Renesas RZ/N1S-DB User manual
Other Renesas Computer Hardware manuals

Renesas
Renesas HD74HCT1G66 User manual
Renesas
Renesas 7200 Series User manual

Renesas
Renesas SH7147 User manual

Renesas
Renesas M16C/29 User manual
Renesas
Renesas M16C FAMILY User manual

Renesas
Renesas R-IN32M4-CL2 TESSERA Installation and operating instructions

Renesas
Renesas SH7780 Series User manual

Renesas
Renesas H8/325 Series User manual

Renesas
Renesas E200F User manual

Renesas
Renesas RH850 Series Installation and operating instructions

Renesas
Renesas RL78G14 Installation and operating instructions

Renesas
Renesas H8SX/1638 User manual

Renesas
Renesas Stub Generator V.1.00 User manual

Renesas
Renesas RZ/G1E User manual
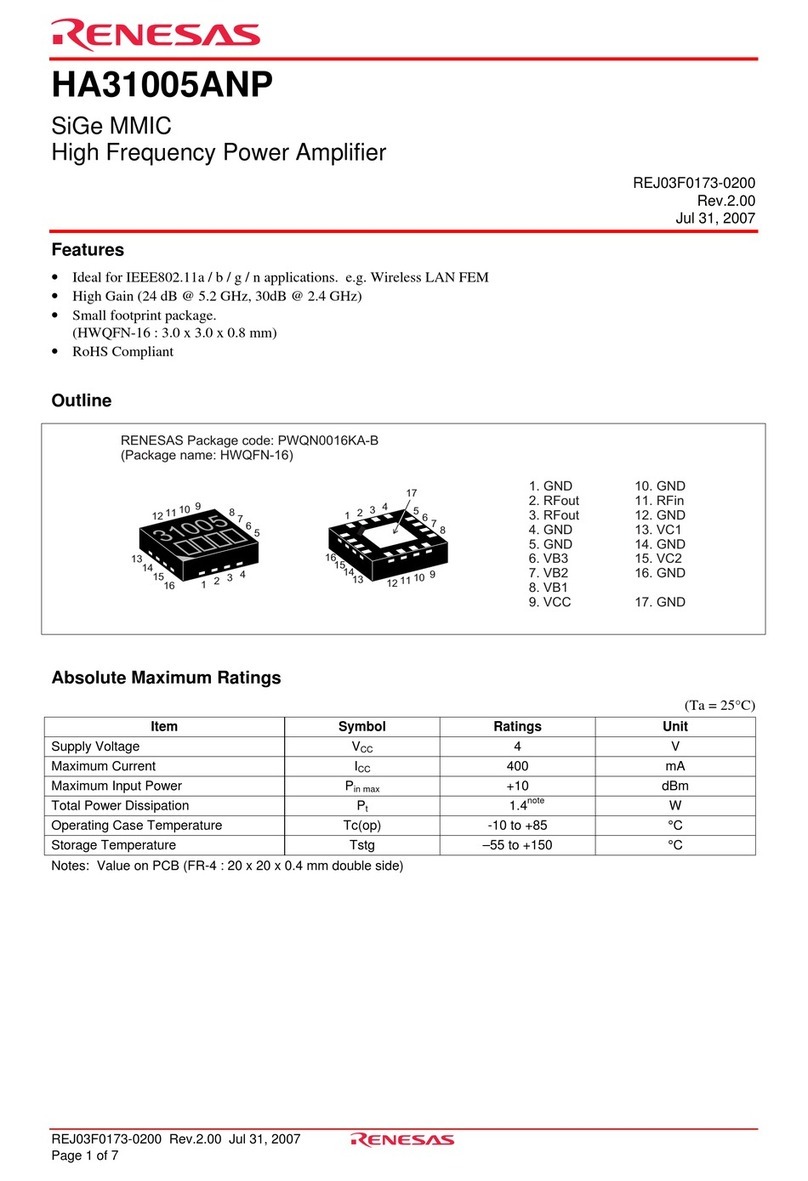
Renesas
Renesas HA31005ANP User manual

Renesas
Renesas RZ/A Series Instruction Manual
Renesas
Renesas R0E53032ACSJC0 User manual

Renesas
Renesas R0E521000CPE00 User manual

Renesas
Renesas H8 Series User manual
Renesas
Renesas M16C FAMILY User manual
Popular Computer Hardware manuals by other brands

EMC2
EMC2 VNX Series Hardware Information Guide

Panasonic
Panasonic DV0PM20105 Operation manual

Mitsubishi Electric
Mitsubishi Electric Q81BD-J61BT11 user manual

Gigabyte
Gigabyte B660M DS3H AX DDR4 user manual

Raidon
Raidon iT2300 Quick installation guide

National Instruments
National Instruments PXI-8186 user manual