Linksys HGA9N User manual
Other Linksys Antenna manuals

Linksys
Linksys WRT610N V2 User manual

Linksys
Linksys HGA9N Original operating instructions

Linksys
Linksys HGA7T Operation manual

Linksys
Linksys AS2TNC Operation manual

Linksys
Linksys HGA9N Operation manual

Linksys
Linksys AE3000 User manual

Linksys
Linksys HGA7S Operation manual

Linksys
Linksys AS1SMA Operation manual
Popular Antenna manuals by other brands

Alfa Network
Alfa Network APA-L01 Specifications

Naval
Naval PR-422CA Operation manual

Feig Electronic
Feig Electronic ID ISC.ANTH200/200 Series manual

TERK Technologies
TERK Technologies TV44 owner's manual

Directive Systems & Engineering
Directive Systems & Engineering DSE2324LYRMK quick start guide

HP
HP J8999A instructions

CommScope
CommScope CMAX-OMFX-43M-I53 Installation instruction

Ramsey Electronics
Ramsey Electronics DAP25 Kit assembly and instruction manual

COBHAM
COBHAM SAILOR 800 VSAT Replacement procedure
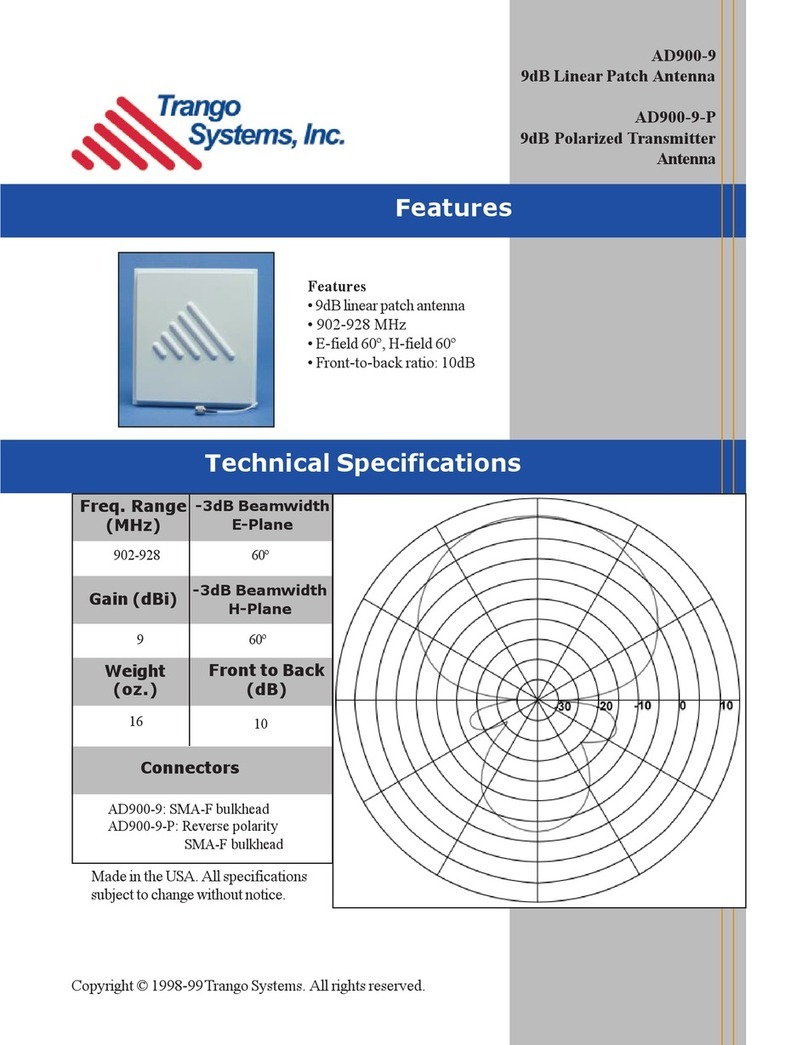
Trango Systems
Trango Systems AD900-9 Specification sheet

Steren
Steren ANT-100 user manual

IWCS
IWCS iriBelt II Quick start user guide















