Version: 1.2 Confidential and Proprietary 3of 40
INDEX Page
1Conventions .................................................................................................................................. 4
1.1Text Conventions.................................................................................................................. 4
1.2Applicable Models................................................................................................................ 4
1.3Model Naming Convention................................................................................................... 5
2Introduction................................................................................................................................... 6
2.1Principles of Operation......................................................................................................... 6
3Getting Started.............................................................................................................................. 7
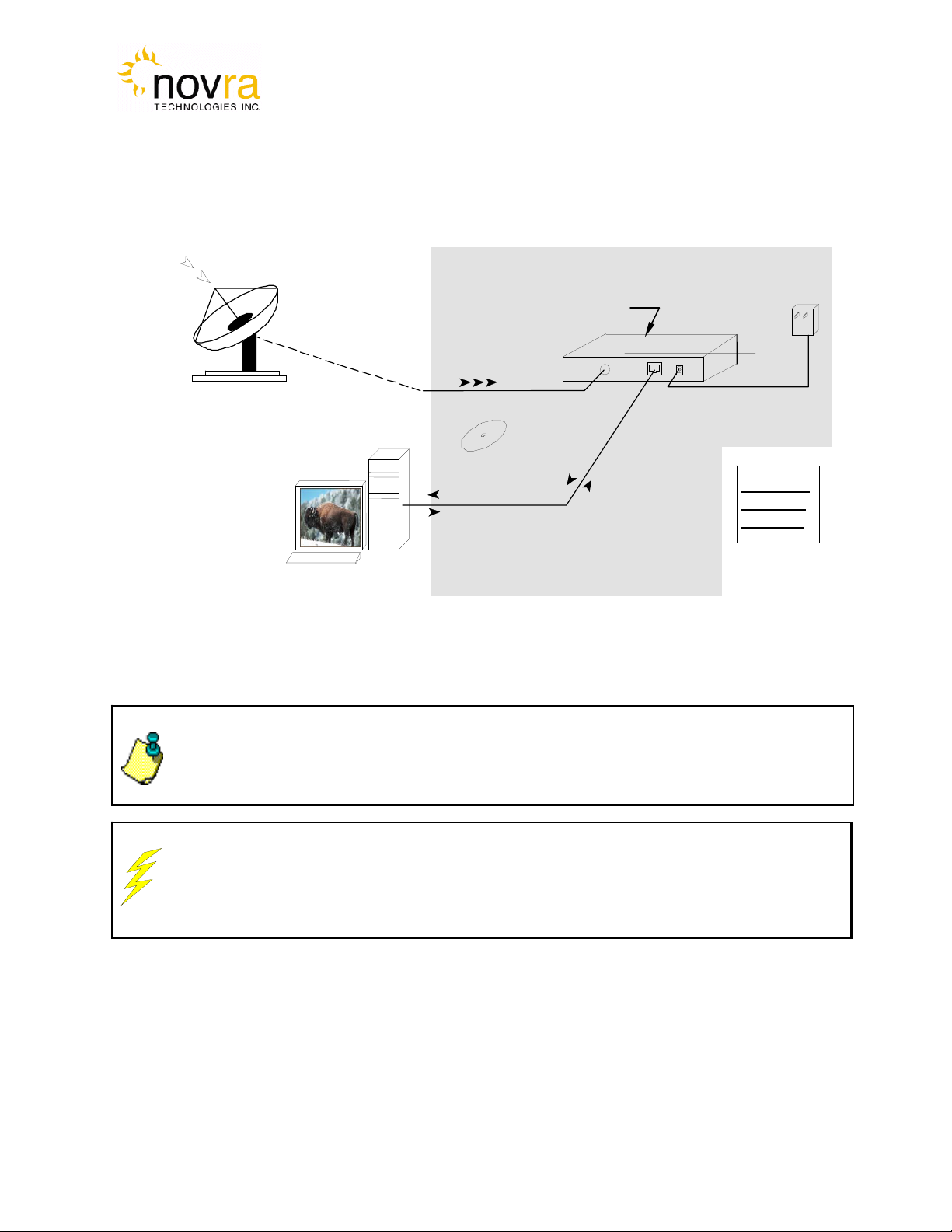
3.1Typical S300 Installation...................................................................................................... 7
3.2What Information do I Need – Basic Configuration?........................................................... 8
3.3SOFTWARE Installation on Windows 7.............................................................................. 9
3.4S300 Startup........................................................................................................................ 10
3.5Main Screen........................................................................................................................ 13
4Configuring the S300.................................................................................................................. 18
4.1Interfaces............................................................................................................................. 18
4.1.1Network Button............................................................................................................... 18
4.1.2Satellite Button................................................................................................................ 19
4.2IP Data ................................................................................................................................ 24
4.2.1Content Button................................................................................................................ 24
4.2.2IP Re-Mapping Button.................................................................................................... 25
4.3Control ................................................................................................................................ 28
4.3.1Reboot Button................................................................................................................. 28
4.4File Drop Down .................................................................................................................. 28
4.5Control Drop Down ............................................................................................................ 31
4.6Help Drop Down................................................................................................................. 32
4.6.1Help................................................................................................................................. 32
4.6.2About............................................................................................................................... 32
5Troubleshooting.......................................................................................................................... 33
6Specifications.............................................................................................................................. 35
6.1Receiver Characteristics...................................................................................................... 35
7Industry Canada Compliance Declaration.................................................................................. 37
8Minimum System Requirements................................................................................................. 37
9Supplied Equipment.................................................................................................................... 37
APPENDIX Terms, Definitions, and Tidbits of Information……………………………….....38