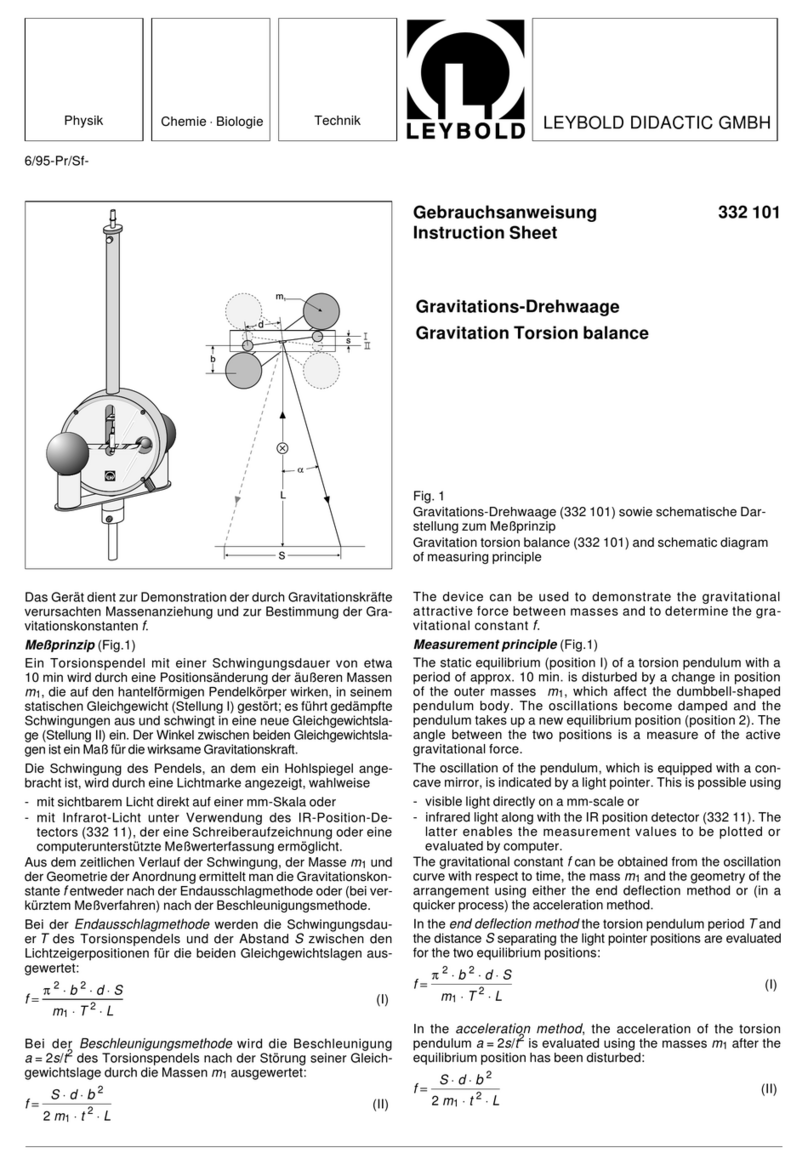
an erroneous reading. To check this, you may need to connect
an oscilloscope at output
6
.
3.2 Current measurement
Connect the screened cable at BNC input
3
and supply the
measurement signal.
Set the current measuring range on
8
so that (depending on
the measuring instrument) the output signal connected is about
0.3 V to 3 V (maximum 10 V).
The measured value is determined by multiplying the measu-
ring range by the numerical value of the output voltage (measu-
red in volts).
Example: Measuring range: 10-8 A
Output voltage: 1.3 V
Measured value: 1.3 ⋅10-8 A
Important:
- Screen the input as well as possible to avoid input interference,
e.g. from the mains frequency. When conducting stationary cur-
rent measurement, a capacitor, e.g. 0.5 µF (538 04), can be con-
nected parallel to the screened-cable input for smoothing (see
also 3.1).
- Do not disturb the screened cable during the experimentto
prevent charge shifts.
- Isolate the measuring point from other current sources (e.g.
also from the insulation of voltage-bearing leads and the
benchtop) to minimize leakage currents. Compensate any re-
maining input offset currents using the zero-point adjuster on
7
.
3.3 Voltage measurement
Attention:
use only non-hazardous contact voltages (see secti-
on 1)
Connect the measuring lead at BNC input
2
and supply the
measurement signal.
Set the voltage-measuring range on
8
so that (depending on
the measuring instrument) the output signal connected is about
0.3 V to 3 V (maximum 10 V).
The measured value is determined by multiplying the measu-
ring range by the numerical value of the output voltage (measu-
red in volts).
Example: Measuring range: 101V
Output voltage: 0.7 V
Measured value: 7 V
3.4 Charge measurement
Important:
The input current may not be greater than approx. 5 mA, as
otherwise the amplifier is overdriven and the measuring result
is falsified. Therefore, at e.m.f. values greater than 500 V an
additional resistor of e.g. 1 MΩ(for voltages up to 5 kV) must be
connected in front of the amplifier input.
Connect the measuring lead at BNC input
3
and supply the
measurement signal; for e.m.f. values over 500 V, always use
an additional resistor of e.g. 1MΩ.
Set the measuring range so that (depending on the measuring
instrument) the output signal connected is about 0.3 V to 3 V
(maximum 10 V).
The measured value of the charge is determined by multiplying
the selected measuring range by the numerical value of the out-
put voltage (measured in volts).
Example: Measuring range: 10-8 As
Output voltage: 3 V
Measured value: 3 ⋅10-8 As
metrischen Brumm zu Null. Das Brumm-Signal am Ausgang
darf 10 VSnicht überschreiten, weil es sonst unsymmetrisch
begrenzt wird und deshalb zu einer Fehlanzeige führt. Im Zwei-
fel mit Oszilloskop am Ausgang
6
überprüfen.
3.2 Strommessung
Meßkabel am BNC-Eingang
3
anschließen und Meßsignal zu-
führen.
Strom-Meßbereich an
8
so wählen, daß Ausgangssignal (je
nach angeschlossenem Meßinstrument) etwa 0,3 V bis 3 V
(maximal 10 V) beträgt.
Der Meßwert ergibt sich durch Multiplikation des Meßbereiches
mit dem Zahlenwert der (in Volt gemessenen) Ausgangsspan-
nung.
Beispiel: Meßbereich: 10-8 A
Ausgangsspannung: 1,3 V
Meßwert: 1,3 ⋅10-8 A
Wichtig:
- Eingang möglichst abschirmen, um Einstreuungen z.B. der
Netzfrequenz zu vermeiden. Bei stationärer Strommessung
kann zur Glättung ein Kondensator, z.B. 0,5 µF (538 04), par-
allel zum Meßkabeleingang gelegt werden (siehe auch 3.1).
- Meßkabel während der Messung nicht verformen, um La-
dungsverschiebungen zu vermeiden.
- Meßstelle von anderen Stromquellen (z.B. auch von der Iso-
lierung spannungsführender Kabel und Tischplatte) separie-
ren, um Kriechströme zu minimieren. Verbleibende Fehlströ-
me über den Nullpunkt-Stellen an
7
kompensieren.
3.3 Spannungsmessung
Achtung:
Nur mit nicht berührungsgefährlichen Spannungen ar-
beiten (s. Abschnitt 1)
Meßkabel an BNC-Eingang
2
anschließen und Meßsignal zu-
führen.
Spannungs-Meßbereich an
8
so wählen, daß das Ausgangssig-
nal (je nach angeschlossenem Meßinstrument) etwa 0,3 V bis
3 V (maximal 10 V) beträgt.
Der Meßwert ergibt sich durch Multiplikation des Meßbereiches
mit dem Zahlenwert der (in Volt gemessenen) Ausgangsspan-
nung.
Beispiel: Meßbereich: 101V
Ausgangsspannung: 0,7 V
Meßwert: 7 V
3.4 Ladungsmessung
Wichtig:
Der Eingangsstrom darf nicht größer als etwa 5 mA werden,
sonst ist der Verstärker übersteuert und das Meßergebnis wird
verfälscht. Bei Urspannungen über 500 V muß deshalb ein
zusätzlicher Widerstand von z.B. 1 MΩ(für Spannungen bis
5 kV) vor den Verstärkereingang gelegt werden.
Meßkabel am BNC-Eingang
3
anschließen und Meßsignal zu-
führen, bei Urspannungen über 500 V nur über zusätzlichen
Widerstand von z.B. 1MΩ.
Meßbereich so wählen, daß das Ausgangssignal (je nach an-
geschlossenem Meßinstrument) etwa 0,3 V bis 3 V (maximal
10 V) beträgt.
Der Ladungs-Meßwert ergibt sich durch Multiplikation des ge-
wählten Meßbereiches mit dem Zahlenwert der (in Volt gemes-
senen) Ausgangsspannung.
Beispiel: Meßbereich: 10-8 As
Ausgangsspannung: 3 V
Meßwert: 3 ⋅10-8 As
3