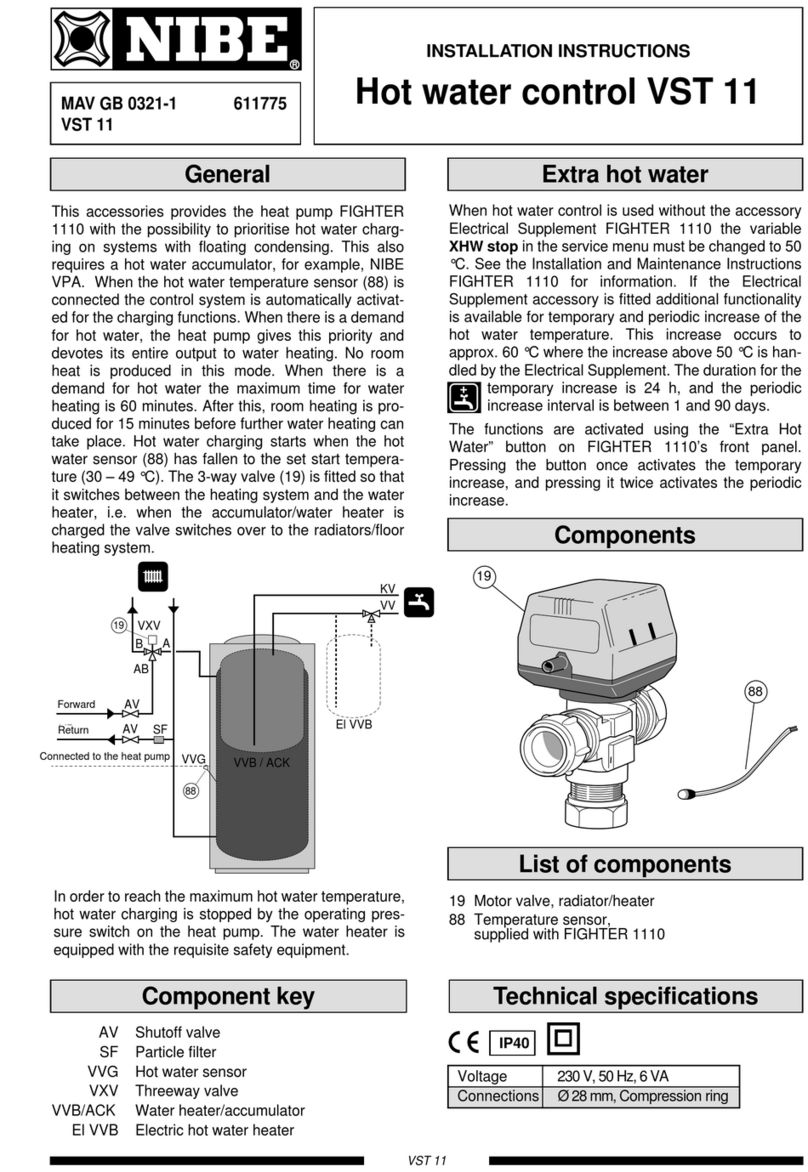
■Reusable mechanical connectors and collared joints
are not permitted indoors.
■Refrigerant pipes must be protected or recessed to
prevent damage.
■Must be accessible for future maintenance.
National gas regulations must be observed.
Maximum amount of refrigerant: See Technical specific-
ations.
■Everyone who works with or opens a refrigerant cir-
cuit must have a current, valid certificate from an
accredited industry issuing body, which states that,
according to the industry's recognised assessment
standard, they have the authority to safely handle
refrigerants.
■Servicing must only be performed according to the
equipment manufacturer's recommendations.
Maintenance and repairs that require the assistance
of another trained person must be carried out under
the supervision of person with the authority to handle
combustible refrigerants.
Maintenance and repair that requires the skill of anoth-
er person must be carried out under the supervision of
someone with the above expertise.
Before work is started on systems that contains com-
bustible refrigerants, safety checks must be performed
to ensure that the ignition risk is kept to a minimum.
The work must be carried out in a controlled way to
minimise the risk of contact with combustible gas or
liquid during the work.
All maintenance staff and those who work in close
proximity to the product must be instructed which type
of work is to be carried out. Avoid carrying out work
in enclosed spaces. The area surrounding the worksite
must be cordoned off. Ensure that the area is made
safe by removing combustible material.
Check whether there is refrigerant in the area using a
suitable refrigerant detector prior to and during work,
to notify the service technician whether there is a pos-
sible flammable atmosphere or not. Ensure that the
refrigerant detector is suitable for combustible refriger-
ant, i.e. does not generate sparks or cause ignition in
any other way.
If hot work is carried out on the heat pump, a powder
or carbon dioxide fire extinguisher must be to hand.
Those who carry out work with refrigerant system
connections, including exposing pipes that contain or
have contained combustible refrigerant, may not use
potential ignition sources in such a way that that can
lead to risks of fire or explosions.
All potential ignition sources, including cigarette
smoking, should be kept at a safe distance from the
service work area where combustible refrigerant can
leak out. Before carrying out work, the area surround-
ing the equipment must be checked to ensure that
there are no ignition risks. "No smoking" signs must be
displayed.
Ensure that the work is carried out outdoors or that
the work area is ventilated before the system is opened
and before any hot work is carried out. The area must
be ventilated whilst the work is being carried out. There
must be ventilation around any refrigerant that comes
out, which should be routed outdoors.
If electrical components are replaced, the replacement
parts must be fit for purpose and have the correct
technical specifications. Always follow the manufac-
turer's guidelines regarding maintenance and servicing.
Contact the manufacturer's technical department in
the event of any doubts.
The following checks must be carried out for installa-
tions that use combustible refrigerants.
■The filling quantity is appropriate for the size of the
space where the parts that contain refrigerant are
installed.
■Ventilation equipment and outlet work correctly and
without obstructions.
■If an indirect refrigerant circuit is used, check
whether the secondary circuit contains refrigerant.
■All markings of equipment are visible and clear.
Markings, signs and similar that are not clear must
be replaced.
■Refrigerant pipes and components are positioned in
such a way that it is not likely that they be subjected
to substances that can corrode components contain-
ing refrigerant, if these components are not made
of material that is resistant against corrosion, or not
appropriately protected against such corrosion.
Repair and maintenance of electrical components must
include initial safety checks and procedures for com-
ponent inspection. In the event of a fault, which can
cause a safety risk, do not supply any power to the cir-
cuit until the fault has been rectified. If the fault cannot
be rectified immediately, and operation must continue,
an adequate temporary solution must be implemented.
This must be reported to the equipment owner, so that
all parties have been informed.
The following checks must be carried out at the initial
safety checks.
■That the capacitors are discharged. Discharging must
be done safely, to prevent the risk of sparking.
■That no powered electrical components or live cables
are exposed when filling or collecting refrigerant or
when the system is flushed.
■That the system is continually grounded.
Removal and draining
When a cooling circuit is opened for repairs – or for
another reason– work must be carried out in a conven-
tional manner. Due to the risk of fire it is important that
best practice is applied. Follow the procedure below.
1. Drain the refrigerant.
2. Flush the circuit with inert gas.
3. Drain the circuit.
4. Flush again with inert gas.
5. Open the circuit by cutting or burning.
Collect the refrigerant in the intended container. Flush
the system with oxygen-free nitrogen to make the
device safe. This process may need to be repeated
several times. Compressed air and oxygen may not be
used.
3Chapter 1 | Important informationNIBE™ F470