3. OPERATING GUIDE - CHARGING
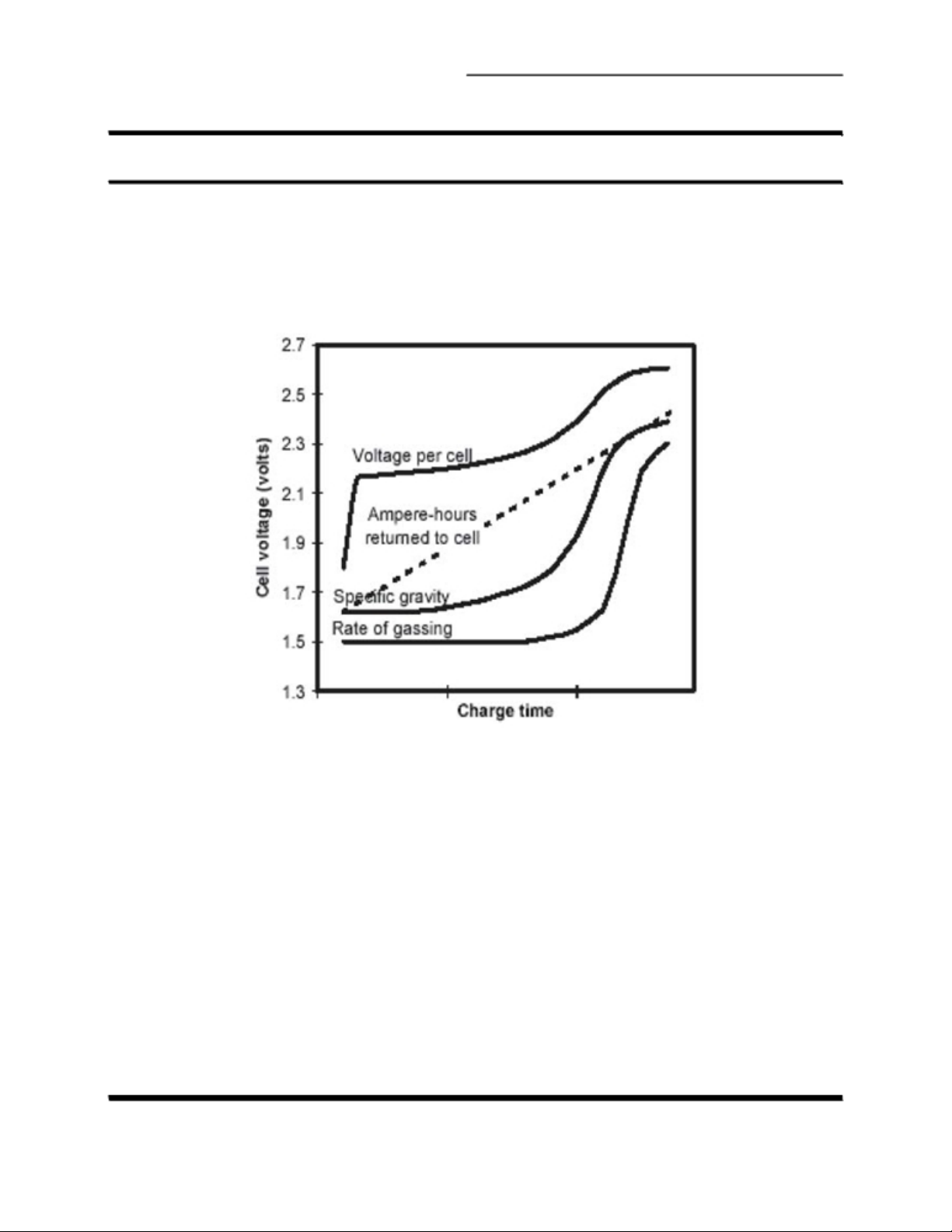
acid batteries should never be charged in a constant-current mode with a current
greater than C /10 (C equals the rated ampere-hour capacity of the battery). During
constant current charging at a rate in excess of C /10, oxygen is produced at an
excessive rate. The resulting increasing pressure will cause the cell to vent. Venting
of gasses results in a depletion of electrolyte. As the electrolyte cannot be replaced in
a sealed battery, the cell will dry out resulting in a decrease in capacity and
eventually battery failure. Therefore constant-potential charging is the
recommended charge method for sealed batteries (SLAB).
3.2
CHARGING METHODS
There are two main methods of charging a battery: 1) constant current; and 2)
constant potential. In what follows both methods will be described in some detail.
3.2.1 CONSTANT-CURRENT CHARGE METHOD (CI)
In this method the current remains at a preset level while the voltage can reach a
high level, e.g. 34-37 volts.
An advantage of the constant-current charge method is that the ampere-hour input
into the battery can be determined precisely by multiplying the charging current
with the charge time in hours. However, it is necessary to ensure that the battery is
not charged at a high rate for an excessive period of time. Such overcharging can
result in overheating, excessive gassing, and possible damage to the battery.
3.2.2 CONSTANT-POTENTIAL CHARGE METHOD (CP)
A charge source applies a fixed (constant) voltage (potential) to the battery. The
current supplied by the charge source fluctuates (rises and falls) with the battery
voltage.
There are several advantages of the constant-potential charge method. First, there
is less danger of gassing at an excessive rate. Secondly, batteries of the same
nominal voltage but with different capacities can be connected in parallel directly to
the charging source. Thirdly, batteries are charged more rapidly and with less
attention.
3.2.3 LEAD-ACID BATTERIES
With the constant-current charge method the voltage can climb to 34-37 volts.
Therefore, this method should normally not be used to charge lead-acid batteries,
especially not the sealed type (SLAB). It is preferred to charge a sealed lead-acid
battery in constant-potential mode at a voltage of 28.6 ± 0.2 volts for four hours or
until the charge current drops below one ampere.
CA-1550 CHARGER / ANALYZER - OPERATING MANUAL LI-4159-CML Rev A Page 6