SHORT FOREWORD.......................................................................................................5
INTRODUCTION................................................................................................................6
1 TEST SET DESCRIPTION AND USE...................................................................9
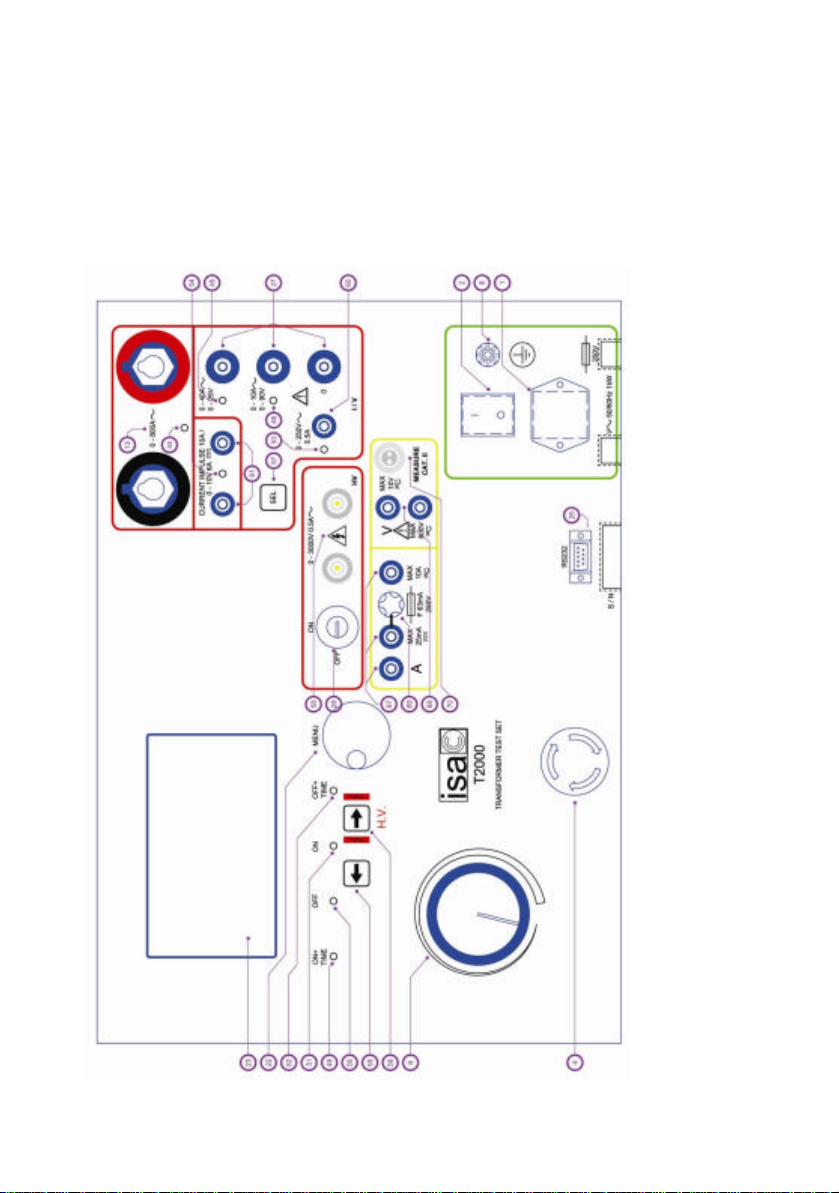
1.1 THE FRONT PANEL....................................................................................................9
1.2 THE POP-UP MENU.................................................................................................12
1.2.1 Transformers selection....................................................................13
1.3 POWER-ON...............................................................................................................18
1.4 OUTPUTS DESCRIPTION AND HAZARDOUS SITUATIONS .........................20
1.4.1 Main current and voltage outputs............................................20
1.4.2 HV voltage output................................................................................22
1.4.3 Hazardous situation summary...................................................23
1.5 CURRENT GENERATION.........................................................................................24
1.6 OPTIONAL THERMAL PRINTER.............................................................................26
1.7 PROTECTIONS .........................................................................................................26
2 TRANSFORMERS TESTING FUNDAMENTALS...........................................30
2.1 CURRENT TRANSFORMERS...................................................................................30
2.2 REMANENCE..............................................................................................................31
2.3 HIGH CURRENT TESTS..........................................................................................31
2.4WINDING RESISTANCE TEST.............................................................................31
3 WHAT’S INSIDE?.......................................................................................................33
3.1 PHYSICAL DESCRIPTION.....................................................................................33
3.2 DETAILED FUNCTION DESCRIPTION................................................................37
3.2.1 Main output transformer, XTF10350 (5).............................37
3.2.2 Main front board PWA11411 (17).............................................38
3.2.3 TRANSFORMERS board PWA21412 (83)...............................38
3.2.4 CONV-T 3000 board PWA21401 (16).....................................39
3.2.5 INTE ON-OFF T 3000 board PWA11410 (7)........................40
3.2.6 MICR T1000 board PWA41300 (15)........................................40
4 THE HELL, IT DOESN’T WORK..........................................................................42
4.1 INTRODUCTION.......................................................................................................42
4.2 ERROR MESSAGES.................................................................................................42
4.3 TROUBLE SHOOTING.............................................................................................46
4.4 AT POWER-ON DOES NOT TURN ON.................................................................47
4.5 NO OUTPUT FROM THE MAIN CURRENT AND VOLTAGE..............................48
4.6 THE AC VOLTAGE MEASUREMENT IS NOT STABLE......................................48
4.7 PROBLEMS DURING UPGRADE............................................................................48
4.8 FALSE ALARM OF MISSING GROUND CONNECTION....................................49