INOXPA HLR Manual



(A) 2021/11 1.Safety 3
1. Safety
1.1. INSTRUCTION MANUAL
This instruction manual contains information on the reception, installation, operation, fitting, stripping and maintenance for the
HLR pump.
The information given herein is based on the most up-to-date data available.
INOXPA reserves the right to modify this instructions manual without having to give prior notice.
1.2. START-UP INSTRUCTIONS
This instruction manual contains vital and useful information for properly operating the pump and for keeping it in good
running condition.
Not only should the safety instructions set forth in this chapter be carefully read before putting the pump into operation, but
those concerned must also familiarise themselves with the operating features of the pump and strictly adhere to the
instructions given herein. It is extremely important that these instructions be kept in a set place near the installation.
1.3. SAFETY
1.3.1. Warning signs
Danger for people in general.
Danger of injury caused by rotating parts
of the equipment.
Danger! Electricity.
Danger! Caustic or corrosive agents.
Danger! Suspended loads.
Danger to the proper operating of the
machine.
Obligation to ensure safety at work.
Use of safety goggles obligatory.
1.4. GENERAL SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
Please read the instruction manual carefully before installing and commissioning the pump. Should
you have any doubts or queries, contact INOXPA.
1.4.1. During the installation
You must always bear in mind the
Technical Specifications
set forth in Chapter 8.
Do not put the pump into operation before connecting it to the pipes.
Do not put the pump into operation if the rotor case of the pump has not been fitted and the lobe
rotors fixed in the pump.
Check that the motor/drive specifications are correct, especially if there is a special risk of explosion
due to the work conditions.
During the installation procedure, all the electrical work must be carried out by duly authorised
personnel.
1.4.2. During operation
You must always bear in mind the
Technical Specifications
set forth in Chapter 8. The limit values that
have been set must NEVER be exceeded.
NEVER touch the pump or pipes whenever the pump is being used to transfer hot liquids or during
the cleaning procedure.

4 1.Safety (A) 2021/11
The pump has moving parts. Do not put your fingers into the pump when it is operating.
NEVER work with the suction and the delivery valves shut off.
NEVER directly sprinkle the electric motor with water. Standard motor protection is IP-55: dust and
water sprinkling protection.
1.4.3. During maintenance
You must always bear in mind the
Technical Specifications
set forth in Chapter 8.
NEVER strip the pump down until the pipes have been drained. Remember that there will always be
some liquid left in the rotor case (if it has not been fitted with a drain). Always remember that the
liquid that has been pumped may be dangerous or subject to high temperatures. For situations of
this type, please consult the prevailing regulations in the country in question.
Do not leave loose parts on the floor.
ALWAYS turn the power supply to the pump off before embarking on maintenance work. Take out
the fuses and disconnect the wires from the motor terminals.
All electrical work must be carried out by duly authorized personnel.
1.4.4. In accordance with the instructions
Any failure to comply with the instructions could lead to a hazard for the operators, the atmospheric conditions of the room,
and the machine, and it could lead to a loss to any right to make a claim for damages.
Such non-compliance could bring with it the following risks:
•Important operating failures of the machine / plant.
•Failure to comply with specific maintenance and repair procedures.
•Potential electrical, mechanical and chemical hazards.
•Atmospheric conditions in the room could be hazardous due to the release of chemical substances.
1.4.5. Warranty
We wish to point out that any warranty issued will be null and void and that we are entitled to an indemnity for any civil liability
claim for products which might be filed by third parties if:
•Operation and maintenance work has not been done following the corresponding instructions; the repairs have not
been made by our personnel or have been made without our written authorization;
•Modifications are made to our material without prior written authorization;
•The parts or lubricants used are not original INOXPA parts/lubricants;
•The material has been improperly used due to error or negligence or has not been used according to the indications
and the intended purpose.
•The parts of the pump have been damaged as a result of having been exposed to strong pressure as there was no
pressure relief valve.
The General Delivery Terms which you have already received are also applicable.
No modification can be made to the machine without the prior consent of the manufacturer. For your
safety, use spare parts and original accessories. The use of other parts exempts the manufacturer
from any and all responsibility.
Any change in operating conditions can only be done with the prior written consent of INOXPA.
In the event of doubt or should you require a fuller explanation on particular data (adjustment, assembly, disassembly...),
please do not hesitate to contact us

(A) 2021/11 2.Index 5
2. Index
1. Safety 3
1.1. Instruction manual ........................................................................................................ 3
1.2. Start-up instructions ...................................................................................................... 3
1.3. Safety .......................................................................................................................... 3
1.4. General safety instructions ............................................................................................. 3
2. Index 5
3. General Information 6
3.1. Description ................................................................................................................... 6
3.2. Operating principle........................................................................................................ 6
3.3. Application ................................................................................................................... 6
4. Installation 8
4.1. Pump reception............................................................................................................. 8
4.2. Transport and storage ................................................................................................... 8
4.3. Location ....................................................................................................................... 9
4.4. Coupling....................................................................................................................... 9
4.5. Pipes.......................................................................................................................... 10
4.6. Secondary piping......................................................................................................... 11
4.7. Pressure relief valve .................................................................................................... 12
4.8. Electrical installation .................................................................................................... 12
5. Start-up 13
5.1. Start-up ..................................................................................................................... 13
5.2. Pressure By-pass......................................................................................................... 13
6. Operating Problems 15
7. Maintenance 16
7.1. General maintenance................................................................................................... 16
7.2. Storage ...................................................................................................................... 16
7.3. Cleaning..................................................................................................................... 17
7.4. Pump disassembly....................................................................................................... 18
7.5. Pump assembly........................................................................................................... 21
7.6. Lobe adjustment ......................................................................................................... 24
7.7. Mechanical seal assembly and disassembly.................................................................... 26
8. Technical Specifications 28
8.1. Technical specifications................................................................................................ 28
8.2. Weights...................................................................................................................... 30
8.3. HLR dimensions .......................................................................................................... 31
8.4. pump with flushing dimensions..................................................................................... 33
8.5. HLR 0......................................................................................................................... 34
8.6. HLR 1......................................................................................................................... 36
8.7. HLR 2......................................................................................................................... 38
8.8. HLR 3......................................................................................................................... 40
8.9. HLR 4......................................................................................................................... 42
6 3.General Information (A) 2021/11
3. General Information
3.1. DESCRIPTION
The HLR rotary lobe pumps by INOXPA are part of our wide range of positive displacement rotary lobe pumps for viscous
liquids.
The following models exist in the hygienic rotary lobe pump range:
•The HLR pump normal flow rate suitable for differential pressure of up to 12 bar.
•The HLR with wider lobes, delivers a higher flow rate, and is suitable for differential pressure of up to 7 bar.
The HLR model has been specially developed to respond to all hygienic requirements in the Bio-Pharm and Food industries.
As regards hygiene, reliability and sturdiness, the complete range of rotary lobe pumps satisfies all requirements set by the
aforesaid industries.
Its modular design enables optimal part interchange between the different pumps.
The rotary lobe pumps are positive displacement pumps. Owing to the contact between the internal parts, the pressure
variations, etc. they make a louder noise than centrifugal pumps. This noise must be taken into consideration when installing
these pumps.
The HLR rotary lobe pumps by INOXPA have been certified by EHEDG and designed so that they meet the requirements of 3A
Sanitary Authority.
This equipment is suitable for use in food processing applications with strict hygienic requirements.
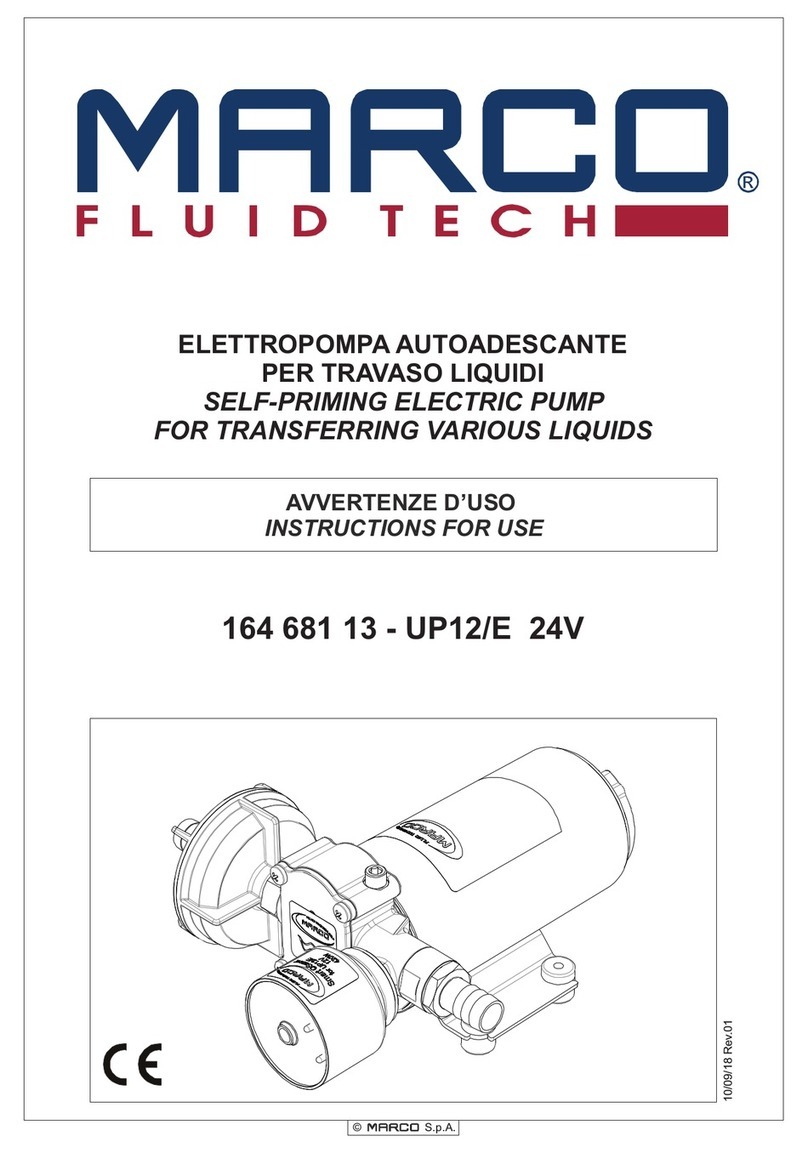
3.2. OPERATING PRINCIPLE
The rotary lobe pump is a positive displacement rotary pump. The left lobe (except in the case of pump size 0) is driven by the
driving shaft. The right lobe (except in the case of pump size 0) is located on the driven shaft, and is driven via a helical gear.
Both lobes rotate in synchronism without one touching the other. When the pump is running they displace a set volume of
liquid. Figure below shows how a rotary lobe pump operates.
A: When the lobes rotate, the space on the suction side increases because one lobe moves away from the other, thus causing
a partial vacuum that draws the liquid into the pumping chamber.
B: Each lobe void is filled consecutively as the shafts rotate and the liquid is displaced towards the discharge side. The small
clearances between the lobes, and between the lobes and the walls of the rotor case, duly cause the spaces to be rather well
closed.
C: The rotor case is completely full and the liquid leaks through the meshing of the lobes, knocking against the space walls so
as to thus complete the pumping action.
3.3. APPLICATION
The main advantage of the INOXPA HLR rotary lobe pump is its capacity to pump a great variety of viscous liquids, from 1
mPa.s up to 100.000 mPa.s
Furthermore, it is capable of pumping liquid products that require very careful handling and liquids that contain soft solids thus
causing only a minimum degradation of same.
(A) 2021/11 3.General Information 7
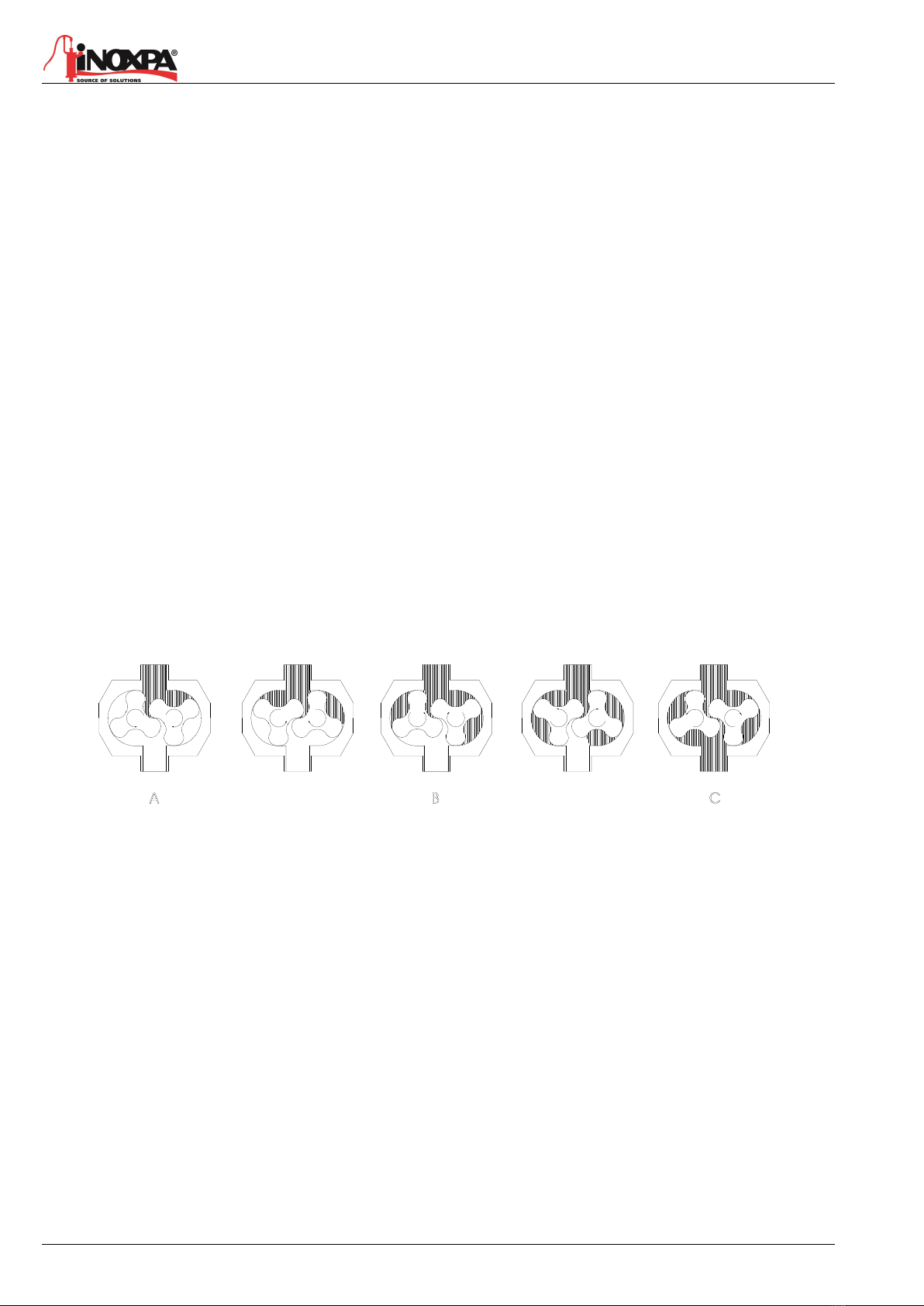
3.3.1. Field of application
The range of application for each type of pump is limited. The pump was selected for a given set of
pumping conditions when the order was placed. INOXPA shall not be liable for any damage resulting
from the incompleteness of the information provided by the purchaser (nature of the fluid, rpm,
etc.).
P [bar]
8 4.Installation (A) 2021/11
4. Installation
4.1. PUMP RECEPTION
INOXPA is not responsible for any deterioration of the material as a result of its transportation or
unpacking. Visually check that the packing has not suffered any damage.
The pump will be accompanied by the following documentation:
•Dispatch notes.
•Pump Instruction and Service Manual.
•Drive Instruction and Service Manual (*).
(*) If the pump has been supplied with a drive from INOXPA.
Unpack the pump and check the following:
•The pump suction and delivery connections, removing the
remains of any packing material.
•Check that the pump and the motor have not suffered any
damage.
•Should the pump not be in proper condition and/or does not
have all the parts, the haulier must draw up a report as
soon as possible with regard to the same.
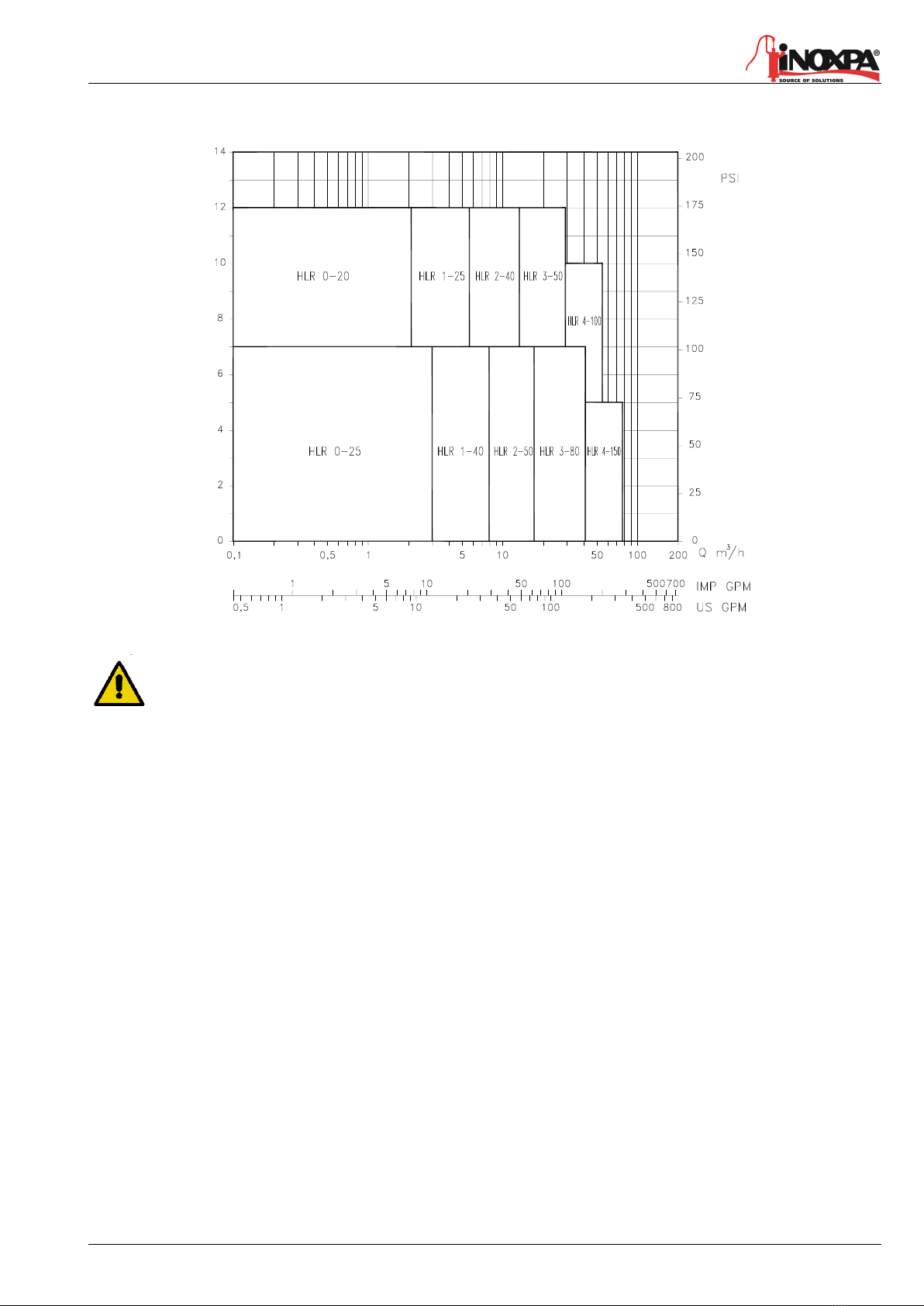
4.1.1. Pump identification and marking
Pump plate
4.2. TRANSPORT AND STORAGE
HLR pumps and pumping units are often too heavy to be handled manually. Use an adequate means
of transport.
Use the points which are indicated in the drawing for lifting the pump.
Only authorized personnel should transport the pump.
Do not work or walk under heavy loads.
Lift the pump as shown below:
•Always use two support points placed as
far apart as possible.
•Secure the support so that it will not
move.
•See chapter 8.
Technical Specifications
to
consult dimensions and weights.
Serial number
(A) 2021/11 4.Installation 9
4.3. LOCATION
•Position the pump as near as possible to the suction tank, and whenever possible below the level of the liquid.
•Place the pump in such a way that there is enough space around it to provide access both to the same and to the motor.
(See Chapter 8.
Technical Specifications
to consult dimensions and weights).
•Place the pump on a level and flat surface.
•The basement must be rigid, horizontal and against any vibration.
Install the pump in such a way that it can be properly ventilated. If the pump is to be installed
outside, it must be done so under cover. Its positioning must enable easy access for any inspection
and maintenance operations that may need to be carried out.
4.3.1. Foundation
Install the pump base so that the drive and pump are level and well supported. Therefore the pump unit should be installed on
a base plate –according to DIN 24259-, or on a frame, both placed exactly level on the foundation. The foundation must be
hard, level, flat, vibrations free ...to prevent base distortion (to keep the alignment pump –drive guaranteed while
commissioning).
To install the pump unit on the foundation proceed as follows:
•Make holes in the foundation to fit foundation bolts. This is unnecessary when expanding screws are used instead of
foundation bolts.
•Place base plate or frame with the aid of shims horizontally on the foundation.
•Grout
•When the grout has entirely hardened the pump unit can be placed on the base plate or the frame. Tighten the nuts on
the foundation bolts carefully.
For other foundations consult INOXPA.
4.4. COUPLING
For the couplings selection and assembly consult to the supplier manual. Sometimes the torque of the positive displacement
pumps can be high enough. Therefore, a coupling have been chosen 1.5 to 2 the adequate torque.
4.4.1. Alignment
The pump and motor shaft of complete units have been accurately pre-aligned in our factory.
After installations of the pump unit, the pump and motor shaft should be re-aligned.
•After unit is installed recheck alignment of pump and motor shaft and alignment of piping. Realign if necessary.
•In the case of applications dealing with high temperatures the pump can be operated temporarily at its working
temperature. Then recheck alignment pump - piping.
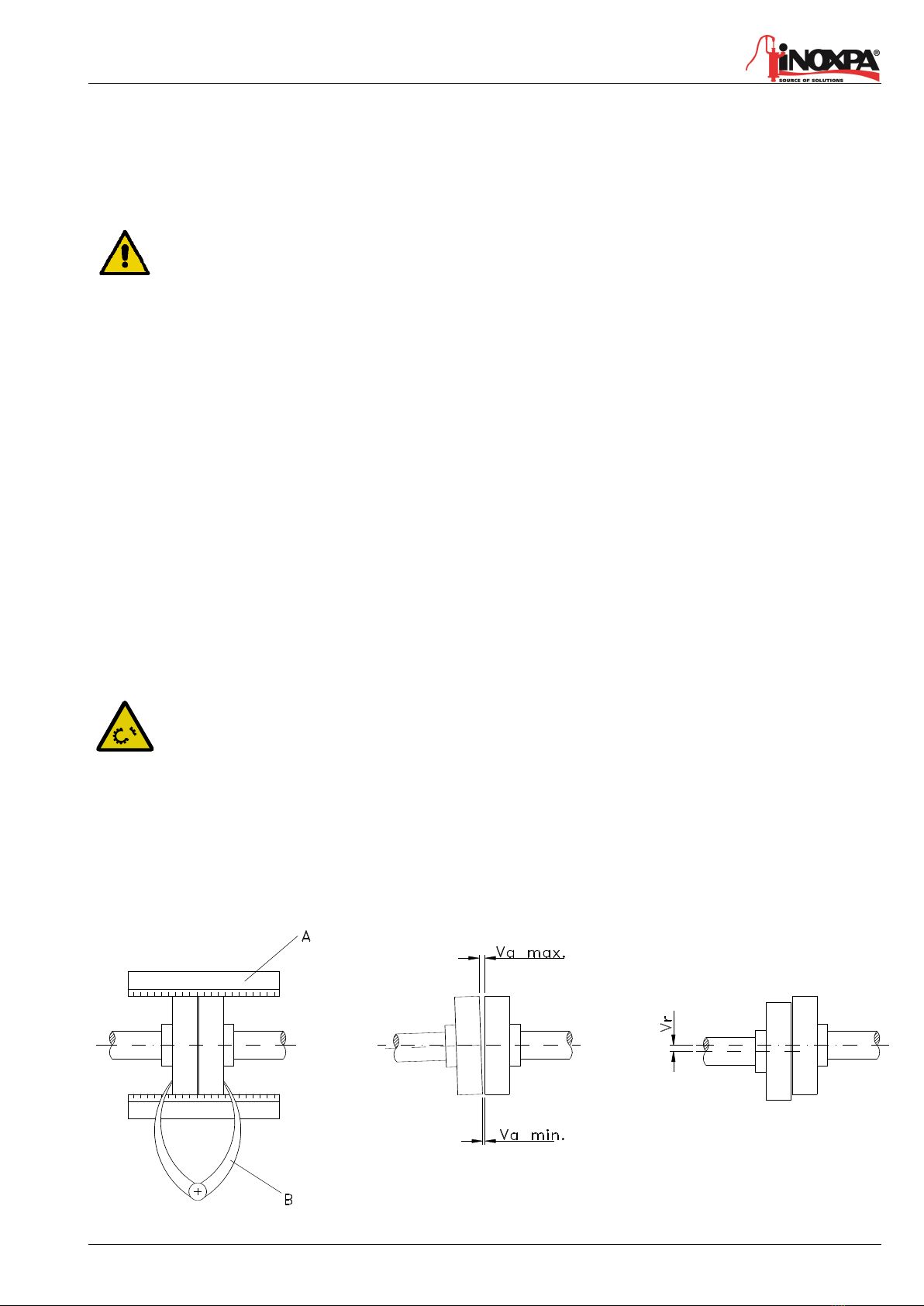
Place a straight-edge (A) on top of the coupling: the straight should make contact with both halves of the coupling over their
entire length. See figure.
Repeat the check, but this time on both sides of the coupling near the shaft. For the sake of accuracy, this check should also
be done using an outside caliper (B) at two diametrically opposite points on the outside surfaces of the two halves of the
coupling.
10 4.Installation (A) 2021/11
Maximum alignment deviations:
Outside diameter of
the coupling [mm]
Vamin
[mm]
Vamax
[mm]
Vamax - Vamin
[mm]
Vr.
[mm]
70 - 80
2
4
0,13
0,13
81 - 95
2
4
0,15
0,15
96 - 110
2
4
0,18
0,18
111 - 130
2
4
0,21
0,21
131 - 140
2
4
0,24
0,24
141 - 160
2
6
0,27
0,27
161 - 180
2
6
0,3
0,3
181 - 200
2
6
0,34
0,34
201 - 225
2
6
0,38
0,38
4.5. PIPES
•In general, suction and delivery pipes should be fitted in straight stretches, with the minimum amount of elbows and
accessories, in order to reduce, as far as possible, any head loss that might be produced by friction.
•Make sure that the pump ports are well aligned with respect to the piping and that they are similar in diameter to that of
the pipe connections.
•Position the pump as near as possible to the suction tank, and whenever possible below the level of the liquid or even
lower with respect to the tank in order for the static suction head to be at its maximum.
•Place brackets for the piping as near as possible to the suction and delivery ports of the pump.
4.5.1. Shut-off valves
The pump can be isolated for the purpose of carrying out maintenance work. To this end, shut-off valves should be fitted at the
pump’s suction and delivery connections.
These valves must ALWAYS be open whenever the pump is operating.
4.5.2. Self-priming process
In general terms --if the self-priming process is followed-- the pump ought to contain sufficient liquid to fill the internal
recesses and the void spaces thus enabling the pump to create a pressure difference.
However, if low viscosity fluids are to be pumped, a foot valve of the same or greater diameter as that of the suction pipe
should be installed; alternatively, the pump can be installed with a "U" shaped piping.
The use of a foot valve is not recommended for pumping viscous liquids.
•In order to eliminate air and gases from the suction pipe, the counter-
pressure on the discharge pipe should be reduced. When the self-
priming process is used, the pump's start-up should be done by
opening and emptying the discharge pipe which allows the air and
gases to escape at a low counter-pressure.
•Another possibility involves long pipes or when a check valve is
installed in the discharge pipe; it is also possible to install a by-pass
with a shut-off valve on the discharge side of the pump. This valve
shall be opened in the case of priming and will allow air and gases to
escape at a minimum counter-pressure.
•The by-pass should not lead back to the intake orifice but to the
supply tank instead.

(A) 2021/11 4.Installation 11
4.5.3. Barrier fluid with pressure tank
As the HLR Double Mechanical seal is of balanced design, the installation of a pressure tank is not necessary.
Pressure tank is only necessary if the pumped liquid, process safety rules…requires it.
1...2m
Mechanical seal
Pressure tank connection lay out
To obtain further information about the pressure tank (installation, operation, maintenance, …), consult the instruction manual
supplied by the manufacturer.
4.6. SECONDARY PIPING
4.6.1. Quench
If the seal requires flush media, the media supply and the purchase and installation of piping, valves ... for the media are not
the responsibility of INOXPA.
The flush shaft seal option is available on all seal types. Use the sectional drawings of the HLR seal options to purchase
additional parts.
Attention should be given to the compatibility of the handled liquid with the flush media. Choose the
sealing liquid so that unwanted chemical reactions are avoided. Also check the compatibility of the
flush media with seal elastomers.
HLR rotor cases have female threaded inlet and outlet connections and are dependent upon frame of the pump and type of
quench system employed.
4.6.2. Liquid flush media
Use a flush media which is filtered free from impurities to obtain maximum service life of the seal. If the product is sticky or
crystalline then use media which is able to dissolve the product.
Connect the quench so that the inlet is at the bottom and outlet is at the top. This will make a better evacuation or air or gases
possible.
4.6.3. Heating / cooling jackets
Heating / cooling jackets (S) are available on the front cover. Heating or cooling media can be provided via connections
according to the next figure.
Install ALWAYS the pressure tank between 1 and 2 meters above the mechanical seals. See the
figure below.
Connect ALWAYS the barrier fluid input connection with the bottom chamber seal connection. So,
the barrier fluid outlet will be carried out by the top chamber connection. See the figure below

12 4.Installation (A) 2021/11
4.7. PRESSURE RELIEF VALVE
The positive displacement lobe pumps must be protected from excess pressure when they are
operating. Consequently, all the HLR pumps can be fitted with a stainless steel pressure relief valve
or a pressure by-pass
4.7.1. Protection
This valve protects the pump and prevents excessively high pressure arising in the circuit. It reduces the differential pressure
(p) between suction and discharge, but not the maximum pressure within the plant.
Do not use the pressure relief valve to protect the system from excess pressure. It is designed to
protect the pump only as it is not a safety outlet.
4.7.2. Operation principle
The pressure by-pass valve is located in the rotor case and prevents excess pressure arising inside the pump. For example,
when the pump's discharge port is clogged and the liquid cannot be pumped out, too high a pressure can cause serious
damage to some of the pump's parts. The pressure relief valve opens a passage from the pump's discharge side to its suction
side: an escape route, redirecting the flow again to the suction side whenever specifically high pressure levels are reached. The
by-pass is effective in both directions of rotation (only front cover assembly).
If the relief valve operates, this will mean that the equipment is not working properly. The pump
should be disconnected immediately. Identify and solve the problem before re-starting the pump.
Remember that the pressure relief valve is not able to be used to regulate the flow rate.
The pressure relief valve can be adjusted to any determined pressure, according to the type of pump being used.
4.8. ELECTRICAL INSTALLATION
Leave the connecting of the electrical motors to qualified personnel. Take the necessary measures to
prevent any breakdowns in the connections and wires.
The electrical equipment, the terminals and the components of the control systems may still carry an
electric charge even when disconnected. Contact with them may put the safety of operators at risk,
or cause irreparable damage to the material.
Before manoeuvring the pump, make sure that the electric box is switched off.
•Connect the motor in accordance with the instructions supplied by the manufacturer of the same.
•Check the direction of the rotation (see the signalling label on the pump).
•Start the pump motor briefly. Make sure the pumping direction is the right one. If the pump operates in the wrong
direction it may cause severe damage.
Pumps size 1, 2, 3, and 4 Pumps size 0
Check ALWAYS the direction of the motor’s rotation with liquid inside the pump.
For the models with sealing chamber, make sure always that it is filled of liquid before checking the
rotating direction.

(A) 2021/11 5.Start-up 13
5. Start-up
Before putting the pump into operation read carefully the instructions on installation given in
Chapter 4.
Installation
.
5.1. START-UP
Read Chapter 8.
Technical Specifications
carefully. INOXPA will not assume responsibility for any
improper or incorrect use of the equipment.
Do not touch the pump or the piping while it is pumping products at a high temperature.
5.1.1. Checks to be carried out before putting the pump into operation
•Completely open the pipes’ suction and delivery shut-off valves.
•Check oil level of the pump. Add correct grade of oil as necessary to maintain level in center of oil sight glass (In the case
of first start-up: pumps are shipped with oil in the gearbox).
•If the liquid fails to flow toward the pump, fill it with the liquid to be pumped.
The pump must NEVER rotate without fluid inside it.
•Check that the power supply matches the rating indicated on the motor plate.
•Check that the direction of rotation of motor is the right one.
•If the pump has a single or double mechanical seal with buffer or barrier fluid, mount the auxiliary connection
corresponding to the values indicated in Chapter 8,
Technical Specification.
5.1.2. Checks to be carried out on putting the pump into operation
•Check to make sure that the pump is not making any strange noises.
•Check to see if the absolute inlet pressure is sufficient, in order to avoid cavitations in the pump. Consult the curve for
the minimum required pressure above the steam pressure (NPIPr).
•Monitor the delivery pressure.
•Check that there are no leaks in the sealed areas.
A shut-off valve should not be used in the suction pipe to regulate the flow rate. It must be
completely open during operation.
Monitor motor consumption in order to avoid a circuit overload.
Reduce flow and motor power consumption by reducing motor speed.
5.2. PRESSURE BY-PASS
When pump has a pressure by-pass, pump only can rotate in one direction. To reverse the direction of the pump’s rotation,
the assembly of the by-pass must also be reversed.
The valve's opening pressure depends on the fluid to be pumped, its viscosity, its rpm ..., and so before starting-up the pump,
the operator ought to adjust the pressure relief valve's opening pressure.
When an overflow valve or a pressure bypass is installed, the valve is adjusted to the maximum
working pressure of the pump. The end user must adjust the valve to the correct pressure.
When an overflow valve or a pressure bypass does not operate properly, the pump must immediately
be removed from service for repair.
The valve must be examined by the INOXPA technical assistance personnel.
14 5.Start-up (A) 2021/11
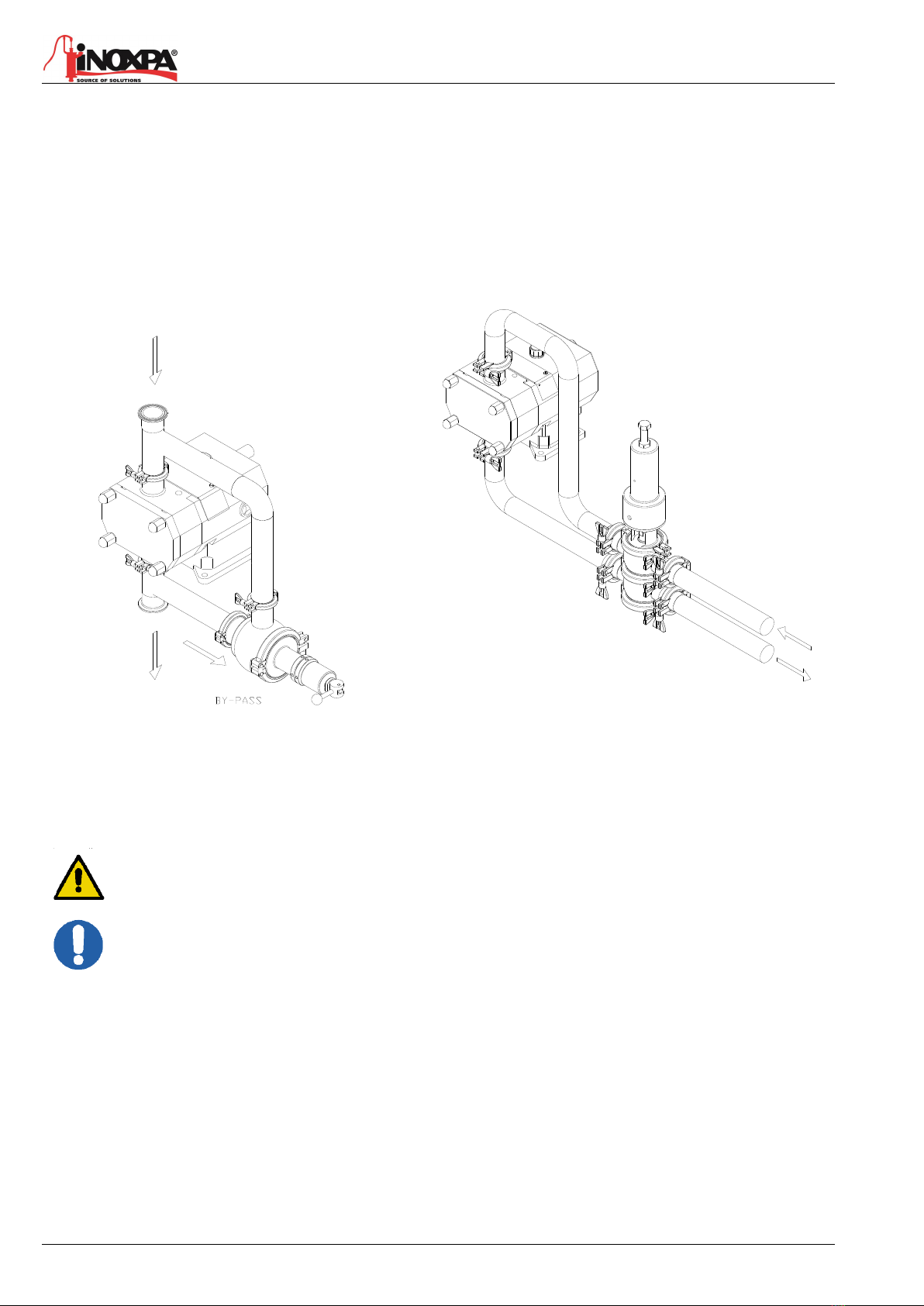
5.2.1. External Assembly
When installing a pressure relief valve, some points shall be considered:
•To avoid dead legs
•Drainability of the pump and pipeline
Please see figure below where recommended installation is shown:
Wrong Installation
Correct installation
Example of standard Pressure Relief Valve installation.
This arrangement creates a dead leg with a large amount
of product.
Example of Hygienic NCS Pressure Relief Valve installation, with
air actuated rising.
It allows pump and pipeline to drain, avoiding dead areas.
When checking the relief valve also make sure the pump's pressure will NEVER exceed the pressure
setting + 2 bar.
When the relief valve does not work properly, the pump must be taken out of service immediately.
The valve must be inspected by an INOXPA service technician.
(A) 2021/11 6.Operating Problems 15
6. Operating Problems
The table given below provides solutions to problems that might arise during pump operation. With respect to the same, it is
assumed that the pump has been properly installed and has been correctly selected for the application in question.
Should there be a need for technical service please contact INOXPA.
Operating problems
Probable causes
Motor Overload
8, 9, 12, 16, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 26.
Insufficient discharge flow rate
2, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 13, 14.
No pressure on the discharge side
1, 2, 3, 6, 7.
Irregular discharge flow rate/pressure
2, 4, 5, 6, 9, 12.
Noise and vibrations
2, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 11, 12, 13, 16, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26.
The pump gets clogged
8, 9, 11, 16, 19, 20, 21, 22, 24, 25, 26.
Overheating of pump
7, 8, 9, 11, 12, 16, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 26.
Abnormal wear
4, 5, 11, 15, 16, 19, 24, 25.
Leak through mechanical seal
17, 18.
Probable causes
Solutions
1
Wrong rotation direction
Invert the rotation direction
2
Insufficient NPIP
Increase available NPIP:
•Rise the suction tank
•Lower the pump
•Reduce the speed
•Increase the diameter of the suction pipe
•Shorten and simplify the suction piping.
3
Pump not purged
Purge or fill
4
Cavitation
Increase suction pressure ( see 2)
5
The pump sucks in air
Check suction pipe and all its connections.
6
Suction pipe clogged
Check the suction pipe and filter(s), if any.
7
Wrong setting of pressure relief valve
Check the pressure relief valve's setting
8
Discharge pressure too high
If necessary, reduce the loss of head by increasing the diameter
of the discharge pipe
9
Viscosity of the liquid is too high
•Reduce the pump speed
•Reduce the viscosity, for example, by heating the liquid.
10
Viscosity of liquid too low.
•Increase the pump speed
•Increase the viscosity, for example, by cooling the liquid.
11
Temperature of liquid too high.
Reduce the temperature by cooling the liquid.
12
Pump speed too high
Reduce the pump speed
13
The lobes are worn
Replace the lobes
14
Pump speed too low
Increase the pump speed
15
Product very abrasive
Fit hardened lobe hubs
16
Worn bearings
Replace the bearings, check the pump
17
Worn or damaged mechanical seal
Replace the seal
18
O-rings and gaskets are not the right ones for the
liquid
Fit the proper O-ring and gaskets; check with the supplier.
19
Worn gears
Replace and readjust the gears
20
Insufficient lubricating oil level
Fill up with oil
21
Unsuitable lubricating oil
Use an appropriate oil
22
The lobes rub
•Reduce the temperature
•Reduce the discharge pressure
•Adjust the clearance
23
Coupling misalignment
Align the coupling
24
Tension on the pipelines
Connect the pipelines to the pump free of tensions
25
Foreign bodies in the liquid
Insert a filter in the suction pipe
26
Pump and / or electric motor not fixed on
foundation
Tighten, check that the piping has been connected stress-
free and align the coupling
If the problem persists, use of the pump must cease immediately. Contact the pump’s manufacturer
or its representatives.

16 7.Maintenance (A) 2021/11
7. Maintenance
7.1. GENERAL MAINTENANCE
This pump, as with any other machine, needs to be maintained. The instructions contained in this manual deal with the
identification and replacement of the spare parts. These instructions have been drawn up by maintenance staff and are
destined for those people who are responsible for supplying spare parts.
Read carefully Chapter 8.
Technical specifications
.
All the parts or materials that are changed must be duly eliminated / recycled in accordance with the
prevailing directives in each area.
ALWAYS disconnect the pump before starting out on any maintenance work.
7.1.1. Check the mechanical seal
Periodically check that there are no leaks in the shaft area. Should there be any leaks in the mechanical seal area, replace the
same pursuant to the instructions given in the
Pump Disassembly and Assembly
sections.
7.1.2. Dry thread torque
Material
Dry thread torque [N.m.]
M5
M6
M8
M10
M12
M14
M16
M18
M20
8.8
6
10
25
49
86
135
210
290
410
A2
5
9
21
42
74
112
160
210
300
7.1.3. Oiling
The bearings are oiled by immersion in an oil bath.
The pumps are supplied with oil.
•Regularly check the oil level, for example, weekly or every 150 operating hours.
•The first oil change must be carried out after 150 hours of operation.
•Afterwards, it can be changed every 2500 operating hours or at least once a year when operating under normal
conditions.
When change the oil: the oil sump must be filled up to the level in the middle of the peephole.
Do not pour too much oil into the sump.
Leave the pump switched off for a while and then re-check the oil level; if necessary, add a little oil.
Oils for environment temperatures of 5 to 50ºC: SAE 90 or ISO VG 220
PUMP SIZE
Quantity of oil in
the gear case (l.)
HLR 0
0,3
HLR 1
0,5
HLR 2
0,75
HLR 3
1,75
HLR 4
4,5
7.2. STORAGE
Before being stored the pump must be completely emptied of liquids. Avoid, as far as possible, the exposure of the parts to
excessively damp atmospheres.

(A) 2021/11 7.Maintenance 17
7.3. CLEANING
7.3.1. Manual cleaning
The use of aggressive cleaning products such as caustic soda and nitric acid may give rise to skin
burns.
Use rubber gloves during the cleaning process.
Always use protective goggles.
7.3.2. Automatic CIP (cleaning-in-place)
If the pump is installed in a system fitted with a CIP process, there will be no need for stripping.
The recommended minimum liquid speed for an effective process of cleaning is 1,8 m/s (minimum Re > 100 000 at 1,0~2,5
bar).
It is recommended to run the pump during the CIP process (rotation speed ~ nominal speed at 50 Hz).
If it is not fitted with an automatic cleaning process, strip the pump pursuant to the instructions given in the section entitled
Stripping and Assembly of the pump.
Cleaning solutions for CIP processes.
Only use clear water (chloride free) to mix with the cleaning agents:
a) Alkaline solution: 1% in weight of caustic soda (NaOH) to 70ºC (150ºF)
1 kg NaOH + 100 l. water = cleaning solution
or
2.2 l. NaOH to 33% + 100 l. of water = cleaning solution
b) Acid solution: 0.5% in weight of nitric acid (HNO3) to 70ºC (150ºF)
or
0.7 litres HNO3to 53% + 100 l. water = cleaning solution
Monitor the concentration of cleaning solutions; it could give rise to the deterioration of the pump
sealing gaskets.
These solutions are given as examples and should be validated before use on an application.
In order to remove any remains of cleaning products, ALWAYS rinse the element in question with clean water after completing
the cleaning process.
7.3.3. Automatic SIP (sterilization-in-place)
The process of sterilization with steam is applied to all the equipment including the pump.
Do NOT start the pump during the process of sterilization with steam.
The parts/materials suffer no damage if the indications specified in this manual are observed.
No cold liquid can enter the pump till the temperature of the pump is lower than 60°C (140°F).
A flow by-pass is recommended to be used in order to assure the flow of sterile product after the
pump.
Maximum conditions during the SIP process with steam or overheated water
a) Max. temperature: 140°C (284°F)
b) Max. time: 30 min
c) Cooling: Sterile air or inert gas
d) Gasket materials: EPDM / PTFE (recommended)
FPM / NBR (not recommended)

18 7.Maintenance (A) 2021/11
7.4. PUMP DISASSEMBLY
The assembly and disassembly of the pumps should only be done by qualified personnel. Make sure that the personnel read
carefully this instruction manual and, in particular, those instructions which refer to the work they will perform.
Incorrect assembly or disassembly may cause damage in the pump's operation and lead to high
repair costs and a long period of down-time.
INOXPA is not responsible for accidents or damages caused by a failure to comply with the
instructions in this manual.
Preparations
Provide for a clean working environment as some parts, including the mechanical seal, require very careful handling and others
have close tolerances.
Check that the parts which are used are not damaged during transport. When doing this, you need to inspect the adjustment
edge, the butted faces, the tight fit, burrs, etc.
After each disassembly, carefully clean the parts and check for any damage. Replace all damaged parts.
Tools
Use the proper tools for assembly and disassembly operations. Use them correctly.
Cleaning
Before disassembling the pump, clean it on the outside and on the inside.
NEVER clean the pump by hand when it is running
7.4.1. Pump cover disassembly
CAUTION! Liquid may spill from the rotor case when removing the pump cover.
▪Close the suction and delivery valves.
▪Remove the cap nuts (45). Indents have been provided at four
points around the perimeter of the pump cover (03) to assist, if
necessary, in removing it from the rotor case (that is, with the help
of a screwdriver).
▪Check that the seal (80A) is in good condition.
7.4.2. Lobe disassembly
▪Loosen the lobe screws (25) using a spanner. This spanner can be
requested from INOXPA. See spare parts list (Document:
01.504.31.000)
▪These screws have a right-hand thread. In order to prevent the
lobes from turning simultaneously, blocks of wood or plastic can be
placed between the lobes.
▪Check that the O-ring (80) is in good condition.
▪Remove both lobes (02). If necessary, use a tool to assist for this
purpose.
▪Pump size 1, 2, 3, 4: Remove the shims (32) mounted on each
shaft. If more than one is mounted on each shaft, keep them
separate to prevent them from getting mixed up.
▪Pump size 0: Remove the shaft sleeve (13) mounted on each
shaft. Sleeves are not interchangeable. Remember the shaft each
sleeve was mounted on.

(A) 2021/11 7.Maintenance 19
7.4.3. Disassembly of mechanical seals
As a result of the pump design, it is not necessary to disassemble the rotor case (01) in order to assemble/disassemble the
mechanical seals. Rotatory part is directly mounted to lobe housing. Stationary part is directly mounted to the rotor case.
Pump size 0
Due to the compact design, Mechanical Seals are mounted on shaft sleeves.
Consult section 7.7
Assembly and Disassembly of the Mechanical Seals
7.4.4. Rotor case disassembly
Pumps Size 0:
•Remove the Allen screws (51B) that fix the rotor case to the gear
case (06).
•Remove the rotor case (01) using Nylon hammer if necessary.
Pumps Size 1, 2, 3, 4:
•Loosen and remove the nuts (54A) that fix the rotor case (01) to
the gear case (06).
•Remove the rotor case (01) using Nylon hammer if necessary.
7.4.5. Lubrication oil drainage
•Place a container underneath the gear case (06) to collect the
lubricant oil so that it can be recycled.
•Remove the drainage plug (87) located to the rear of gear case.
HLR 0 HLR 1,2,3,4
Table of contents
Other INOXPA Water Pump manuals

INOXPA
INOXPA HYGINOX SE Series Manual

INOXPA
INOXPA RV Manual

INOXPA
INOXPA TLS Series Manual

INOXPA
INOXPA KIBER KSF Series Installation and user guide

INOXPA
INOXPA Hyclean Series Manual

INOXPA
INOXPA ESTAMPINOX EFI Manual

INOXPA
INOXPA HLR Ex Manual

INOXPA
INOXPA KIBER KS Series Manual

INOXPA
INOXPA ASPIR A-50 Manual

INOXPA
INOXPA SLRT 3-90 Manual