Murata GQM2195C2E2R0WB12 Series User manual
Other Murata Industrial Electrical manuals
Murata
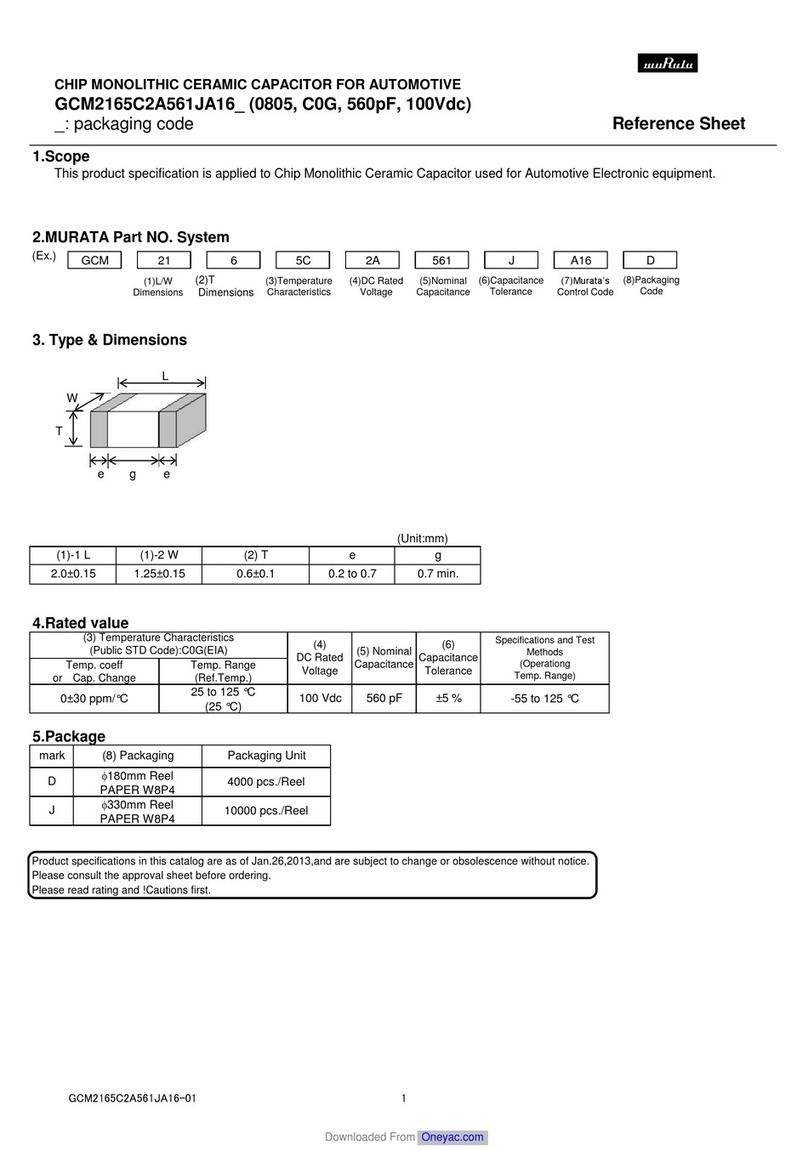
Murata GCM2165C2A561JA16 Series User manual
Murata
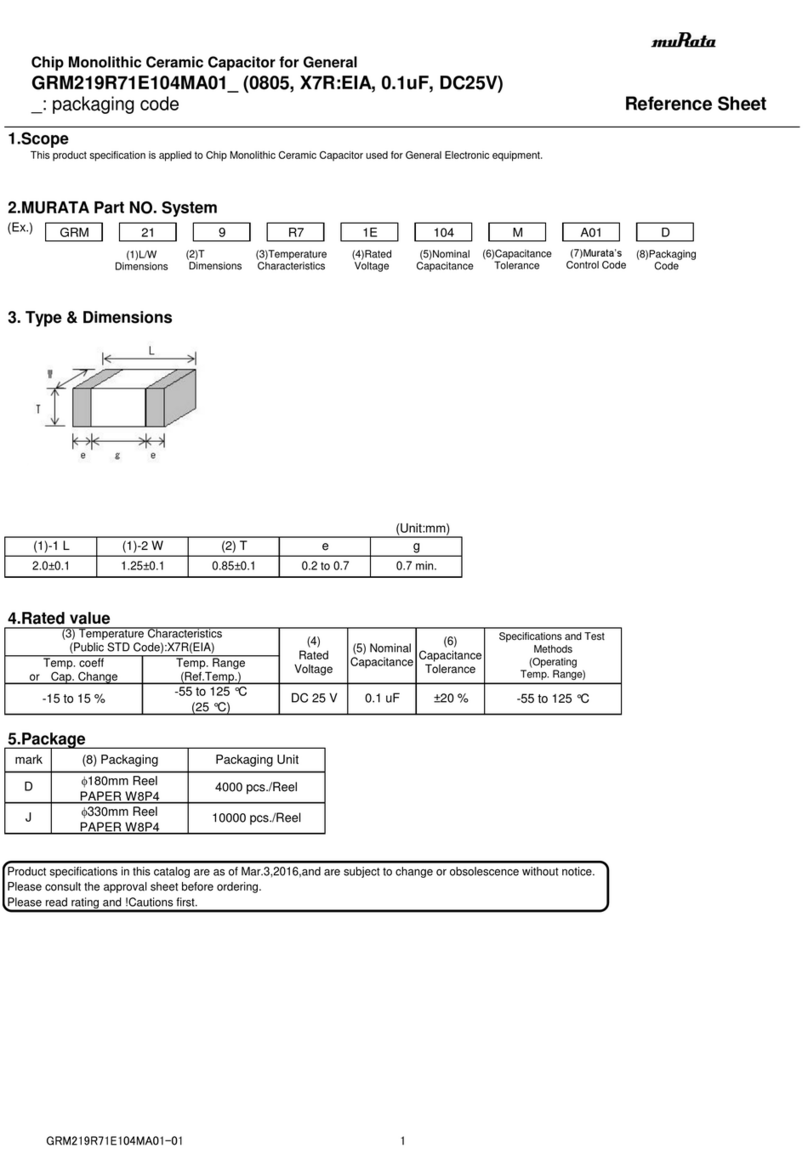
Murata GRM219R71E104MA01 Series User manual
Murata
Murata GRM32ER61A226KE20 Series User manual
Murata
Murata GRM2165C1H362JA01 Series User manual

Murata
Murata GRT32DC81E106ME01 Series User manual
Murata
Murata GRM0335C1H5R6CA01 Series User manual
Murata
Murata GRM0335C1H300JA01 Series User manual
Murata
Murata GRT155R61A225KE01 Series User manual
Murata
Murata GRM0335C1H1R8WA01 Series User manual
Murata
Murata GRM21BR60G336ME15 Series User manual

Murata
Murata GRM219R71E224KA01 Series User manual
Murata
Murata GRM1555C1H8R2CA01 Series User manual
Murata
Murata GRM0225C1E6R3DA03 Series User manual
Murata
Murata GRM033R61C563KE84 Series User manual
Murata
Murata GRM0335C1H5R9BA01 Series User manual

Murata
Murata GRM219R71C564KA01 Series User manual
Murata
Murata GRM0225C1E1R2WA03 Series User manual

Murata
Murata GCM1885C1H1R5CA16 Series User manual

Murata
Murata GQM2195C2E1R8WB12 Series User manual
Murata
Murata GRM0225C1E8R7BA03 Seres User manual
Popular Industrial Electrical manuals by other brands

Rexroth Indramat
Rexroth Indramat DURADRIVE SYSTEM200 Project planning manual

Abtech
Abtech HVJB Series Installation, operation & maintenance instructions

SAF-HOLLAND
SAF-HOLLAND CBX 5415.5 Installation and operation manual

Eaton
Eaton Ulusoy HMH24-04 user manual

Newlong
Newlong NP-7H NSTRUCTION MANUAL/PARTS LIST

Stahl
Stahl 8575/12 operating instructions
SI
SI Pegasus installation instructions

Cooper Power Systems
Cooper Power Systems VXE15 Installation and operation instructions
S&C
S&C Vista SD manual

Siemens
Siemens 3VA9988-0BM10 operating instructions

Siemens
Siemens SITRANS LVS100 operating instructions
Rockwell Automation
Rockwell Automation Allen-Bradley MP-Series installation instructions