3
2.0 Table of Contents
Section Page
1.0 Warranty and Service.....................................................................................................................................2
2.0 Table of Contents...........................................................................................................................................3
3.0 Safety Warnings.............................................................................................................................................4
4.0 Specifications.................................................................................................................................................6
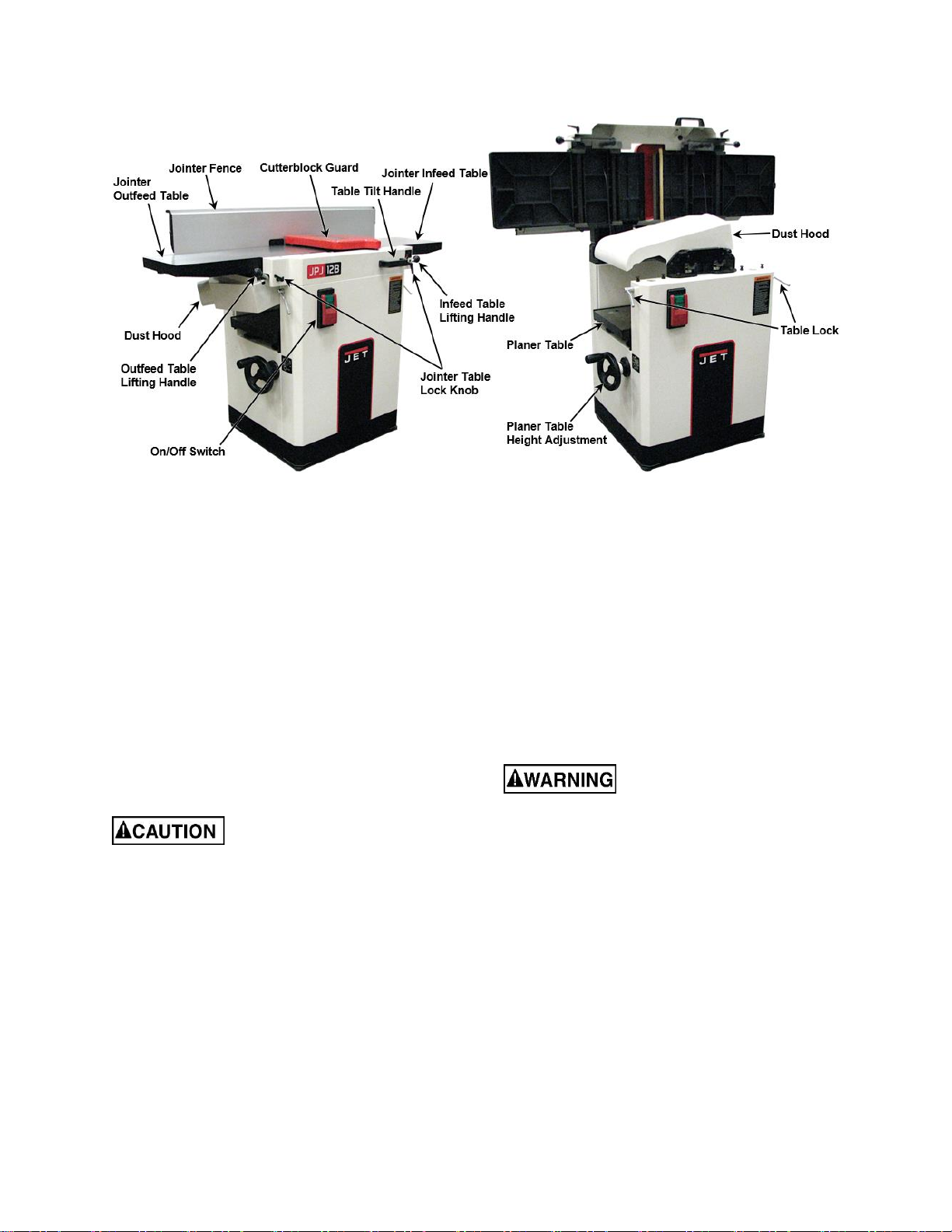
5.0 Features and Terminology .............................................................................................................................7
6.0 Receiving .......................................................................................................................................................7
7.0 Unpacking ......................................................................................................................................................7
9.1 Contents of Shipping Container .................................................................................................................7
8.0 Electrical Connection .....................................................................................................................................7
9.0 Operating Controls.........................................................................................................................................8
9.1 Jointer to Planer Setup...............................................................................................................................8
9.2 Planer to Jointer Setup...............................................................................................................................8
9.3 Control Switch............................................................................................................................................9
9.4 Planer Controls and Adjustments...............................................................................................................9
9.5 Jointer Controls and Adjustments ..............................................................................................................9
10.0 Adjustments ...............................................................................................................................................10
10.1 Fence Stop Adjustments ........................................................................................................................10
10.2 Table and Knife Adjustments .................................................................................................................11
10.3 Coplanar Alignment................................................................................................................................11
10.4 Setting Knives at Correct Height and Parallel to Outfeed Table ............................................................13
10.5 Replacing Cutterhead Knives (Straight Knives Only).............................................................................15
10.6 Replacing or Rotating Knife Inserts (Helical Cutterhead Only) ..............................................................16
10.7 Jointer Table Lock Handle Adjustment...................................................................................................16
10.8 Belt Replacement...................................................................................................................................17
10.9 Feed Roller Height Adjustment ..............................................................................................................18
10.10 Feed Roller Pressure Adjustment ........................................................................................................18
10.11 Planer Table Adjustment......................................................................................................................19
11.0 Basic Operations........................................................................................................................................20
11.1 Dust Collection .......................................................................................................................................20
11.2 Initial Startup ..........................................................................................................................................20
11.3 Changing Mode of Operation .................................................................................................................20
11.4 Jointer Operations..................................................................................................................................20
11.5 Planer Operations ..................................................................................................................................22
12.0 Maintenance...............................................................................................................................................23
12.1 Blade Care .............................................................................................................................................23
12.2 Sharpening the Knives (Straight Knives Only) .......................................................................................24
13.0 Lubrication..................................................................................................................................................24
14.0 Troubleshooting the JPJ-12B,JPJ-12BHH.................................................................................................25
14.1 Performance Troubleshooting –Jointer.................................................................................................25
14.2 Performance Troubleshooting –Planer..................................................................................................26
14.3 Mechanical Troubleshooting –Planer/Jointer........................................................................................27
15.0 Replacement Parts.....................................................................................................................................27
15.1 Infeed Table Assembly –Exploded View...............................................................................................28
15.2 Infeed Table Assembly –Parts List........................................................................................................29
15.3 Outfeed Table Assembly –Exploded View............................................................................................30
15.4 Outfeed Table Assembly –Parts List.....................................................................................................31
15.5 Cutterhead Assembly –Exploded View.................................................................................................32
15.6 Cutterhead Assembly –Parts List..........................................................................................................33
15.7 Planer Table Assembly –Exploded View...............................................................................................34
15.8 Planer Table Assembly –Parts List .......................................................................................................35
15.9 Blade Guard Assembly –Exploded View...............................................................................................36
15.10 Blade Guard Assembly –Parts List......................................................................................................37
15.11 Gearbox Assembly –Exploded View...................................................................................................38
15.12 Gearbox Assembly –Parts List............................................................................................................39
15.13 Cabinet Assembly –Exploded View.....................................................................................................40
15.14 Cabinet Assembly –Parts List .............................................................................................................41
15.15 Fence Assembly –Exploded View.......................................................................................................43
15.16 Fence Assembly –Parts List................................................................................................................44
16.0 Electrical Connections for JPJ-12B, JPJ-12BHH.......................................................................................45
17.0 Optional Accessories .................................................................................................................................46