Panasonic SA-HT535EE User manual
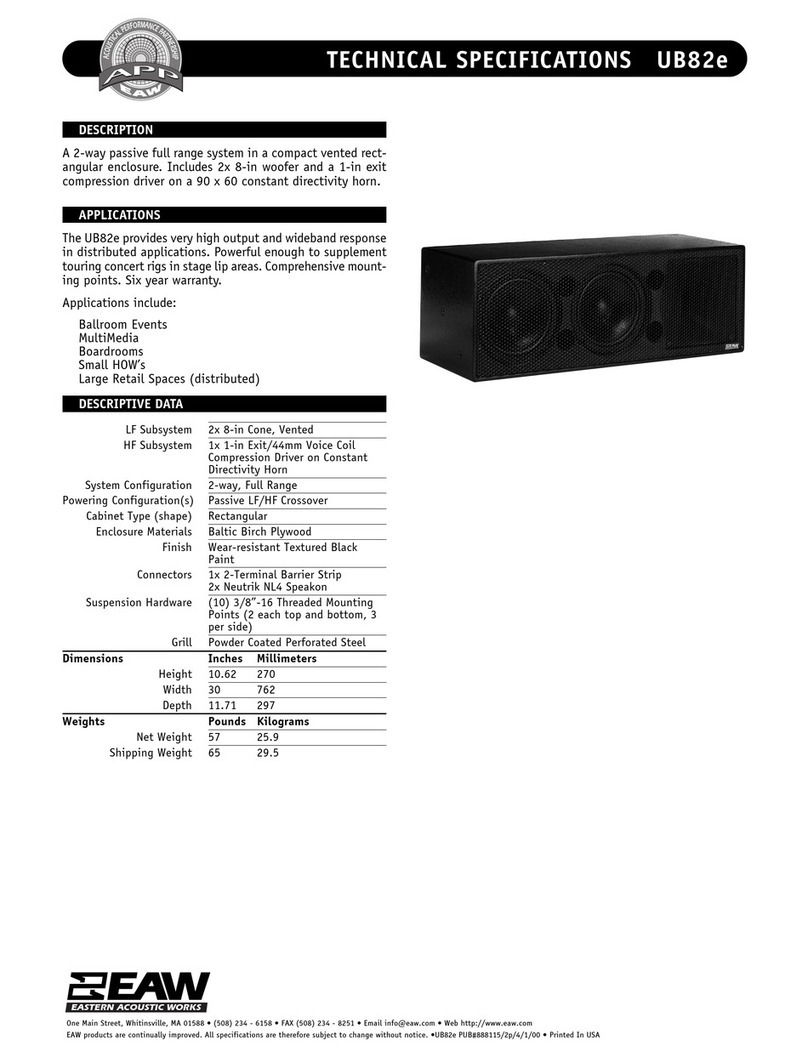
Other Panasonic Speakers System manuals
Panasonic
Panasonic SC-NE5 User manual
Panasonic
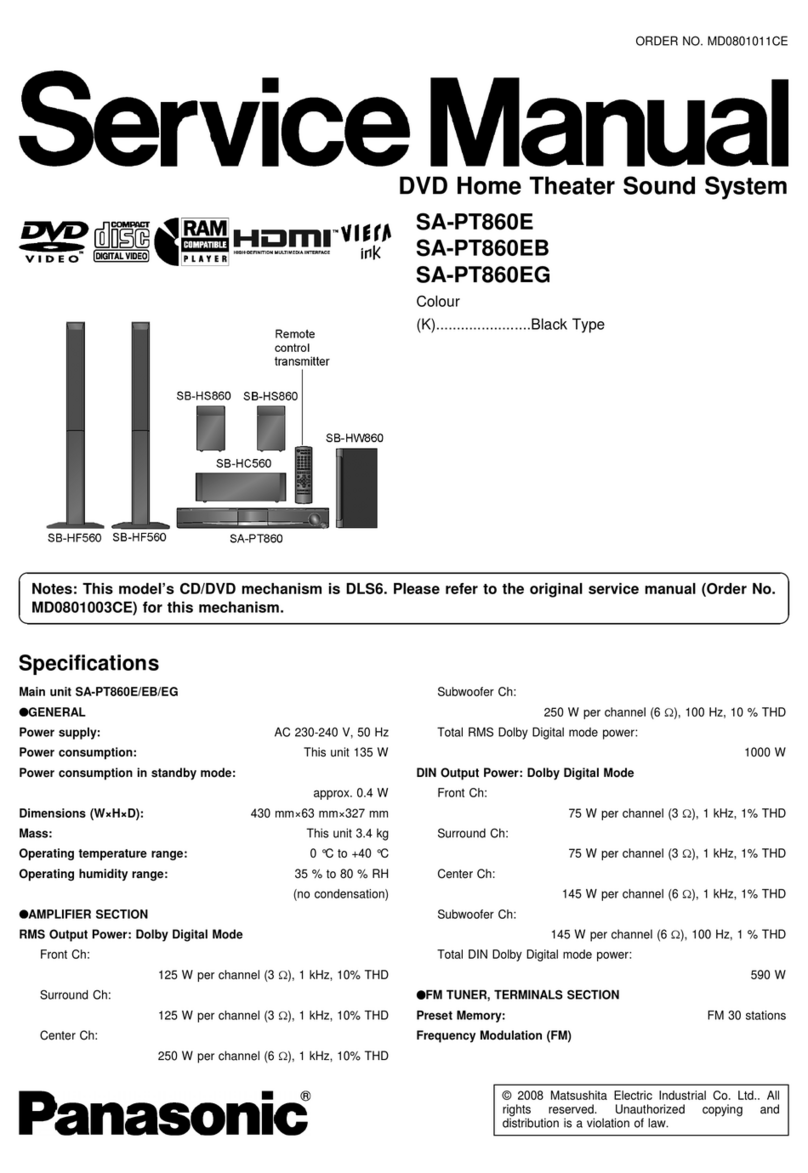
Panasonic SA-PT860E User manual

Panasonic
Panasonic SC-HD515 User manual

Panasonic
Panasonic SC-ALL2GN User manual

Panasonic
Panasonic SC-BTT885 User manual

Panasonic
Panasonic SB-AK450PL User manual

Panasonic
Panasonic SB-WAK640P User manual

Panasonic
Panasonic SA-PT465EE User manual

Panasonic
Panasonic SB-AK450 User manual
Panasonic
Panasonic SB-AFC500K User manual

Panasonic
Panasonic SB-HEP20 User manual

Panasonic
Panasonic SB-HF190P User manual

Panasonic
Panasonic SC-GN01GE User manual

Panasonic
Panasonic SA-BT230P User manual

Panasonic
Panasonic SCHDX2 - AMPLIFIER SPEAKER SYSTEM User manual

Panasonic
Panasonic SB-HC750P User manual

Panasonic
Panasonic SC-TMAX40 User manual

Panasonic
Panasonic SCHT720 - RECEIVER W/5-DISK DV User manual

Panasonic
Panasonic SB-AKX14LM-K User manual

Panasonic
Panasonic SC-UA7 User manual