HOBO Micro Station User’s Guide iii
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Introduction................................................................................................................................1
Specifications...................................................................................................................................1
How to use this manual....................................................................................................................2
Smart sensors supported.................................................................................................................2
Chapter 2 Assembly and testing ...............................................................................................................3
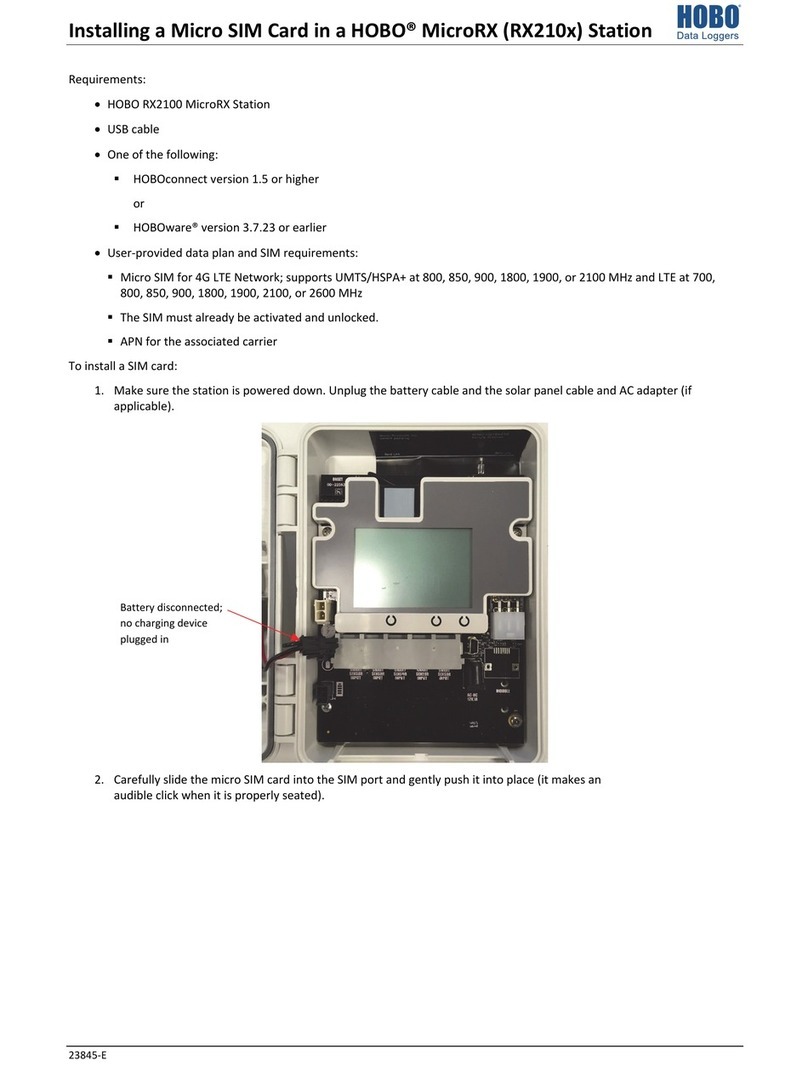
Items required..................................................................................................................................3
Logger and smart sensor setup instructions....................................................................................3
Testing the logger ............................................................................................................................6
Configuring HOBOware for a Keyspan®USB-to-Serial Adapter .....................................................7
Chapter 3 Logger operation.......................................................................................................................8
Logger components .........................................................................................................................8
Status lights.......................................................................................................................................9
Communicating with the logger........................................................................................................9
Launching........................................................................................................................................10
Selecting and installing batteries ...................................................................................................11
Estimating battery life......................................................................................................................12
Checking battery status...................................................................................................................13
Adding and removing sensors .......................................................................................................13
Time accuracy................................................................................................................................14
Logger memory..............................................................................................................................15
Chapter 4 Field setup and mounting.......................................................................................................17
Guidelines for typical field setup ....................................................................................................17
Guidelines for a tripod system setup ...............................................................................................18
Guidelines for installing sensors......................................................................................................18
Mounting instructions for a flat surface..........................................................................................19
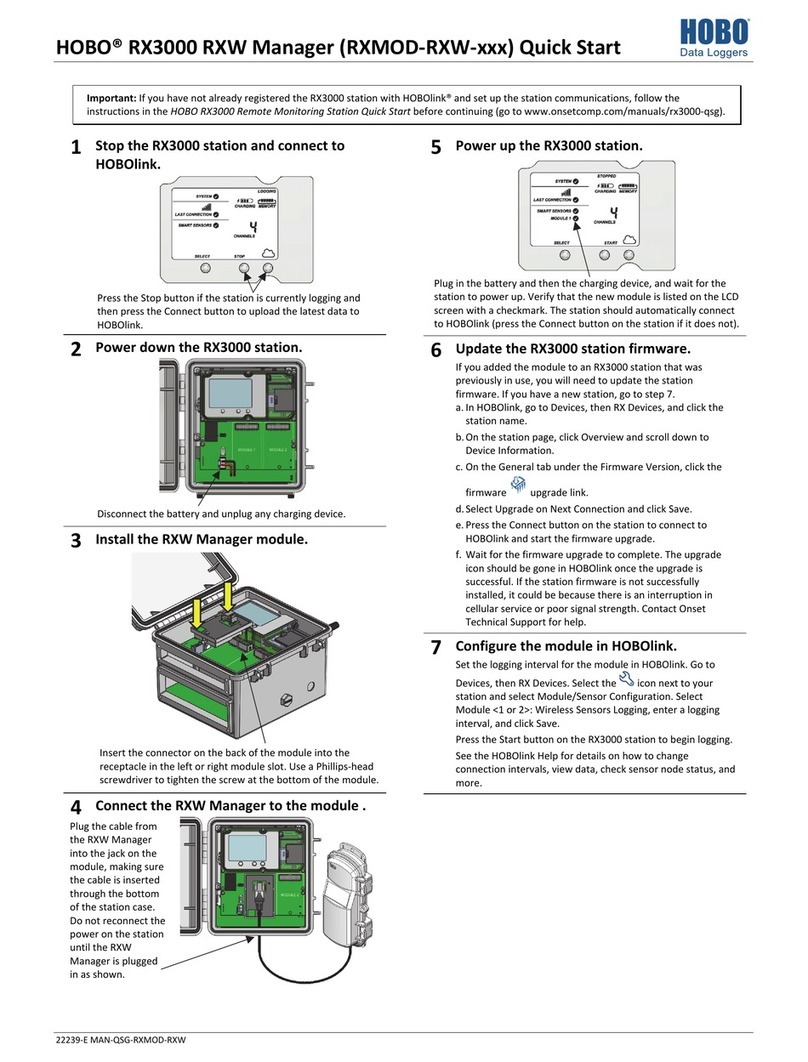
Using Micro Station accessories....................................................................................................20
Mounting the logger with the Mast Mounting Kit..............................................................................20
Connecting the External Grounding Wire Adapter Cable ................................................................21
Connecting the External Communications Port Adapter Cable .......................................................22
Field preparation checklist .............................................................................................................23
Set up the tripod, cross arm, and sensors.....................................................................................26
Chapter 5 Troubleshooting......................................................................................................................28
Chapter 6 Maintenance.............................................................................................................................30
Maintenance...................................................................................................................................30
Performing a visual inspection.........................................................................................................30
Cleaning the Micro Station ..............................................................................................................30
Checking the desiccant pack...........................................................................................................31
Replacing the batteries....................................................................................................................31
Verifying the sensor accuracy..........................................................................................................31