Leuze electronic MLC 520 EX 3
1 About this document . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
1.1 Used symbols and signal words . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
1.2 Checklists . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
2 Safety . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
2.1 Approved purpose and foreseeable improper operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
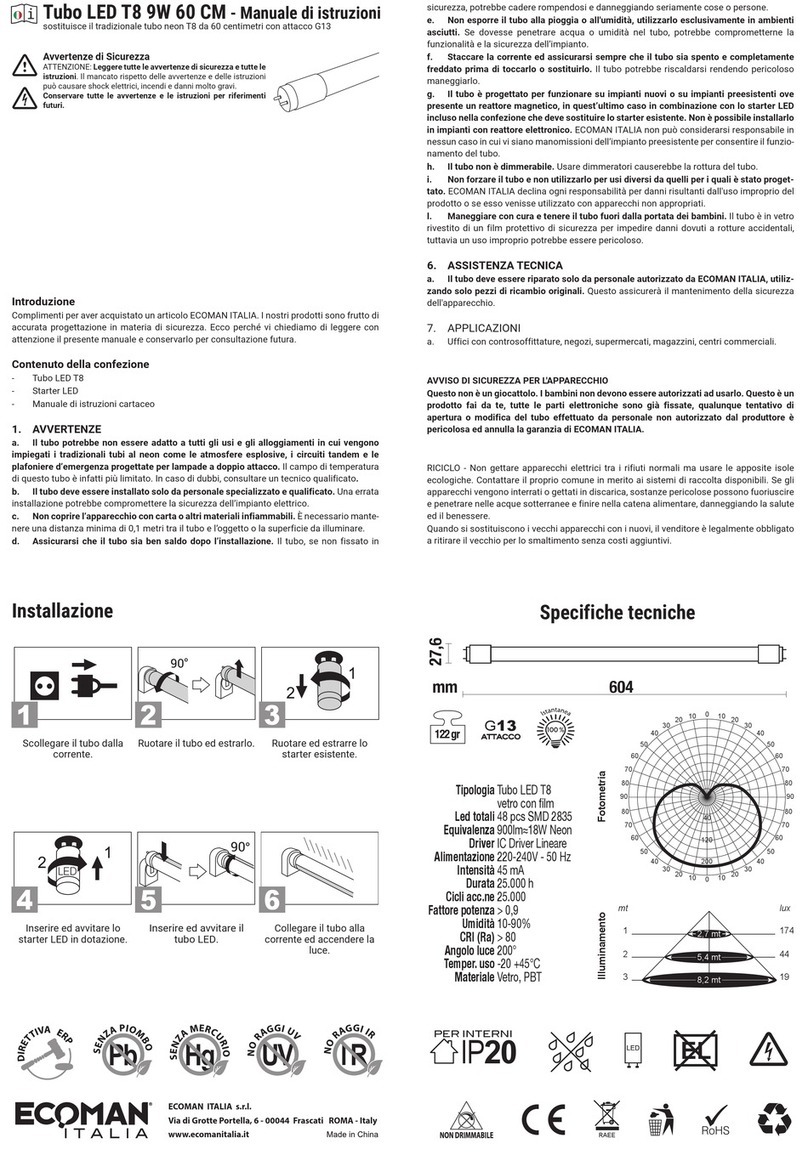
2.1.1 Intended use . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
2.1.2 Foreseeable misuse . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
2.2 Competent persons . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
2.3 Responsibility for safety. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
2.4 Disclaimer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
2.5 Notices for the safe use of sensors in potentially explosive areas . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
3 Device description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
3.1 Device overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
3.2 Connection technology . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
3.3 Display elements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
3.3.1 Operating indicators on the MLC 520 receiver . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
3.3.2 Alignment display . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
4 Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
4.1 Start/restart interlock RES . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
4.2 EDM contactor monitoring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
4.3 Transmission channel changeover . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
4.4 Range reduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
5 Applications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
5.1 Point of operation guarding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
5.2 Access guarding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
5.3 Danger zone guarding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
6 Mounting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
6.1 Arrangement of transmitter and receiver . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
6.1.1 Calculation of safety distance S . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
6.1.2 Calculation of safety distance SRT or SRO if protective fields act orthogonally
to the approach direction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
6.1.3 Calculation of safety distance S for parallel approach to the protective field . . . . . . . . . . 24
6.1.4 Minimum distance to reflective surfaces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
6.1.5 Preventing mutual interference between adjacent devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
6.2 Mounting the safety sensor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
6.2.1 Suitable mounting locations. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
6.2.2 Definition of directions of movement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
6.2.3 Fastening via BT-NC60 sliding blocks. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
6.2.4 Fastening with BT-R swivel mount . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
6.2.5 One-sided mounting on the machine table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
6.3 Mounting accessories . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
6.3.1 Deflecting mirror for multiple-side guarding. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
7 Electrical connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
7.1 Pin assignment transmitter and receiver . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
7.1.1 MLC 500 transmitter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
7.1.2 MLC 520 receiver . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
7.2 Circuit diagram examples . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36