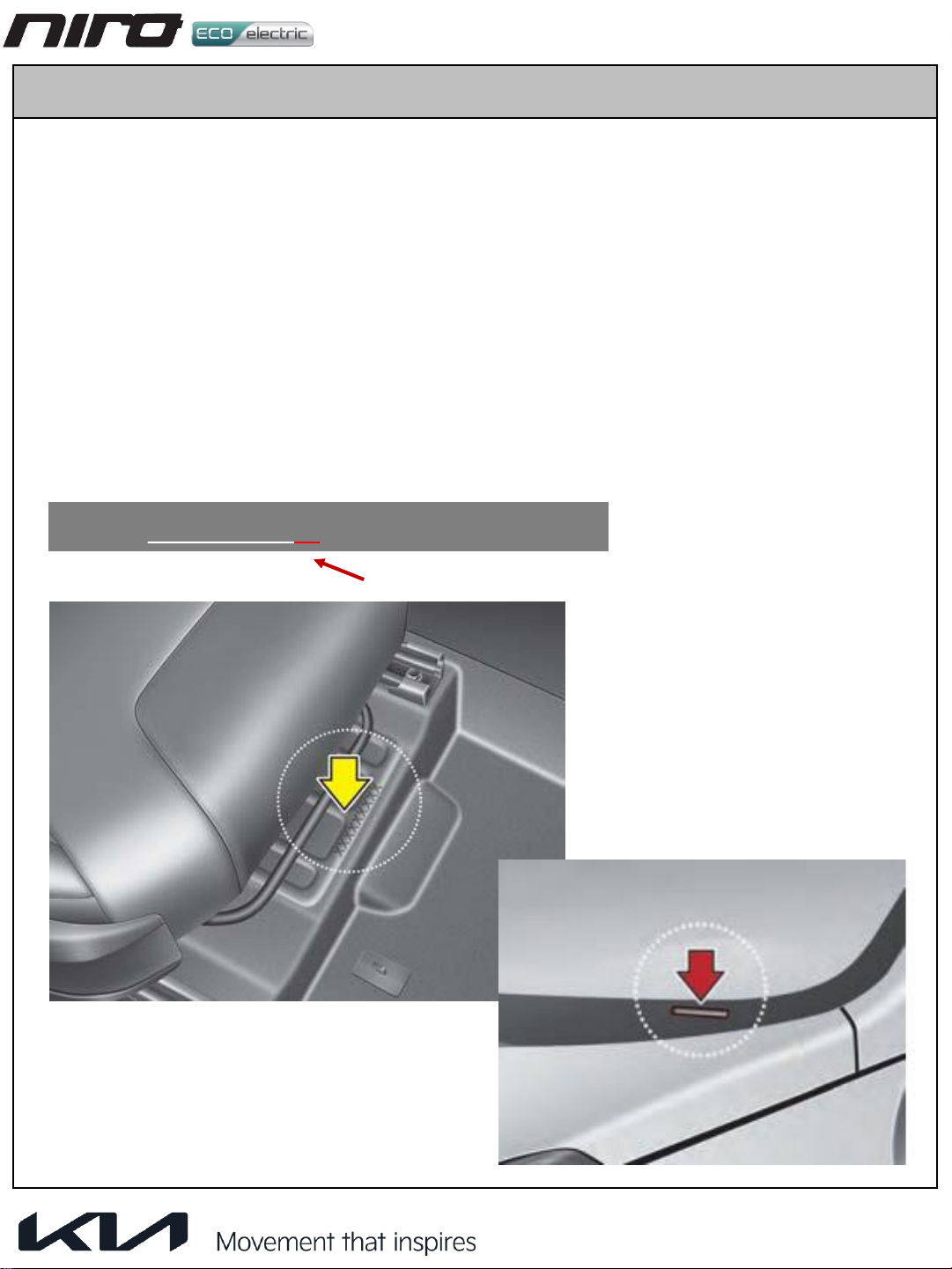
Kia Niro EV User manual
Other Kia Automobile manuals
Kia
Kia Sorento 4wd 2011 Instruction manual

Kia
Kia Cadenza User manual

Kia
Kia SEPHIA 2000 User manual

Kia
Kia stinger 2022 User manual

Kia
Kia Rio 2008 User manual

Kia
Kia Niro 2018 User manual

Kia
Kia Automobile User manual

Kia
Kia Carnival 2022 Assembly instructions

Kia
Kia 2015 Soul Parts list manual

Kia
Kia Soul 2024 User manual

Kia
Kia niro hybrid 2021 Parts list manual

Kia
Kia Soul 2022 User manual

Kia
Kia Automobile User manual

Kia
Kia Sorento 2018 Parts list manual

Kia
Kia Sportage 2013 User manual

Kia
Kia Carnival User manual

Kia
Kia Sorenta User manual

Kia
Kia Carens 2022 User manual

Kia
Kia Niro EV User manual

Kia
Kia Carnival 2007 Instruction manual