KOBELT MANUFACTURING CO. LTD MNL-5040-SA.docx (rev B) 2
Table of Contents
1Introduction ..................................................................................................................4
1.1 Contact Information......................................................................................................4
1.2 Safety Information ........................................................................................................4
1.2.1 Safety Instructions ....................................................................................................4
1.2.2 Hazards .....................................................................................................................5
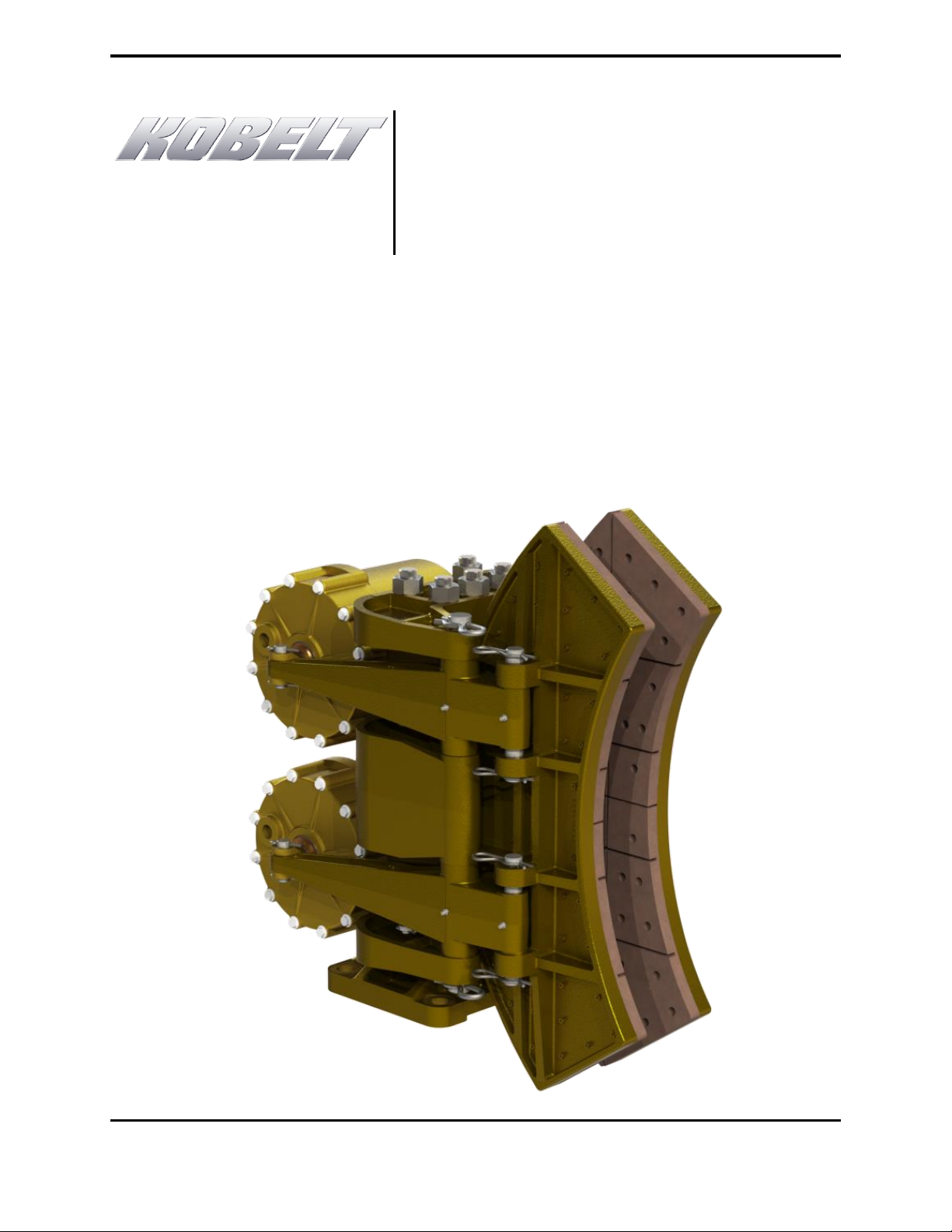
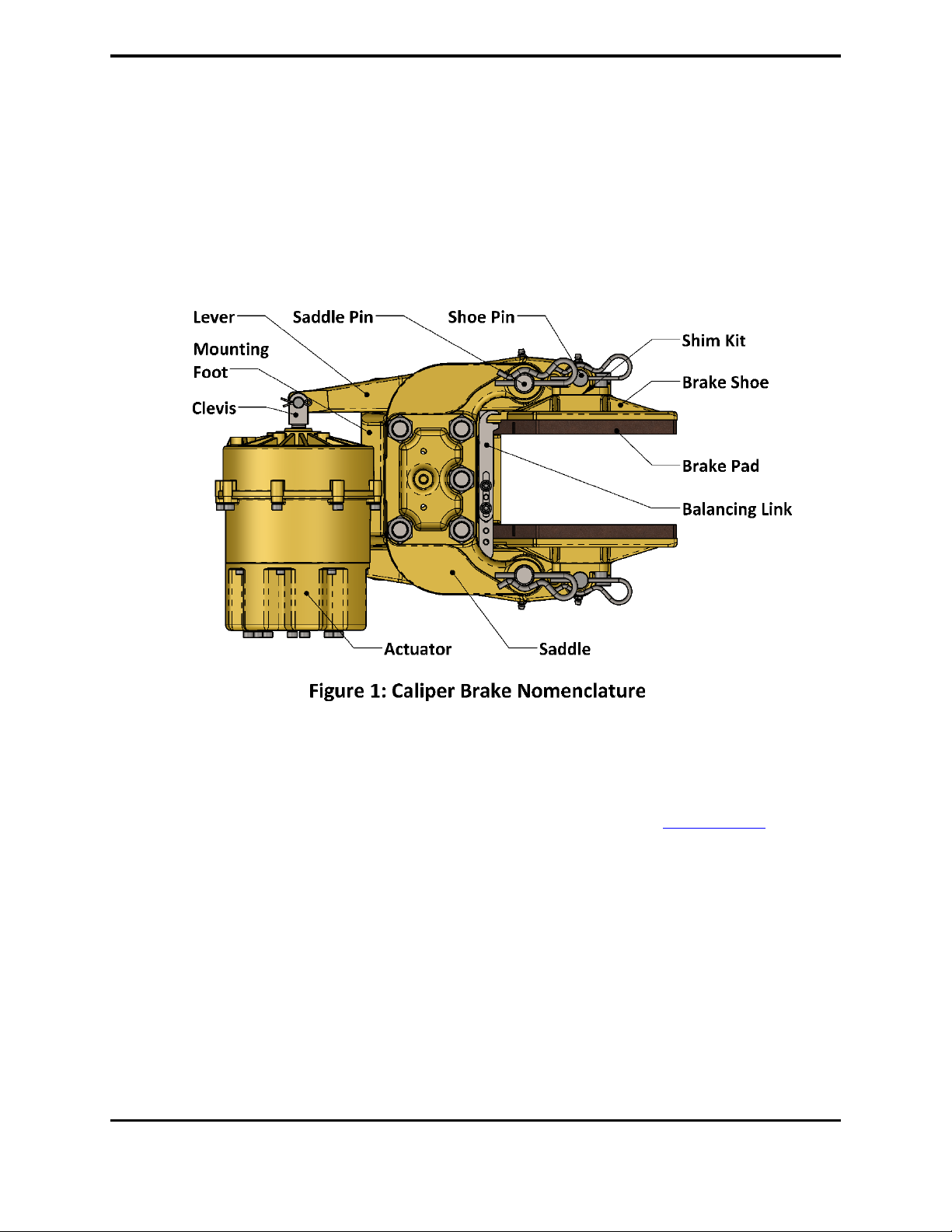
1.3 Product Description.......................................................................................................6
1.3.1 Overview...................................................................................................................6
1.4 Technical Data...............................................................................................................6
2Installation ....................................................................................................................7
2.1 Preparation ...................................................................................................................7
2.2 Brake Discs ....................................................................................................................7
2.3 Caliper brakes................................................................................................................9
2.3.1 Mechanical................................................................................................................9
2.3.2 Piping ........................................................................................................................9
2.3.3 Instrumentation......................................................................................................10
3Commissioning ............................................................................................................11
3.1 Flushing.......................................................................................................................11
3.2 Air Gap ........................................................................................................................11
3.3 Function Test...............................................................................................................11
3.4 Burnishing ...................................................................................................................11
3.5 Torque Test .................................................................................................................12
4Operation....................................................................................................................13
4.1 Functional Requirements ............................................................................................13
4.1.1 Pressure Supply.......................................................................................................13
4.1.2 Control ....................................................................................................................14
4.2 Service Limits ..............................................................................................................14
4.2.1 Disc Temperature....................................................................................................14
4.2.2 Ambient Temperature ............................................................................................14
4.2.3 Pressure ..................................................................................................................14
4.2.4 Disc speed...............................................................................................................14
5Maintenance ...............................................................................................................15
5.1 Preventative Maintenance..........................................................................................15
5.2 Inspection....................................................................................................................15
5.2.1 Pad Wear ................................................................................................................15
5.2.2 Seals........................................................................................................................16
5.2.3 Actuator Test ..........................................................................................................16
5.2.4 Pin Wear .................................................................................................................16
5.2.5 Brake Disc ...............................................................................................................16