Clearing thermal capacity effectively reset
to cold start condition, user is not encouraged to
clear thermal capacity until motor is cool enough to
start/run within its thermal limit.
3.2.3 t6X Thermal overload Time Constant
t6X sets the themal overload time constant (heating
constant), which is the maximum period of time when
motor current is allowed to reach a 6 x IB. Cooling
constant time is defined as 4 times of heating constant
time and is applicable when motor current is less than
0.2 x IB. Refer to the thermal tripping curve on Figure 4.
3.2.4 Short Circuit
This protection is to trip the relay quickly when high
current is detected due to short circuit. I>> is normally
set higher than motor starting current to avoid false
tripping during motor starting and t>> is set to very short
duration.
Tripping takes place when any phase of motor current is
larger than I>> for longer than t>>. It can be disabled by
setting t>> to 'off'.
3.2.5 Undercurrent
Undercurrent protection is activated when average motor
current is larger than 0.1 x IB. Tripping takes place when
average motor current is smaller than I<< for longer than
t<<. It can be disabled by setting t<< to 'off'.
4
(a) With 0% thermal capacity (cold start)
time
t6x
I/IB
10s
1s
2s
3s
5s
21 3 4
5
6
20s
30s
40s
1min
2min
3min
5min
10min
20min
30min
1hour
2hour
2s
5s
10s
20s
30s
40s
1s
where:
Imax is the maximum phase current among the 3 phases.
Imin is the minimum phase current among the 3 phases.
Tripping takes place when unbalance value is more than
unbalance setting % for longer than unbalance delay. It
can be disabled by setting unbalance delay to 'off'.
time
t6x
I/IB
10s
1s
2s
3s
5s
20s
30s
40s
1min
2min
3min
5min
10min
20min
30min
1hour
2hour
2s
5s
10s
20s
30s
40s
1s
Figure 4: Thermal tripping curve
(b) With prior 50% thermal capacity
3.2.6 Unbalance
Unbalance is calculated as:
Imax - Imin
Imin
X 100 %
21 3 4
5
6
1.05
1.05

3.2.12 External CT Ratio
The CT ratio shall be set accordingly for the display to
show primary current. For example when using 150/5
CT, set the value to:
5
3.2.7 Phase Loss
Phase loss fault is detected when average motor current
is larger than 0.28 x IBbut any phase current is less than
0.1 x IB. Tripping takes place in less than 120ms when
phase loss is detected.
3.2.8 Phase Sequence
Phase sequence fault is detected when the phase
sequence in any 2 or all the phases are reversed.
Tripping takes place in less than 120ms when phase
sequence fault is detected.
Phase loss and phase sequence protection can be
enabled and disabled separately. Refer to
3.2.16 Phase
sequence / phase loss option
3.2.9 Prolonged Starting and Stalled Rotor
For prolonged starting and stalled rotor there is one IS>>
setting and separate delay time setting for each
protection. IS>> shall be set below the motor starting/
stalled current. These protections are useful when
thermal overload protection is not fast enough to protect
the motor during stalling.
Delay time for prolonged starting, tStart>> shall be set
longer than specified motor starting time. Tripping takes
place when any phase current is larger than IS> for
longer than tStart during motor starting.
Delay time for stalled rotor, tStall>> is activated upon
completing the motor starting. Tripping occurs when any
phase current is larger than IS>> for longer than tStall>>
during motor running.
Both protections can be disabled by setting IS>> to 'off'.
To disable only one of the protection, set the respective
delay time for the protection to be disabled to much
longer than specified.
3.2.10 Earth Fault
Earth fault protection is based on zero sequence current
calculation. Tripping takes place when the current is
larger than earth fault setting in % of IBfor longer than
t0>. It can be disabled by setting t0>> to 'off'.
3.2.11 Base Current
Base current is the motor full load current. The range of
setting is model dependent.
The formula is:
For example to use the relay with motor that has full load
current of 138A, using external CT of 150/5,
Motor full load current
IB = X CT ratio
1
138
= 4.6A
IB =
5
150
X
150
5
= 30
3.2.13 Manual or Auto Reset
The relay can be set to manual or auto reset when the
relay trips. Resetting of relay is allowed when the tripping
condition cleared. Manual reset is performed by pressing
the "RESET/MODE" (or using binary input if it is
configured as 1 - Reset trip). Thermal overload is always
auto reset.
3.2.14 Binary Input
The binary input is a dry contact input that can be
configured to perform various functions.
0 - Block relay 1
The input, when triggered, will force relay 1 off.
1 - Reset tripping
The input is used to manually reset a tripping.
2 - Instant tripping
The input will generate a tripping condition. Refer to
4.4 Binary Input Tripping.
3.2.15 Relay 2
The relay 2 output can be configured to turn on in these
conditions:
0 - On any tripping
Relay 2 on during any tripping.
1 - On thermal tripping
Relay 2 on during thermal tripping only.
2 - On thermal warning
Relay 2 on when motor current is more than 1.05 x IB.
3.2.16 Phase sequence / phase loss option
Phase sequence and phase loss detection can be on
(enabled) and off (disabled) separately.
0 - Phase sequence and phase loss off
1 - Phase sequence on
2 - Phase loss on
3 - Phase sequence and phase loss on
3.2.17 Frequency
Nominal value of the network frequency. Select either 50
or 60 Hz.
External CT ratio =

6
4. Tripping
4.1 Tripping Display
During tripping, Trip LED on, Thermal LED also on
during thermal overload tripping. Function LED and Data
LED blinks showing tripping current or source as shown
below:
4.2 Tripping Reset
During tripping condition, press "RESET/MODE" to
reset, the relay will reset if condition permits. If relay is
set to auto reset, the relay will reset automatically if the
tripping condition is cleared with a 5% hysteresis.
4.3 Tripping Test
Press and hold "TEST" for 3.5 seconds to simulate a
tripping condition, Trip LED blinks when "TEST" is
pressed. During Test Tripping, "tESt" blinks, R1 off and
R2 on if set to "On any tripping". Press "RESET/MODE"
to reset. Tripping Test is disabled when motor is
starting/running.
4.4 Binary Input Tripping
When Binary input is set to 2 - Instant tripping, binary
input will generate a tripping condition. "triP" will blink,
R1 off and R2 on if set to "On any tripping". Press
"RESET/MODE" to reset. If relay is set to auto reset, the
relay will reset after the input is normal for 1s.
4.5 Tripping History Display
During Current/Thermal display, press "RESET/MODE"
to jump to Tripping History Display. Display shows the
previous tripping status with a 'dot' blinking at Function
LED. To clear tripping history, press "UP" and "DOWN"
simultaneously.
5. Typical Application Diagram
Trip LED
Thermal
LED
Function
LED
Data LED
Description
On
On
t
oL
Thermal Overload
On
Off
2
tripping current
Short circuit tripping
On
Off
4
tripping current
Undercurrent tripping
On
Off
6
Ub
Unbalance tripping
On
Off
6
PS
Phase sequence error
tripping
On
Off
6
PL
Phase loss tripping
On
Off
8
tripping current
Earth fault tripping
On
Off
A
tripping current
Prolonged
starting/Stalled rotor
tripping
On
On
t
ESt
Trip Test
On
Off
t
riP
Binary input tripping
Aux
6
2
3
4
5
L
R1
R2
N
9
10
11
12
13
14
7
15
8
16
1
MPR 500
Table 2: Tripping display
L1
L2
L3
M
K1
N
K1
H1
S2
S1 K1
BlockR1/
Reset/
Trip
Start
Stop
NO
NC
COM
COM
NC
NO
Binary
input
Figure 5: Example of application
F1F2F3
F4
tripping
3-Phase Motor
Aux
6
2
3
4
5
L
R1
R2
N
9
10
11
12
13
14
7
15
8
16
1
MPR 500
L
M
K1
N
K1
H1
S2
S1
K1
Block R1/
Reset/
Trip
Start
Stop
NO
NC
COM
COM
NC
NO
Binary
input
F1
F2
Single-Phase Motor*
* To use MPR500 for single-phase protection, Io>> Earth
fault, Phase sequence and phase loss protection should be
set to off.

Figure 6
7
6. Techinical Data
SETTING RANGES
Thermal Overload time constant, t6X
Short circuit, I>>
Short circuit delay time, t>>
Undercurrent, I<<
Undercurrent delay time, t<<
Unbalance,
Unbalance delay time, t
Earth fault, I0>>
Earth fault delay time, t0>>
Phass loss
Phase sequence
Prolonged starting/stalled rotor, IS
Prolonged starting delay time, tStart
Stalled rotor delay time, tStall
CT RATINGS
Rated current
Rated frequency
Burden
Thermal withstand
BINARY INPUT
Rated input voltage
AUXILIARY SUPPLY
Model MPR 500-240A
Supply frequency
Maximum power consumption
CONTACTS
Contact arrangement
Contact rating
Contact material
Operating time
Expected electrical life
Expected mechanical life
INDICATORS
Run
Trip/Pickup
Thermal
ENVIRONMENTAL CONDITIONS
Temperature
Humidity
MECHANICAL
Mounting
Front panel
Approximate weight
CASE DIMENSION
110mm
100mm
90mm
90mm
96 mm
96 mm
Front
: 1
–
40s. In steps of 0.1s for 1-10s, in steps of 1s for 10-40s
: off, 2
–
12 x IB. In steps of 1 x IB
: 0
– 25s.
In steps of 0.1s for 1-10s, in steps of 1s for 10-25s
: off, 20 – 90% of IB.
In steps of 1%
: 0 – 60s.
In steps of 0.1s for 1-10s, in steps of 1s for 10-60s
: off, 10 – 50%. In steps of 1%
: 0 – 25s.
In steps of 0.1s for 1-10s, in steps of 1s for 10-25s
: off, 10 – 60% of IB. In steps of 1%
: 0 – 25s.
In steps of 0.1s for 1-10s, in steps of 1s for 10-25s
: <120ms
: <120ms
: off, 2 – 12 x IB.
In steps of 0.1 x IB
: 0 – 60s.
In steps of 0.1s for 1-10s, in steps of 1s for 10-60s
: 0 – 60s.
In steps of 0.1s for 1-10s, in steps of 1s for 10-60s
: 2-10A
: 50 or 60Hz
: <0.3VA at rated current
: Continuous: 2 x maximum rated
For 30s: 6 x maximum rated
For 1s: 10 x maximum rated
: 12V (Supplied internally)
: 85 ~ 265 V AC
110 ~ 370 V DC
: 50 or 60 Hz
: 3 VA typical
: Change-over
: 5A, 250V AC (cosf = 1)
: Silver alloy
: 15ms max
: 100,000 operations at rated current
: 5 x 106operations
: Green indicator
: 7-segment display and red indicators
: Yellow indicator
: -5ºC to +55ºC
: 56 days at 93% RH
and 40ºC non-condensing
: Panel mounting
: Standard DIN
96 mm x 96mm
: 0.75kg
Table of contents
Other Mikro Relay manuals